Abstract
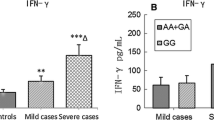
Interleukin-6 (IL-6), as one of pro-inflammatory cytokines, plays a key role in Enterovirus 71 (EV71) encephalitis. We investigated the association of IL-6-572C/G polymorphism and serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) IL-6 level with EV71 encephalitis in patients with hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). This study was carried out in 59 Chinese Han patients with EV71 encephalitis, 128 EV71-related HFMD without complications, and 232 controls. The IL-6-572C/G polymorphism was detected by polymerase chain reaction-restricted fragment length polymorphism gene analysis. Serum or CSF IL-6 levels were determined using a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The patients with EV71 encephalitis had a higher frequency of IL-6-572GG/GC genotype compared to the patients with EV71-related HFMD without encephalitis complications (40.7 vs. 15.6 %, odds ratio (OR) = 3.70, 95 % confidence interval (CI) = 1.83–7.50, p = 0.001). Similarly, the frequency of IL-6-572 G allele among the patients with EV71 encephalitis was also higher than that of patients with EV71-related HFMD without encephalitis complications (23.7 vs. 8.6 %, OR = 3.31, 95 % CI = 1.80–6.08, p < 0.001). Serum IL-6 levels in G carries (CG + GG) (195.1 ± 11.8 pg/ml) elevated significantly compared to CC homozygotes (167.7 ± 6.7 pg/ml) in EV71-infected patients (p < 0.001), but no significant differences were observed in CSF IL-6 levels among different genotypes in patients with EV71 encephalitis. Furthermore, G carriers (GG + GC) (10.6 ± 1.29 mg/l) had significantly higher blood CRP levels compared to CC homozygotes (9.31 ± 1.93 mg/l) in patients with EV71 encephalitis (p = 0.005). These findings suggested that IL-6-572 G allele was significantly associated with the susceptibility to EV71 encephalitis in Chinese Han patients, and IL-6-572 G allele might elevate the risk to EV71 encephalitis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, P.C., L.M. Huang, C.L. Kao, T.Y. Fan, A.L. Cheng, and L.Y. Chang. 2010. An outbreak of coxsackievirus A16infection: comparison with other enteroviruses in a preschool in Taipei. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection 43: 271–277.
McMinn, P.C. 2002. An overview of the evolution of enterovirus 71 and its clinical and public health significance. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 26: 91–107.
Weng, K.F., L.L. Chen, P.N. Huang, and S.R. Shih. 2010. Neural pathogenesis of enterovirus 71 infection. Microbes and Infection 12: 505–510.
AbuBakar, S., I.C. Sam, J. Yusof, M.K. Lim, S. Misbah, N. MatRahim, and P.S. Hooi. 2009. Enterovirus 71 outbreak, Brunei. Emerging Infectious Diseases 15: 79–82.
Yang, F., L. Ren, Z. **ong, J. Li, Y. **ao, R. Zhao, Y. He, G. Bu, S. Zhou, J. Wang, and J. Qi. 2009. Enterovirus 71 outbreak in the People’s Republic of China in 2008. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 47: 2351–2352.
Ooi, M.H., S.C. Wong, P. Lewthwaite, M.J. Cardosa, and T. Solomon. 2010. Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of enterovirus 71. Lancet Neurology 9: 1097–1105.
Ma, E., K.C. Chan, P. Cheng, C. Wong, and S.K. Chuang. 2010. The enterovirus 71 epidemic in 2008—public health implications for Hong Kong. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 14: e775–e780.
Chua, K.B., and A.R. Kasri. 2011. Hand foot and mouth disease due to enterovirus 71 in Malaysia. Virologica Sinica 26: 221–228.
Li, L., Y. He, H. Yang, J. Zhu, X. Xu, J. Dong, Y. Zhu, and Q. **. 2005. Genetic characteristics of human enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16 circulating from 1999 to 2004 in Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 43: 3835–3839.
Chang, L.Y., C.A. Hsiung, C.Y. Lu, T.Y. Lin, F.Y. Huang, Y.H. Lai, Y.P. Chiang, B.L. Chiang, C.Y. Lee, and L.M. Huang. 2006. Status of cellular rather than humoral immunity is correlated with clinical outcome of enterovirus 71. Pediatric Research 60: 466–471.
Lin, T.Y., L.Y. Chang, Y.C. Huang, K.H. Hsu, C.H. Chiu, and K.D. Yang. 2002. Different proinflammatory reactions in fatal and non-fatal enterovirus 71 infections: implications for early recognition and therapy. Acta Paediatrica 91: 632–635.
Zhang, Y., H. Liu, L. Wang, F. Yang, Y. Hu, X. Ren, G. Li, Y. Yang, S. Sun, Y. Li, X. Chen, X. Li, and Q. **. 2013. Comparative study of the cytokine/chemokine response in children with differing disease severity in enterovirus 71-induced hand, foot, and mouth disease. PloS One 8: e67430.
Lin, Y.W., S.L. Yu, H.Y. Shao, H.Y. Lin, C.C. Liu, K.N. Hsiao, E. Chitra, Y.L. Tsou, H.W. Chang, C. Sia, P. Chong, and Y.H. Chow. 2013. Human SCARB2 transgenic mice as an infectious animal model for enterovirus 71. PLoS One 8: e57591.
Heinrich, P.C., J.V. Castell, and T. Andus. 1990. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. The Biochemical Journal 265: 621–636.
Lehtimäki, T., P. Ojala, R. Rontu, S. Goebeler, P.J. Karhunen, M. Jylhä, K. Mattila, S. Metso, H. Jokela, M. Nikkilä, E. Wuolijoki, A. Hervonen, and M. Hurme. 2005. Interleukin-6 modulates plasma cholesterol and C-reactive protein concentrations in nonagenarians. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 53: 1552–1558.
Michalek, J., P. Svetlikova, M. Fedora, M. Klimovic, L. Klapacova, D. Bartosova, H. Hrstkova, and J.A. Hubacek. 2007. Interleukin-6 gene variants and the risk of sepsis development in children. Human Immunology 68: 756–760.
Yan, J., J. Liu, C.Y. Lin, A.N. Anzgene, P.A. Csurhes, M.P. Pender, P.A. McCombe, and J.M. Greer. 2012. Interleukin-6 gene promoter-572 C allele may play a role in rate of disease progression in multiple sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13: 13667–13679.
Sen, A., S.K. Paine, I.H. Chowdhury, A. Mukherjee, S. Choudhuri, A. Saha, L.K. Mandal, and B. Bhattacharya. 2011. Impact of interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism and serum interleukin-6 level on the acute inflammation and neovascularization stages of patients with Eales’ disease. Molecular Vision 17: 2552–2563.
Chiaretti, A., S. Pulitanò, G. Barone, P. Ferrara, V. Romano, D. Capozzi, and R. Riccardi. 2013. IL-1 β and IL-6 upregulation in children with H1N1 influenza virus infection. Mediators of Inflammation 495848.
Levitz, R., R. Wattier, P. Phillips, A. Solomon, J. Lawler, I. Lazar, C. Weibel, and J.S. Kahn. 2012. Induction of IL-6 and CCL5 (RANTES) in human respiratory epithelial (A549) cells by clinical isolates of respiratory syncytial virus is strain specific. Virology Journal 9: 190.
Fishman, D., G. Faulds, R. Jeffery, V. Mohamed-Ali, J.S. Yudkin, S. Humphries, and P. Woo. 1998. The effect of novel polymorphisms in the interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene on IL-6 transcription and plasma IL-6 levels, and an association with systemic-onset juvenile chronic arthritis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 102: 1369–1376.
Hulkkonen, J., M. Pertovaara, J. Antonen, A. Pasternack, and M. Hurme. 2001. Elevated interleukin-6 plasma levels are regulated by the promoter region polymorphism of the IL6 gene in primary Sjögren’s syndrome and correlate with the clinical manifestations of the disease. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 40: 656–661.
Patel, J.A., S. Nair, E.E. Ochoa, R. Huda, N.J. Roberts, and T. Chonmaitree. 2010. Interleukin-6−174 and tumor necrosis factor α−308 polymorphisms enhance cytokine production by human macrophages exposed to respiratory viruses. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research 30: 917–921.
Zhai, R., G. Liu, C. Yang, C. Huang, C. Wu, and D.C. Christiani. 2001. The G to C polymorphism at −174 of the interleukin-6 gene is rare in a Southern Chinese population. Pharmacogenetics 11: 699–701.
Ota, N., T. Nakajima, I. Nakazawa, T. Suzuki, T. Hosoi, H. Orimo, S. Inoue, Y. Shirai, and M. Emi. 2001. A nucleotide variant in the promoter region of the interleukin-6 gene associated with decreased bone mineral density. Journal of Human Genetics 46: 267–272.
Boiardi, L., B. Casali, E. Farnetti, N. Pipitone, D. Nicoli, F. Cantini, P. Macchioni, G. Bajocchi, M.G. Catanoso, L. Pulsatelli, D. Consonni, and C. Salvarani. 2006. Relationship between interleukin 6 promoter polymorphism at position −174, IL-6 serum levels, and the risk of relapse/recurrence in polymyalgia rheumatica. The Journal of Rheumatology 33: 703–708.
Bennermo, M., M. Nordin, P. Lundman, S. Boqvist, C. Held, A. Samnegård, C.G. Ericsson, A. Silveira, A. Hamsten, M.M. Nastase, and P. Tornvall. 2011. Genetic and environmental influences on the plasma interleukin-6 concentration in patients with a recent myocardial infarction: a case-control study. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research 31: 259–264.
Shah, V.A., C.Y. Chong, K.P. Chan, W. Ng, and A.E. Ling. 2003. Clinical characteristics of an outbreak of hand, foot and mouth disease in Singapore. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore 32: 381–387.
Zhou, H., S.Z. Guo, H. Zhou, Y.F. Zhu, L.J. Zhang, and W. Zhang. 2012. Clinical characteristics of hand, foot and mouth disease in Harbin and the prediction of severe cases. Chinese Medical Journal 125: 1261–1265.
Eklund, C.M. 2009. Proinflammatory cytokines in CRP baseline regulation. Advances in Clinical Chemistry 48: 111–136.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this project was supported by grants from the Natural Science of China (no. 31171212), and there are no ethical/legal conflicts involved in the article.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no competing of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, A., Li, J., Liu, P. et al. Association of Interleukin-6-572C/G Gene Polymorphism and Serum or Cerebrospinal Fluid Interleukin-6 Level with Enterovirus 71 Encephalitis in Chinese Han Patients with Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease. Inflammation 38, 728–735 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9983-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9983-1