Abstract
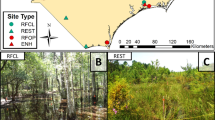
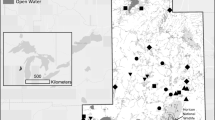
Many wetlands have been constructed in West Virginia as mitigation for a variety of human disturbances, but no comprehensive evaluation on their success has been conducted. Macroinvertebrates are extremely valuable components of functioning wetland ecosystems. As such, benthic and water column invertebrate communities were chosen as surrogates for wetland function in the evaluation of 11 mitigation and 4 reference wetlands in West Virginia. Mitigation wetlands ranged in age from 4 to 21 years old. Overall familial richness, diversity, density and biomass were similar between mitigation and reference wetlands (p > 0.05). Within open water habitats, total benthic invertebrate density was higher in reference wetlands, but mass of common taxa from water column samples was higher in mitigation wetlands (p < 0.05) Planorbidae density from benthic samples in emergent habitats was higher in reference than mitigated wetlands. Benthic Oligochaeta density was higher across open water habitats in mitigation wetlands. All other benthic taxa were similar between wetland types. Among the most common water column orders, Isopoda density was higher in reference wetlands, but Physidae density was higher in mitigation wetlands. Within mitigation wetlands, emergent areas contained higher richness and diversity than open areas. These data indicate that mitigation and reference wetlands generally support similar invertebrate assemblages, especially among benthic populations. The few observed differences are likely attributable to differences in vegetative community composition and structure. Mitigation wetlands currently support abundant and productive invertebrate communities, and as such, provide quality habitat for wetland dependent wildlife species, especially waterbirds and anurans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. M. Anderson D. A. Haukos J. T. Anderson (1999) ArticleTitleDiet composition of three anurans from the playa wetlands of northwest Texas Copeia 1999 515–520
J. T. Anderson L. M. Smith (1996) ArticleTitleA comparison of methods for sampling epiphytic and nektonic aquatic invertebrates in playa wetlands Journal of Freshwater Ecology 11 219–224
J. T. Anderson L. M. Smith (1998) ArticleTitleProtein and energy production in playas: implications for migratory bird management Wetlands 18 437–446
J. T. Anderson L. M. Smith (1999) ArticleTitleCarrying capacity and diel use of managed playa wetlands by nonbreeding waterbirds Wildlife Society Bulletin 27 281–291
J. T. Anderson L. M. Smith (2000) ArticleTitleInvertebrate response to moist-soil management of playa wetlands Ecological Applications 10 550–558
J. T. Anderson L. M. Smith D. A. Haukos (2000) ArticleTitleFeather molt influence on diet selection of non-breeding green-winged teal in playas Journal of Wildlife Management 64 222–230
J. T. Anderson L. M. Smith (2004) ArticleTitlePersistence and colonization strategies of playa wetland invertebrates Hydrobiologia 513 77–86 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:hydr.0000018171.44844.20
M. C. Ashley J. A. Robinson L. W. Oring G. A. Vinyard (2000) ArticleTitleDipteran standing stock biomass and effects of aquatic bird predation at a constructed wetland Wetlands 20 84–90
Balcombe C. K., (2003). An evaluation of vegetation and wildlife communities in mitigation and natural wetlands of West Virginia. Thesis, West Virginia University, Morgantown, West Virginia, USA. (http://kitkat.wvu.edu:8080/files/2857.1.Balcombe_C_thesis.pdf)
Balcombe C. K., Anderson J. T., Fortney R. H., Kordek W. S., in press a. Vegetation, invertebrate, and wildlife community rankings and habitat analysis of mitigation wetlands in West Virginia. Wetlands Ecology and Management
Balcombe C. K., Anderson J. T., Fortney R. H., Rentch J. S., Grafton W. N., Kordek W. S., in press b. A comparison of plant communities in mitigation and reference wetlands in the mid-Appalachians. Wetlands
D. P. Batzer M. McGee V. H. Resh R. R. Smith (1993) ArticleTitleCharacteristics of invertebrates consumed by mallards and prey response to wetland flooding schedules Wetlands 13 41–49
D. P. Batzer C. R. Pusateri R. Vetter (2000) ArticleTitleImpacts of fish predation on marsh invertebrates: direct and indirect effects Wetlands 20 307–312
Brinson M. M., (1993). A hydrogeomorphic classification for wetlands. U.S. Army Engineers Waterways Experiment Station, Technical Report WRP-DE-4, Vicksburg, Mississippi, USA
M. M. Brinson R. Rheinhardt (1996) ArticleTitleThe role of reference wetlands in functional assessment and mitigation Ecological Applications 6 69–76
R. T. Brooks (2000) ArticleTitleAnnual and seasonal variation and the effects of hydroperiod on benthic macroinvertebrates of seasonal forest (“vernal”) ponds in central Massachusetts, USA Wetlands 20 707–715
C. L. Brown T. P. Poe J. P. French SuffixIII D. W. Schloesser (1988) ArticleTitleRelationships of phytomacrofauna to surface area in naturally occurring macrophyte stands Journal of the North American Benthological Society 7 129–139
S. C. Brown K. Smith D. Batzer (1997) ArticleTitleMacroinvertebrate responses to wetland restoration in northern New York Environmental Entomology 26 1016–1024
D. A. Campbell C. A. Cole R. P. Brooks (2002) ArticleTitleA comparison of created and natural wetlands in Pennsylvania, USA Wetlands 10 41–49 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1014335618914
S. R. Carpenter D. M. Lodge (1986) ArticleTitleEffects of submersed macrophytes on ecosystem processes Aquatic Botany 26 341–370 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3770(86)90031-8
W. J. Conover R. L. Iman (1981) ArticleTitleRank transformations as a bridge between parametric and nonparametric statistics American Statistician 35 124–129
Cowardin L. M., Carter V., Golet F. C., LaRoe E. T., (1979). Classification of wetlands and deepwater habitats of the United States. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Report FWS/OBS-79/31
L. B. Crowder W. E. Cooper (1982) ArticleTitleHabitat structural complexity and the interaction between bluegills and their prey Ecology 63 1802–1813
K. W. Cummins (1973) ArticleTitleTrophic relations of aquatic insects Annual Review of Entomology 18 183–206 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.en.18.010173.001151
F. A. De Szalay V. H. Resh (1996) ArticleTitleSpatial and temporal variability of trophic relationships among aquatic macroinverterates in a seasonal marsh Wetlands 16 458–466
S. I. Dodson (2001) ArticleTitleZooplankton communities of restored depressional wetlands in Wisconsin, USA Wetlands 21 292–300
R. G. Doupe P. Horwitz (1995) ArticleTitleThe value of macroinvertebrate assemblages for determining priorities in wetland rehabilitation: a case study from Lake Toolibin, Western Australia Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia 78 33–38
S. Dowdy S. Wearden (1991) Statistics for Research, 2 Wiley New York 656
K. L. Erwin (1990) Freshwater marsh creation and restoration in the Southeast J. A. Kusler M. E. Kentula (Eds) Wetland Creation and Restoration: The Status of the Science Island Press Washington DC 233–265
N. H. Euliss SuffixJr. R. L. Jarvis D. S. Gilmer (1991) ArticleTitleFeeding ecology of waterfowl wintering on evaporation ponds in California Condor 93 582–900
N. H. Euliss SuffixJr. D. M. Mushet D. H. Johnson (2002) ArticleTitleUsing aquatic invertebrates to delineate seasonal and temporary wetlands in the prairie pothole region of North America Wetlands 22 256–262
G. W. Fairchild A. M. Faulds L. L. Saunders (1999) Constructed marshes in southeast Pennsylvania-invertebrate food-web structure D. P. Batzer R. B. Rader S. A. Wissinger (Eds) Invertebrates in freshwater wetlands of North America: Ecology and Management Wiley New York 423–446
G. W. Fairchild A. M. Faulds J. F. Matta (2000) ArticleTitleBeetle assemblages in ponds: effects of habitat and site age Freshwater Biology 44 523–530 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2000.00601.x
S. J. Gonzalez X. Bernadi X. Ruiz (1996) ArticleTitleSeasonal variation of waterbird prey in the Ebro Delta rice fields Colonial Waterbirds 19 135–142
J. D. Huener J. A. Kadlec (1992) ArticleTitleMacroinvertebrate response to marsh management strategies in Utah Wetlands 12 72–78
N. M. Jarman R. A. Doberteen B. Windmiller P. R. Lelito (1991) ArticleTitleEvaluation of created freshwater wetlands in Massachusetts Restoration and Management Notes 9 26–29
B. R. Johnson D. C. Tarter J. J. Hutchens SuffixJr. (2000) ArticleTitleLife history and trophic basis of production of the mayfly Callibaetis fluctuans (Walsh) (Ephemeroptera: Baetidae) in a mitigation wetland, West Virginia, USA Wetlands 20 397–405
P. S. Lake I. A. Bayley D. W. Morton (1989) ArticleTitleThe phenology of a temporary pond in western Victoria, Australia, with special reference to invertebrate succession Archiv Für Hydrobiologie 115 171–202
A. P. Lima W. E. Magnusson (2000) ArticleTitleDoes foraging activity change with ontogeny? An assessment for six symaptric species of postmetamorphic litter anurans in central Amazonia Journal of Herpetology 34 192–200
W. P. Magdych (1981) ArticleTitleAn efficient, inexpensive elutriator design for separating benthos from sediment samples Hydrobiologia 85 157–159
P. W. McCafferty (1981) Aquatic Entomology: the Fisherman’s and Ecologist’s Illustrated Guide to Insects and Their Relatives Jones and Bartlett Publishers Sudbury, MA 448
R.W. Merritt K.W. Cummins (Eds) (1984) An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America, 2 Kendall/Hunt Dubuque 722
R. W. Merritt K. W. Cummins T. M. Burton (1984) The role of aquatic insects in the processing and cycling of nutrients V. H. Resh D. M. Rosenberg (Eds) The Ecology of Aquatic Insects. Praeger New York 134–163
W. J. Mitsch J. G. Gosselink (2000) Wetlands, 3 Wiley New York 920
National Research Council, (1995). Wetlands Characteristics and Boundaries. National Academy Press, Washington DC, 328 pp
M. S. Nelson R. A. Roline J. S. Thullen J. J. Sartoris J. E. Boutwell (2000) ArticleTitleInvertebrate assemblages and trace element bioaccumulation associated with constructed wetlands Wetlands 20 406–415
S. Niswander W. J. Mitsch (1995) ArticleTitleFunctional analysis of a two-year-old created in-stream wetland: hydrology, phosphorus retention, and vegetation survival and growth Wetlands 15 212–225
R. W. Pennak (1989) Fresh-water Invertebrates of the United States Protozoa to Mollusca, 3 Wiley New York 628
C. L. Pierce B. D. Hinrichs (1997) ArticleTitleResponse of littoral invertebrates to reduction of fish density: simultaneous experiments in ponds with different fish assemblages Freshwater Biology 37 397–408 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.1997.00169.x
C. Potvin D. A. Roff (1993) ArticleTitleDistribution-free and robust statistical methods: viable alternatives to parametric statistics Ecology 74 1617–1628
J. A. Reinartz E. L. Warne (1993) ArticleTitleDevelopment of vegetation in small created wetlands in southeast Wisconsin Wetlands 13 153–164
Rossiter J. A., Crawford R. D., (1981). Evaluation of constructed ponds as a means of replacing natural wetland habitat affected by highway projects in North Dakota. Federal Highway Administration, Report FHWA-ND-RD-2–79A
J. J. Sartoris J. S. Thullen (1998) Develo** a habitat-driven approach to CWWT (constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment) design D. F. Hayes (Eds) Engineering Approaches to Ecosystem Restoration Proceedings of the 1998 Wetlands Engineering and River Restoration Conference, Denver Colorado, American Society of Civil Engineers Reston (V.A.) 716–721
SAS Institute Inc., (1988). SAS software, Cary, North Carolina. 1028 pp
S. R. Scatolini J. B. Zedler (1996) ArticleTitleEpibenthic invertebrates of natural and constructed marshes of San Diego Bay Wetlands 16 24–37
H. L. Schramm SuffixJr. J. Jirka M. V. Hoyer (1987) ArticleTitleEpiphytic macroinvertebrates on dominant macrophytes in two central Florida lakes Journal of Freshwater Ecology 4 151–161
C. E. Shannon W. Weaver (1949) The Mathematical Theory of Communication University of Illinois Press Urbana, IL
W. J. Streever T. L. Crisman (1993) ArticleTitleA preliminary comparison of meiobenthic cladoceran assemblages in natural and constructed wetlands in central Florida Wetlands 13 229–236
W. J. Streever D. L. Evans C. M. Keenan T. L. Crisman (1995) ArticleTitleChironomidae (Diptera) and vegetation in a created wetland and implications for sampling Wetlands 13 229–236
W. J. Streever K. M. Portier T. L. Crisman (1996) ArticleTitleA comparison of dipterans from ten created and ten natural wetlands Wetlands 16 416–428
G. A. Swanson (1983) ArticleTitleBenthic sampling for waterfowl foods in emergent vegetation Journal of Wildlife Management 47 821–823
J. B. Wallace J. W. Grubaugh M. R. Whiles (1996) ArticleTitleBiotic indices and stream ecosystem processes: results from an experimental study Ecological Applications 6 140–151
M. W. Weller (1994) Freshwater Marshes: Ecology and Wildlife Management, 3 University Minnesota Press Minneapolis 150
G. B. Wiggins R. J. Mackay I. M. Smith (1980) ArticleTitleEvolutionary and ecological strategies of animals in annual temporary pools Archiv Für Hydrobiologie Supplement 58 97–206
D. A. Wilcox (1992) ArticleTitleImplications for faunal habitat related to altered macrophyte structure in regulated lakes in northern Minnesota Wetlands 12 192–203
R. F. Wilson W. J. Mitsch (1996) ArticleTitleFunctional assessment of five wetlands constructed to mitigate wetland loss in Ohio, USA Wetlands 16 436–451
K. D. Zimmer M. A. Hanson M. G. Butler (2000) ArticleTitleFactors influencing invertebrate communities in prairie wetlands: a multivariate approach Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 57 76–85 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjfas-57-1-76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balcombe, C.K., Anderson, J.T., Fortney, R.H. et al. Aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages in mitigated and natural wetlands. Hydrobiologia 541, 175–188 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-5706-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-004-5706-1