Abstract
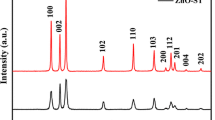
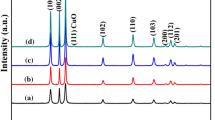
A novel pine-needle-like Zn-doped CuO nanostructures were synthesized by a low-cost and simple hydrothermal method, which were composed of smaller nanosheets. The phase structure, micromorphology, optical property and photocatalytic performance were characterized by X-ray diffraction pattern, field emission scanning electron microscopy, UV–Vis spectrophotometer and photocatalytic measurement device. And the actual elemental distribution was obtained by energy dispersive spectroscopy. Cell Parameters of Zn-doped CuO nanostructures were obtained from Rietveld refinement technique. The results revealed that these pine needles had the length of 1 μm and width of 50 nm. Compared to the undoped CuO, the intensity peaks of Zn-doped CuO had a slight shift, indicating that Zn ions successfully entered into the crystal lattice of CuO without changing the original crystal structure. 2.0 wt% Zn-doped CuO displayed the best light absorption ability especially in visible region. The red shift behavior of band gap can be observed. Moreover, doped samples showed the significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Yildiz, Ş. Horzum, N. Serin, T. Serin, Hop** conduction in in-doped CuO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 318, 105 (2014)
R.N. Mariammal, K. Ramachandran, G. Kalaiselvan, S. Arumugam, B. Renganathan, D. Sastikumar, Effect of magnetism on the ethanol sensitivity of undoped and Mn-doped CuO nanoflakes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 270, 545 (2013)
P. Chand, A. Gaur, A. Kumar, U. Kumar Gaur, Structural and optical study of Li doped CuO thin films on Si (100) substrate deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 307, 280 (2014)
N. Sharma, A. Gaur, R.K. Kotnala, Signature of weak ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism in Mn doped CuO nanostructures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 377, 183 (2015)
T.W. Chen, Y.H. Zheng, J.M. Lin, G.N. Chen, Study on the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in water using Ag/ZnO as catalyst by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization ion-trap mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 19, 997 (2008)
S. Sonia, I. Jose Annsi, P. Suresh Kumar, D. Mangalaraj, C. Viswanathan, N. Ponpandian, Hydrothermal synthesis of novel Zn doped CuO nanoflowers as an efficient photodegradation material for textile dyes. Mater. Lett. 144, 127 (2015)
B.X. Li, Y.F. Wang, Facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic performance of flower-like ZnO hierarchical microstructures. Phys. Chem. C 114, 890 (2010)
N. Mohamed Basith, J. Judith Vijaya, L. John Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Structural, morphological, optical, and magnetic properties of Ni-doped CuO nanostructures prepared by a rapid microwave combustion method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 17, 110 (2014)
N. Mohamed Basith, J. Judith Vijaya, L. John Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Structural, optical and room-temperature ferromagnetic properties of Fe-doped CuO nanostructures. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 53, 193 (2013)
Y.Q. Wang, T.T. Jiang, D.W. Meng, J. Yang, Y.C. Li, Q. Ma, J. Han, Fabrication of nanostructured CuO films by electrodeposition and their photocatalytic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 317, 414 (2014)
A.P. Chen, H. Long, X.C. Li, Y.H. Li, G. Yang, P.X. Lu, Controlled growth and characteristics of single-phase Cu2O and CuO films by pulsed laser deposition. Vacuum 83, 927 (2009)
W. Zhang, S. Ding, Z. Yang, A. Liu, Y. Qian, S. Tang, S. Yang, Growth of novel nanostructured copper oxide (CuO) films on copper foil. J. Cryst. Growth 291, 479–484 (2006)
K. Mageshwari, R. Sathyamoorthy, Physical properties of nanocrystalline CuO thin films prepared by the SILAR method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 16, 337 (2013)
H.W. Qin, Z.L. Zhang, X. Liu, Y.J. Zhang, J.F. Hu, Room-temperature ferromagnetism in CuO sol–gel powders and films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322 (1994)
T. Koh, E. O’Hara, M.J. Gordon, Growth of nanostructured CuO thin films via microplasma-assisted, reactive chemical vapor deposition at high pressures. J. Cryst. Growth 363, 69 (2013)
Y.Q. Wang, T.T. Jiang, D.W. Meng, J.H. Kong, H.X. Jia, M.H. Yu, Controllable fabrication of nanostructured copper compound on a Cu substrate by a one-step route. RSC Adv 5, 16277 (2015)
T.T. Jiang, Y.Q. Wang, D.W. Meng, X.L. Wu, J.X. Wang, J.Y. Chen, Controllable fabrication of CuO nanostructure by hydrothermal method and its properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 311, 602 (2014)
J.H. Kim, A. Katoch, S.W. Choi, S.S. Kim, Growth and sensing properties of networked p-CuO nanowires. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. Chem. 212, 190 (2015)
J. Hong, J. Li, Y. Ni, Urchin-like CuO microspheres: Synthesis, characterization, and properties. J. Alloys Compd. 481, 610 (2009)
W. Jia, E. Reitz, P. Shimpi, E.G. Rodriguez, P.X. Gao, Y. Lei, Spherical CuO synthesized by a simple hydrothermal reaction: Concentration-dependent size and its electrocatalytic application. Mater. Res. Bull. 44, 1681 (2009)
D. Sivalingam, J.B. Gopalakrishnan, J. Bosco, B. Rayappan, Structural, morphological, electrical and vapour sensing properties of Mn doped nanostructured ZnO thin films. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. 166–167, 624 (2012)
J. Tauc, R. Grigorovici, A. Vancu, Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 15, 627 (1966)
Q. Yuan, W. Deng, Q. Zhang, Y. Wang, Osmium-catalyzed selective oxidations of methane and ethane with hydrogen peroxide in aqueous medium. Adv. Synth. Catal. 349, 1199 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Guangxi Experiment Centre of Science and Technology with open Project: YXKT2014027. Another financial support is the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan, CUG120118). They are all gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, T., Wang, Y., Meng, D. et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic performance of pine-needle-like Zn-doped CuO nanostructures. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27, 12884–12890 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5424-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-5424-2