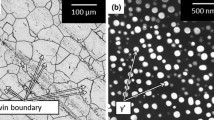
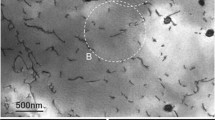
Abstract
Low-cycle-fatigue (LCF) and fatigue-crack-growth (FCG) behaviors of a cobalt-based HAYNES 188 superalloy were studied at temperatures ranging from 816 to 982 °C in laboratory air. Various tensile-hold times were imposed at the maximum strain and load in the LCF and FCG tests, respectively, to examine the high-temperature fatigue and creep–fatigue interactions. In this article, the effects of hold time and temperature on the cyclic-stress response, fatigue life, fracture mode, and crack-growth rate are discussed. Parameters based on the tensile-hysteresis energy are applied to correlate the LCF lives with and without hold time.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haynes online literature, No. H-3001, Haynes 188 alloy product brochure: https://doi.org/www.haynesintl.com/pdf/h3001.pdf
Merrick HF (1974) Metall Trans 5:891
Fournier D, Pineau A (1977) Metall Trans A 8:1095
Burke MA, Beck CG (1984) Metall Trans A 15:661
Antolovich SD, Liu S, Baur R (1981) Metall Trans A 12:473
Bashir S, Taupin P, Antolovich SD (1979) Metall Trans A 10:1481
McMahon CJ, Coffin LF (1970) Metall Trans 1:3443
Lerch BA, Jayaraman N, Antolovich SD (1984) Mater Sci Eng 66:151
Rao KBS, Schiffers H, Schuster H et al (1988) Metall Trans A 19:359
Berling JT, Conway JB (1970) Metall Trans 1:805
Lord DC, Coffin LF (1973) Metall Trans 4:1647
Chen W, Wahi RP (1998) In: Proceedings of the 6th Liege conference on materials for advanced power engineering. Belgium, p 1069
Klarstrom DL, Lai GY (1988) In: Superalloys, p 585
Mondel A, Lang KH, Lohe D et al (1997) Mater Sci Eng A 234:715
Rao KBS, Castelli MG, Allen GP et al (1997) Metall Mater Trans A 28:347
Rao KBS, Castelli MG, Ellis JR (1995) Scripta Mater 33:1005
Chen LJ, Liaw PK, He YH et al (2001) Scripta Mater 44:859
Lee SY, Lu YL, Liaw PK et al (2009) Mater Sci Eng A 504:64
Tawancy HM, Klarstrom DL, Rothman MF (1984) J Metals 36:58
ASTM Standard E647-99: Standard Test Method for Measurement of Fatigue Crack-Growth Rates, 2000 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, vol 03.01, p 591
Johnson HH (1965) Mater Res Stand 5:442
Liaw PK, Leax TR, Williams RS et al (1982) Metall Trans 13:1607
Vecchio KS, Fitzpatrick MD, Klarstrom D (1995) Metall Mater Trans A 26:673
Chen LJ, Liaw PK, Wang H et al (2004) Mech Mater 36:85
Lu YL, Chen LJ, Wang GY et al (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 409:282
Lu YL, Chen LJ, Liaw PK et al (2006) Mater Sci Eng A 429:1
Lee SY, Lu YL, Liaw PK et al (2008) Mech Time-Depend Mater 12:31
Ostergren WJ (1976) J Test Eval 4:327
Halford GR (1966) J Mater 1:3
Coffin LF (1954) Trans Am Soc Mech Eng 76:931
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Solar Turbines, Inc., Haynes International, Inc., the Center for Materials Processing (CMP) at the University of Tennessee (UT), the U. S. Department of Energy’s Advanced Turbine Systems Program, the National Science Foundation (NSF), under Grant No. DMI-9724476, the NSF Combined Research-Curriculum Development (CRCD) Programs, under EEC-9527527 and EEC-0203415, the Integrative Graduate Education and Research Training (IGERT) Program, under DGE-9987548, the International Materials Institutes (IMI) Program under DMR-0231320, and the Major Research Instrumentation (MRI) Program, under DMR-0421219, with Ms. M. Poats, and Drs. C.V. Hartesveldt, J. Giordan, D. Dutta, P.W. Jennings, L.S. Goldberg, L. Clesceri, C. Huber, and C.E. Bouldin as contract monitors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.Y., Lu, Y.L., Liaw, P.K. et al. Hold-time effects on elevated-temperature low-cycle-fatigue and crack-propagation behaviors of HAYNES® 188 superalloy. J Mater Sci 44, 2945–2956 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3391-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3391-1