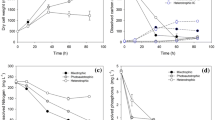
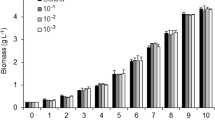
Abstract
Large-scale cultures of freshwater microalgae species demand high volumes of water used for culture media preparation. The recycling of culture media may help decrease cultivation costs, use valuable nutrients that may still remain in the medium after use and make it a green production system. This work investigated the effects of using culture media up to three times to grow Scenedesmus quadricauda. After a first use, culture media were either supplemented with nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) or with all nutrients of the medium composition. The effects of used culture media on the algae were verified through chlorophyll a concentrations, number of cells per coenobium, population density, growth rates, and biochemical composition (lipid classes, proteins, and carbohydrates). Cells were harvested through centrifugation before each culture medium use. The results showed that all nutrients should be added to the used medium at each new inoculation; protein/carbohydrate ratios were the best indicator of cell physiological status (higher in controls and lower in used media), and hydrocarbons accounted for 20 % of total lipids in controls and were produced under healthy conditions in S. quadricauda. According to the present results, at least three culture medium uses may be performed without affecting biomass yield, and it may be as promising as fresh medium for general biomass applications, such as biofuels production, but we do not recommend its reuse for fine biomass applications. Even though cells grew well in recycled media with all nutrients added, they were not as healthy as the ones in the control.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackman RG (1989) Marine biogenic lipids, fats and oils. CRC Press Inc., USA
AFNOR (1980) Association Française de Normalisation. Norme experimental T90-304. Essais de eaux. Determination de L’inhibition de Scenedesmus subspicatus par une substance
APHA (1995) Standard methods, 19th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Barsanti L, Gualtieri P (2006) Algae: anatomy, biochemistry and biotechnology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Becker EW (1994) Microalgae: biotechnology and microbiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Berdalet JE, Latasa M, Estrada M (1994) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus starvation on nucleic acid and protein content of Heterocapsa sp. J Plankton Res 16:303–331
Bhakuni DS, Rawat DS (2005) Bioactive marine natural products. Springer, New York and Anamaya Publisher, New Delhi
Borowitzka MA (1999) Economic evaluation of microalgal processes and products. In: Cohen Z (ed) Chemicals from microalgae. Taylor & Francis Ltd, London, pp 387–409
Borowitzka MA (2013) High-value products from microalgae—their development and commercialisation. J Appl Phycol 25:743–756
Borowitzka MA, Moheimani NR (2013) Sustainable biofuels from algae. Mitig Adapt Strat Glob Chang 18:13–25
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:243–254
Breuer G, Lamers PP, Martens DE, Draaisma RB, Wijffels RH (2012) The impact of nitrogen starvation on the dynamics of triacylglycerol accumulation in nine microalgae strains. Bioresour Technol 124:217–226
Burks RL, Jeppesen E, Lodge DM (2000) Macrophyte and fish chemicals suppress Daphnia growth and alter life-history traits. Oikos 88:139–147
Chen Z, Gong Y, Fang X, Hu H (2012) Scenedesmus sp. NJ-1 isolated from Antarctica: a suitable renewable lipid source for biodiesel production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:3219–3225
Chia MA, Lombardi AT, Melão MGG, Parrish CC (2013) Lipid composition of Chlorella vulgaris (Trebouxiophyceae) as a function of different cadmium and phosphorus concentrations. Aquat Toxicol 128–129:171–182
Cranwell PA, Jaworski GHM, Bickley HM (1990) Hydrocarbons, sterols, esters and fatty acids in six freshwater chlorophytes. Phytochemistry 29:145–151
Devi MP, Subhash GV, Mohan SV (2012) Heterotrophic cultivation of mixed microalgae for lipid accumulation and wastewater treatment during sequential growth and starvation phases: effect of nutrient supplementation. Renew Energy 43:276e283
Fergola P, Cerasuolo M, Pollio A, Pinto G, Della Greca M (2007) Allelopathy and competition between Chorella vulgaris and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata: experiments and mathematical model. Ecol Model 208:205–214
Fernández FGA, González-López CV, Sevilla JMF, Molina Grima E (2012) Conversion of CO2 into biomass by microalgae: how realistic a contribution may it be to significant CO2 removal? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96:577–586
Fogg GE (1983) The ecological significance of extracellular products of phytoplankton potosynthesis. Bot Mar 26:3–14
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Francisco EC, Neves DB, Jacob-Lopes E, Franco TT (2010) Microalgae as feedstock for biodiesel production: carbon dioxide sequestration, lipid production and biofuel quality. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:395–403
Ganf G, Stone S, Oliver R (1986) Use of protein to carbohydrate ratios to analyse for nutrient deficiency in phytoplankton. Aust J Mar Freshwat Res 37:183–197
Gardner R, Peters P, Peyton B, Cooksey KE (2011) Medium pH and nitrate concentration effects on accumulation of triacylglycerol in two members of the chlorophyta. J Appl Phycol 23:1005–1016
Gelpi E, Schneider H, Mann J, Oró J (1970) Hydrocarbons of geochemical significance in microscopic algae. Phytochemistry 9:603–612
Hardie LP, Balkwill DL, Stevens SE Jr (1983) Effects of iron starvation on the physiology of the cyanobacterium Agmenellum quadruplicatum. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:999–1006
Healey FP, Hendzel LL (1980) PhysioIogical indicators of nutrient deficiency in lake phytoplankton. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:442–453
Ho SH, Chen WM, Chang JS (2010) Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N as a potential candidate for CO2 mitigation and biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 101:8725–8730
Jeffrey SW, Humphrey GF (1975) New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem Physiol Pflanz 167:191–194
Kilham S, Kreeger DA, Gouldern CE, Lynn SG (1997) Effects of nutrient limitation on biochemical constituents of Ankistrodesmus falcatus. Freshw Biol 38:591–596
Kim DG, La HJ, Ahn CY, Park YH, Oh HM (2011) Harvest of Scenedesmus sp with bioflocculant and reuse of culture medium for subsequent high-density cultures. Bioresour Technol 102:3163–3168
Lai J, Yua Z, Song X, Cao X, Han X (2011) Responses of the growth and biochemical composition of Prorocentrum donghaiense to different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 405:6–17
Leflaive J, Ten-Hage L (2007) Algal and cyanobacterial secondary metabolites in freshwaters: a comparison of allelopathic compounds and toxins. Freshw Biol 52:199–214
Liu D, Wong PTS, Dutka BJ (1973) Determination of carbohydrate in lake sediment by a modified phenol-sulfuric method. Water Res 7:741–746
Liu J, Yuan C, Hu G, Li F (2012) Effects of light intensity on the growth and lipid accumulation of microalga Scenedesmus sp 11–1 under nitrogen limitation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:2127–2137
Lombardi AT, Wangersky P (1991) Influence of phosphorus and silicon on lipid class production by the marine diatom Chaetoceros gracilis grown in turbidostat cage cultures. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 77:39–47
Lombardi AT, Wangersky P (1995) Particulate lipid class composition of three marine phytoplankters Chaetoceros gracilis, Isochrysis galbana (Tahiti) and Dunaliella tertiolecta grown in batch culture. Hydrobiologia 306:1–6
Lombardi AT, Vieira AAH (1999) Lead- and copper-complexing extracellular ligands released by Kirchneriella aperta (Chlorococcales, Chlorophyta). Phycologia 38:283–288
Lombardi AT, Vieira AAH (2000) Copper complexation by Cyanophyta and Chlorophyta exudates. Phycologia 39:118–125
Lombardi AT, Hidalgo TMR, Vieira AAH, Sartori AL (2007) Toxicity of ionic copper to the freshwater microalga Scenedesmus acuminatus (Chlorophyceae, Chlorococcales). Phycologia 46:74–78
Mandal S, Mallick N (2009) Microalga Scenedesmus obliquus as a potential source for biodiesel production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:281–291
Mandal S, Mallick N (2012) Biodiesel production by the green microalga Scenedesmus obliquus in a recirculatory aquaculture system. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5929–5934
Moseley JL, Page MD, Alder NP, Eriksson M, Quinn J, Soto F, Theg SM, Hippler M, Merchant S (2002) Reciprocal expression of two candidate di-iron enzymes affecting photosystem I and light harvesting complex accumulation. Plant Cell 14:673–688
Parrish CC (1999) Determination of total lipid, lipid classes and fatty acids in aquatic samples. In: Arts MT, Wainman BC (eds) Lipids in Freshwater Ecosystems. Springer, New York, pp 4–20
Pickett-Heaps JD (1975) Green algae. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, p. 606
Poulet SA, Ianora A, Miralto A, Meijer L (1994) Do diatoms arrest embryonic development in copepods? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 111:79–86
Prabakaran P, Ravindran AD (2012) Scenedesmus as a potential source of biodiesel among selected microalgae. Curr Sci 102:616–620
Rausch T (1981) The estimation of micro-algal protein content and its meaning to the evaluation of algal biomass I. Comparison of methods for extracting protein. Hydrobiologia 78:237–251
Richmond A (ed) (2004) Handbook of microalgal culture: biotechnology and applied phycology. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford
Sharp JH (1977) Excretion of organic matter by marine phytoplankton: Do healthy cells do it? Limnol Oceanogr 2:381–399
Shoaf WT, Lium BW (1976) Improved extraction of chlorophyll a and b from algae using dimethyl sulfoxide. Limnol Oceanogr 21:926–928
Tang D, Han W, Li P, Miao X, Zhong J (2011) CO2 biofixation and fatty acid composition of Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa in response to different CO2 levels. Bioresour Technol 102:3071–3076
Tornabene TG (1976) Microbial formation of hydrocarbons. In: Schlegel HG, Barnea J (eds) Microbial energy conversion. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 281–291
Ugwu CU, Aoiyagi H, Uchiyama H (2008) Photobioreactors for mass cultivation of algae. Bioresour Technol 99:4021–4028
UNFCC (1997) The Kyoto protocol to the convention on climate change. Climate Change Secretariat, Bonn
Vasconcelos MTSD, Leal MFC (2008) Exudates of different marine algae promote growth and mediate trace metal binding in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Mar Environ Res 66:499–507
Wagenen JV, Miller TW, Hobbs S, Hook P, Crowe B, Huesemann M (2012) Effects of light and temperature on fatty acid production in Nannochloropsis salina. Energies 5:731–740
Wright DC, Berg LR, Patterson GW (1980) Effect of cultural conditions on the sterols and fatty acids of green algae. Phytochemistry 19:783–785
Yoo C, Jun SY, Lee JY, Ahn AY, Oh HE (2010) Selection of microalgae for lipid production under high levels carbon dioxide. Bioresour Technol 101:S71–S74
Zhao YF, Yu ZM, Song XX, Cao XH (2009) Biochemical compositions of two dominant bloom-forming species isolated from the Yangtze River Estuary in response to different nutrient conditions. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 368:30–36
Zhao G, Yu J, Jiang F, Zhang X, Tan T (2012) The effect of different trophic modes on lipid accumulation of Scenedesmus quadricauda. Bioresour Technol 114:466–471
Zhila NO, Kalacheva GS, Volova TG (2005) Influence of nitrogen deficiency on biochemical composition of the green alga Botryococcus. J Appl Phycol 17:309–315
Zou N, Richmond A (1999) Efficient utilization of high photon irradiance for mass production of photoautotrophic micro-organisms. J Appl Phycol 11:123–127
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the the grants no. 2009/15511-5, 2010/18136-8, 2008/02078-9, and 2008/03487-0, São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP—Brazil). ATL is grateful to CNPq—Brazil (302837/2012-4). The authors also acknowledge two anonymous reviewers, who improved the quality of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, G.S., Pinto, F.H.V., Melão, M.G.G. et al. Growing Scenedesmus quadricauda in used culture media: is it viable?. J Appl Phycol 27, 171–178 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0320-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0320-8