Abstract
Purpose
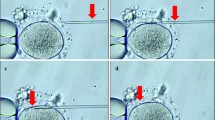
Zona pellucida (ZP)-bound sperm used for intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) enhances embryo quality, implantation, and clinical pregnancy rates. This study aimed to assess the pregnancy outcomes and clinical significance of ICSI with ZP-bound sperm.
Method
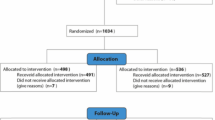
A total of 84 infertile couples who underwent cycles of ICSI following failed in vitro fertilization between June 2012 and February 2014 were enrolled and randomized (1:1): in the treatment group, ICSI was performed using ZP-bound sperm; in the control group, ICSI was performed in a standard manner. Rates of fertilization, cleavage, high-quality embryos, and clinical pregnancy were compared between the two groups.
Results
There were no significant differences in age, infertile period, gonadotrophin dose, number of metaphase II oocytes, and number of embryo transfers between the two groups (P > 0.05). The clinical pregnancy rate was higher in the treatment group than in the control group, but without statistical significance (60.5 vs. 47.6 %, P > 0.05). No significant differences in the rates of fertilization and cleavage were observed (83.0 vs. 81.6 %, and 96.3 vs. 96.5 %, both P > 0.05), but higher rates of high-quality embryos and useable embryos were observed with ZP-bound sperm compared with controls (66.1 vs. 50.8 % and 76.0 vs. 66.3 %, both P < 0.05).
Conclusions
ICSI using ZP-bound sperm might increase the embryo quality and number of useable embryos, possibly improving the clinical pregnancy outcome of ICSI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palermo G, Joris H, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC. Pregnancies after intracytoplasmic injection of single spermatozoon into an oocyte. Lancet. 1992;340(8810):17–8.
Lanzendorf SE, Maloney MK, Veeck LL, Slusser J, Hodgen GD, Rosenwaks Z. A preclinical evaluation of pronuclear formation by microinjection of human spermatozoa into human oocytes. Fertil Steril. 1988;49(5):835–42.
Nyboe Andersen A, Carlsen E, Loft A. Trends in the use of intracytoplasmatic sperm injection marked variability between countries. Hum Reprod Update. 2008;14(6):593–604. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmn032.
Wen-hao Tang Y-JC. The efficacy and safety of ICS treatment for male infertility. Int J Med Sci - Fam Plann. 2004;23(1):4.
Jequier AM. Clinical andrology—still a major problem in the treatment of infertility. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(6):1245–9. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh269.
Liu DY. Could using the zona pellucida bound sperm for intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) enhance the outcome of ICSI? Asian J Androl. 2011;13(2):197–8. doi:10.1038/aja.2010.179.
Liu F, Qiu Y, Zou Y, Deng ZH, Yang H, de Liu Y. Use of zona pellucida-bound sperm for intracytoplasmic sperm injection produces higher embryo quality and implantation than conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril. 2011;95(2):815–8. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2010.09.015.
Casciani V, Minasi MG, Fabozzi G, Scarselli F, Colasante A, Lobascio AM, et al. Traditional intracytoplasmic sperm injection provides equivalent outcomes compared with human zona pellucida-bound selected sperm injection. Zygote. 2014;22(4):565–70. doi:10.1017/S0967199413000191.
Strassburger D, Friedler S, Raziel A, Kasterstein E, Schachter M, Ron-El R. The outcome of ICSI of immature MI oocytes and rescued in vitro matured MII oocytes. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(7):1587–90. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh236.
Liu DY, Baker HW. Frequency of defective sperm-zona pellucida interaction in severely teratozoospermic infertile men. Hum Reprod. 2003;18(4):802–7.
Beaujean N. Epigenetics, embryo quality and developmental potential. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2014;27(1):53–62. doi:10.1071/RD14309.
Hammond ER, Stewart B, Peek JC, Shelling AN, Cree LM. Assessing embryo quality by combining non-invasive markers: early time-lapse parameters reflect gene expression in associated cumulus cells. Hum Reprod. 2015. doi:10.1093/humrep/dev121.
O’Neill C, Saunders DM. Assessment of embryo quality. Lancet. 1984;2(8410):1035.
Ciotti PM, Notarangelo L, Morselli-Labate AM, Felletti V, Porcu E, Venturoli S. First polar body morphology before ICSI is not related to embryo quality or pregnancy rate. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(10):2334–9. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh433.
Ola B, Afnan M, Sharif K, Papaioannou S, Hammadieh N, Barratt CL. Should ICSI be the treatment of choice for all cases of in-vitro conception? Considerations of fertilization and embryo development, cost effectiveness and safety. Hum Reprod. 2001;16(12):2485–90.
Kattera S, Chen C. Short coincubation of gametes in in vitro fertilization improves implantation and pregnancy rates: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. Fertil Steril. 2003;80(4):1017–21.
Bungum M, Bungum L, Humaidan P. A prospective study, using sibling oocytes, examining the effect of 30 seconds versus 90 minutes gamete co-incubation in IVF. Hum Reprod. 2006;21(2):518–23. doi:10.1093/humrep/dei350.
Liu DY, Baker HW. A simple method for assessment of the human acrosome reaction of spermatozoa bound to the zona pellucida: lack of relationship with ionophore A23187-induced acrosome reaction. Hum Reprod. 1996;11(3):551–7.
Liu DY, Baker HW. Relationship between the zona pellucida (ZP) and ionophore A23187-induced acrosome reaction and the ability of sperm to penetrate the ZP in men with normal sperm-ZP binding. Fertil Steril. 1996;66(2):312–5.
Martic M, Moses EK, Adams TE, Liu DY, Gook DA, Garrett C, et al. Recombinant human zona pellucida proteins ZP1, ZP2 and ZP3 co-expressed in a human cell line. Asian J Androl. 2004;6(1):3–13.
Lin WQ, Lin JJ, Ye BL, Chen YQ, Zhao JZ, Zhou Y, et al. Analysis of pregnancy outcomes after in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2004;39(2):108–11.
Papaligoura Z, Panopoulou-Maratou O, Solman M, Arvaniti K, Sarafidou J. Cognitive development of 12 month old Greek infants conceived after ICSI and the effects of the method on their parents. Hum Reprod. 2004;19(6):1488–93. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh270.
Avendano C, Franchi A, Taylor S, Morshedi M, Bocca S, Oehninger S. Fragmentation of DNA in morphologically normal human spermatozoa. Fertil Steril. 2009;91(4):1077–84. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.01.015.
Black M, de Liu Y, Bourne H, Baker HW. Comparison of outcomes of conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection and intracytoplasmic sperm injection using sperm bound to the zona pellucida of immature oocytes. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(2):672–4. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.08.063.
de Paes Almeida Ferreira Braga D, Laconelli Jr A, de Cassia Savio Figueira R, Madaschi C, Semiao-Francisco L, Borges Jr E. Outcome of ICSI using zona pellucida-bound spermatozoa and conventionally selected spermatozoa. Reprod Biomed Online. 2009;19(6):802–7.
Parmegiani L, Cognigni GE, Bernardi S, Troilo E, Taraborrelli S, Arnone A, et al. Comparison of two ready-to-use systems designed for sperm-hyaluronic acid binding selection before intracytoplasmic sperm injection: PICSI vs. sperm slow: a prospective, randomized trial. Fertil Steril. 2012;98(3):632–7. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.05.043.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the participating patients of this study. We thank the staff members of this trial, our colleagues, and all the study staff for their enormous efforts in collecting and ensuring the accuracy and completeness of all the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethical Committees of Maternal and Children Health Care Hospital of Yinchuan and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Capsule ICSI using ZP-bound sperm might increase the embryo quality and number of useable embryos, possibly improving the clinical pregnancy outcome of ICSI.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**, R., Bao, J., Tang, D. et al. Outcomes of intracytoplasmic sperm injection using the zona pellucida-bound sperm or manually selected sperm. J Assist Reprod Genet 33, 597–601 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-016-0676-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-016-0676-6