Abstract
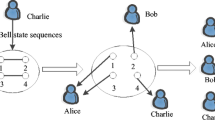
Motivated by the hyperentangled Bell states analysis, an arbitrated quantum proxy blind signature (QPBS) scheme is developed. Four participants accomplish the task of signing and verifying via exchanging the entanglement of polarization and spatial-mode degrees of freedom. Alice blinds message and sends it to a proxy signatory David who is delegated by the original signatory Charlie. David generates a signature using the delegating code while Bob verifies the signing with the help of an arbitrator Trent. Unlike previous schemes, the verifying phase is no longer executed only by a recipient. Analysis shows that when the even numbers of blinding string always equal 1, the scheme protects the proxy blind signature against forgery and disavow while maintaining the properties of verifiability and identifiability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rivest, R.L., Shamir, A., Adleman, L.: A method for obtaining digital signatures and public-key cryptosystems. ACM (1983)
Grover, Lov, K.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proc. Symp. on the Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219 (1996)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. In: Quantum Entanglement and Quantum Information–Proceedings of Ccast, pp. 303–332 (1999)
Zhou, N.R., Li, J.F., Zhen Bo, Y., Li, H.G., Farouk, A.: New quantum dialogue protocol based on continuous-variable two-mode squeezed vacuum states. Quantum Inf. Process 16(1), 4 (2017)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 560, 7–11 (2014)
Bennett, Charles H., Wiesner, Stephen J.: Communication via one- and two-particle operators on einstein-podolsky-rosen states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 69(20), 2881–2884 (1992)
Gong, L.H., Song, H.C., He, C.S., Liu, Y., Zhou, N.R.: A continuous variable quantum deterministic key distribution based on two-mode squeezed states. Physica Scripta 89(89), 035101 (2014)
Wang, J., Li, L., Peng, H., Yang, Y: Quantum-secret-sharing scheme based on local distinguishability of orthogonal multiqudit entangled states. Phys. Rev., 95(2) (2017)
Ouyang, Y, Tan, S.H., Zhao, L., Fitzsimons, J.F.: Computing on quantum shared secrets. Phys. Rev., 96(5) (2017)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev., 65(3) (2002)
Cao, Z.W., Feng, X.Y., Peng, J.Y., Zeng, G.H., Qi, X.F.: Quantum secure direct communication scheme in the non-symmetric channel with high efficiency and security. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(6), 1871–1877 (2015)
Cao, Z.W., Feng, X.Y., Peng, J.Y., Zeng, G.H., Qi, J.: Efficient quantum private communication based on dynamic control code sequence. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(4), 1–9 (2017)
Zeng, G., Keitel, C.H.: Arbitrated quantum-signature scheme. Phys. Rev., 65(4) (2002)
Mambo, M, Usuda, K, Okamoto, E.: Proxy signatures: Delegation of the power to sign messages. Ieice Trans. Fund. 79(9), 1338–1354 (1996)
Chaum, D: Blind signatures for untraceable payments. In: Advances in Cryptology. Proceedings of CRYPTO ’82, Santa Barbara, California, USA, August 199–203 (1982)
Cao, H.J., Zhu, Y.Y., Li, P.F.: A quantum proxy weak blind signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(2), 419–425 (2014)
Shi, J.J., Shi, R.H., Guo, Y., Peng, X.Q., Tang, Y.: Batch proxy quantum blind signature scheme. Sci. Chin. (Inf. Sci.) 56(5), 1–9 (2013)
Cai, X.Q., Yu, H.Z., Zhang, R.L.: Cryptanalysis of a batch proxy quantum blind signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(9), 3109–3115 (2014)
Tian, Y., Chen, H., Yan, G., Tian, J., Wen, X.: A proxy blind signature scheme based on quantum entanglement. Opt. Quant. Electron. 45(12), 1297–1305 (2013)
Cao, H.J., Wang, H.S., Li, P.F.: Quantum proxy multi-signature scheme using genuinely entangled six qubits state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52(4), 1188–1193 (2013)
Zhang, L., Zhang, H.Y., Ke, J.Z., Wang, Q.L.: The security analysis and improvement of some novel quantum proxy signature schemes. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56 (6), 1983–1994 (2017)
Cao, H.J., Huang, J., Yu, Y.F., Jiang, X.L.: A quantum proxy signature scheme based on genuine five-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(9), 3095–3100 (2014)
Cao, H.J., Yu, Y.F., Song, Q., Gao, L.X.: A quantum proxy weak blind signature scheme based on controlled quantum teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54 (4), 1325–1333 (2015)
Ke, J.Z., Jia, H.Y.: Cryptanalysis of a quantum proxy weak blind signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 54(2), 582–588 (2015)
Cao, H.J., Zhang, J.F., Liu, J., Li, Z.Y.: A new quantum proxy multi-signature scheme using maximally entangled seven-qubit states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(2), 774–780 (2016)
Ai, X.S., Zhang, J.Z., **e, S.C.: An e-payment protocol based on quantum multi-proxy blind signature. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(4), 1–8 (2017)
Barreiro, J.T., Langford, N.K., Peters, N.A., Kwiat, P.G.: Generation of hyperentangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(26), 260501 (2005)
Yu, B.S., Fu, G.D.: Deterministic entanglement purification and complete nonlocal bell-state analysis with hyperentanglement. Phys. Rev. A 81(3), 537–542 (2012)
Simon, C, Pan, J.W.: Polarization entanglement purification using spatial entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89(25), 257901 (2001)
Yu, B.S., Fu, G.D., Long, G.L.: Complete hyperentangled-bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys. Rev. A 82(3), 10334–10338 (2012)
Fan, L.-L., **a, Y., Song, J.: Complete hyperentanglement-assisted multi-photon greenberger–horne–zeilinger states analysis with cross-kerr nonlinearity. Opt. Commun. 317(8), 102–106 (2014)
Wang, T.J., Li, T., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: High-capacity quantum secure direct communication based on quantum hyperdense coding with. hyperentanglement 28(4), 040305–1171 (2011)
Acknowledgements
Project supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (61602172), National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2017JJ3223), Science and technology project of Hunan province department of education (16B179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, X., Tang, W., Ma, H. et al. An Arbitrated Proxy Blind Signature Based on Hyper Entanglement Analysis. Int J Theor Phys 57, 2709–2721 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3792-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3792-5