Abstract
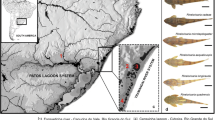
Chromosome analyses were carried out for several fish species in a region impacted by the connection between two hydrographic basins, where a river originally pertaining to the Paraná River basin was transposed to the São Francisco River basin in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. The purpose was to assess the dispersal of invasive species from one hydrographic basin to the other and the consequent new geographical distributions of species that had been previously isolated from each other. Species of the families Parodontidae (Apareiodon piracicabae, A. ibitiensis, Parodon hilarii, and P. nasus), Sternopygidae (Eigenmannia virescens), and Gymnotidae (Gymnotus sylvius) were studied. The four species of Parodontidae had 2n = 54 chromosomes, but species-specific karyotype structures, including the presence of the ZZ/ZW sex chromosome system in A. ibitiensis and P. hilarii. Two distinct karyomorphs (A and B) were identified for E. virescens, although with the same diploid number (2n = 38 chromosomes). G. sylvius had 2n = 40 chromosomes. P. hilarii and E. virescens (karyomorph B) are considered to be native to the São Francisco River basin, whereas A. piracicabae, A. ibitiensis, E. virescens (karyomorph A), and G. sylvius are known for the Paraná River basin, and P. nasus is known for the Paraná-Paraguay basin. The presence of the last five species in the São Francisco River basin indicates that they migrated from the Parana River to the São Francisco River basin due to the transposition of the river, and can therefore be considered invasive species in this basin. Moreover, a natural migratory pathway through the former wetland may have affected this dispersal.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho, C. S. & H. F. Júlio Jr., 2002. Observation of an invasions of piranha Serrasalmus marginatus Valenciennes, 1847 (Osteichthyes, Serrasalmidae) into the Upper Paraná River, Brazil. Acta Scientiarum 24: 391–395.
Agostinho, C. S., N. S. Hahn & E. E. Marques, 2003. Patterns of food resource use by two congeneric species of piranhas (Serrasalmus) on the upper Paraná River floodplain. Brazilian Journal of Biology 63: 177–182.
Albert, J. S. & W. G. R. Crampton, 2003. Seven new species of the Neotropical electric fish Gymnotus (Teleostei, Gymnotiformes) with a redescription of G. carapo (Linnaeus). Zootaxa 287: 1–54.
Albert, J. S., F. M. C. Fernandes-Matioli & L. F. Almeida-Toledo, 1999. New species of Gymnotus (Gymnotiformes, Teleostei) from southeastern Brazil: toward the deconstruction of Gymnotus carapo. Copeia 1999: 410–424.
Alcaraz, C., A. Vila-Gispert & E. García-Berthou, 2005. Profiling invasive fish species: the importance of phylogeny and human use. Diversity and Distributions 11: 289–298.
Almeida Toledo, L. F., M. Z. F. Daniel Silva, C. B. Moysés, S. B. A. Fonteles, C. E. Lopes, A. Akama & F. Foresti, 2002. Chromosome evolution in fish: sex chromosome variability in Eigenmannia virescens (Gymnotiformes: Sternopygidae). Cytogenetic and Genome Research 99: 164–169.
Almeida-Toledo, L. F., F. Foresti, E. V. Péquignot & M. Z. F. Daniel-Silva, 2001. XX:XY sex chromosome system with X heterochromatinization: an early stage of sex chromosome differentiation in the Neotropic electric eel Eigenmannia virescens. Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics 95: 73–78.
Barbieri, G., J. R. Verani & M. C. Barbieri, 1983. Análise do comportamento reprodutivo das espécies de Apareiodon affinis (Steindachner, 1879), Apareiodon ibitiensis Campos, 1944 e Parodon tortuosus Eigenmann & Norris, 1900 do rio Passa-Cinco, Ipeúna, SP (Pisces, Parodontidae). Seminário Regional de Ecologia III: 189–199, São Carlos, São Paulo.
Barbieri, G., J. R. Verani, J. A. Pereira, M. C. Barbieri, A. C. Peret & M. A. Marins, 1985. Curva de maturação e fator de condição de Apareiodon affinis (Steindachner, 1879), Apareiodon ibitiensis (Campos, 1944) e Parodon tortuosus (Eigenmann & Norris, 1900) do rio Passa-Cinco, Ipeúna – SP (Cypriniformes, Parodontidae). Ciência e Cultura 37: 1178–1183.
Bertollo, L. A. C., C. S. Takahashi & O. Moreira-Filho, 1978. Cytotaxonomic considerations on Hoplias lacerdae (Pisces, Erythrinidae). Brazilian Journal of Genetics 1: 103–120.
Bertollo, L. A. C., O. Moreira-Filho & P. M. Galetti Jr., 1986. Cytogenetics and taxonomy: considerations based on chromosome studies of freshwater fish. Journal of Fish Biology 28: 153–159.
Blanco, D. R., R. L. Lui, L. A. C. Bertollo, D. Diniz & O. Moreira-Filho, 2010. Characterization of invasive fish species in a river transposition region: evolutionary chromosome studies in the genus Hoplias (Characiformes, Erythrinidae). Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 20: 1–8.
Britski, H. A., Y. Sato & A. B. S. Rosa, 1988. Manual de identificação de peixes da região de Três Marias: com chaves de identificação para os peixes da Bacia do São Francisco. Câmara dos Deputados, Coordenação de Publicações, CODEVASF, Divisão de Piscicultura e Pesca, Brasília.
Buckup, P. A., N. A. Menezes & M. S. Ghazzi, 2007. Catálogo das espécies de peixes de água doce do Brasil. Museu Nacional do Rio de Janeiro: 195 pp.
Elvira, B. & A. Almodóvar, 2001. Freshwater fish introductions in Spain: facts and figures at the beginning of the 21st century. Journal of Fish Biology 59: 323–331.
Goldschmidt, T., F. Witte & J. Wanink, 1993. Cascading effects of the introduced Nile perch on the detritivorous/phytoplanktivorous species in the sublittoral areas of Lake Victoria. Conservation Biology 7: 686–700.
Henyey, E., B. Kynard & P. Zhuang, 2002. Use of electronarcosis to immobilize juvenile lake and shortnose sturgeons for handling and the effects on their behavior. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 18: 502–504.
Howell, W. M. & D. A. Black, 1980. Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36: 1014–1015.
Levan, A., K. Fredga & A. A. Sandberg, 1964. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52: 201–220.
Margarido, V. P., E. Bellafronte & O. Moreira-Filho, 2007. Cytogenetic analysis of three sympatric Gymnotus (Gymnotiformes, Gymnotidae) species verifies invasive species in the Upper Paraná River basin, Brazil. Journal of Fish Biology 70: 155–164.
Menezes, N. A., 1970. Distribuição e origem da fauna de peixes de água doce das grandes bacias fluviais do Brasil. In Comissão Interestadual da Bacia Paraná-Uruguai (eds), Poluição e Piscicultura, Secretaria da Agricultura, Instituto de Pesca, São Paulo: 73–78.
Moreira Filho, O. & P. A. Buckup, 2005. A poorly known case of watershed transposition between the São Francisco and upper Paraná River basins. Neotropical Ichthyology 3: 449–452.
Moyle, P. B. & T. Light, 1996. Biological invasions of fresh water: empirical rules and assembly theory. Biological Conservation 78: 149–161.
Pazza, R. & H. F. Júlio Jr., 2003. Occurrence of three sympatric cytotypes of Hoplias malabaricus (Pisces, Erythrinidae) in the upper Paraná River foodplain (Brazil). Cytologia 68: 159–163.
Peres, W. A. M., P. A. Buckup, D. L. Z. Kantek, L. A. C. Bertollo & O. Moreira-Filho, 2009. Chromosomal evidence of downstream dispersal of Astyanax fasciatus (Characiformes, Characidae) associated with river shed interconnection. Genetica 137: 305–311.
Rahel, F. J., 2002. Homogenization of freshwater faunas. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 33: 291–315.
Sazima, I., 1980. Behavior of two Brazilian species of Parodontid fishes, Apareiodon piracicabae and A. ibitiensis. Copeia 1980: 166–169.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to IBAMA (Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente (IBAMA/MMA) and to the Instituto Estadual de Floresta (IEF-MG), for authorizing the capture of the fish. This study was financed by FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo), CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico), CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), and the Araucária Foundation (Fundação Araucária de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico do Estado).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: David Dudgeon
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bellafronte, E., Moreira-Filho, O., Vicari, M.R. et al. Cytogenetic identification of invasive fish species following connections between hydrographic basins. Hydrobiologia 649, 347–354 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0277-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0277-9