Abstract
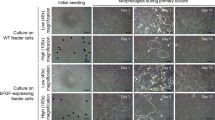
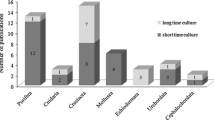
This study was conducted to identify embryonic stem cell (ESC) activities of a long-term cultured embryonic cell line previously derived from blastula-stage Oryzias dancena embryos. Five sub-cell lines were established from the embryonic cell line via clonal expansion of single cells. ESC activities, including clonogenicity, alkaline phosphatase (AP) activity, and differentiation capacity, were examined in the five sub-cell lines. We observed both clonogenicity and AP activity in all five sub-cell lines, but the proportion of cells that exhibited both properties was significantly different among them. Even though we detected different formation rates and sizes of embryoid body (EB) among these cells, all lines were stably able to form EBs and further induction for differentiation showed their capability to differentiate into other cell types in a spontaneous manner. From this study, we determined that the embryonic cell lines examined possessed heterogeneous ESC activities and can be utilized as a marine model system for fish ESC-based research.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Béjar J, Hong Y, Alvarez MC (2002) An ES-like cell line from the marine fish Sparus aurata: characterization and chimaera production. Transgenic Res 11:279–289
Camper SA, Saunders TL, Kendall SK, Keri RA, Seasholtz AF, Gordon DF, Birkmeier TS, Keegan CE, Karolyi IJ, Roller ML, Burrows HL, Samuelson LC (1995) Implementing transgenic and embryonic stem cell technology to study gene expression, cell-cell interactions and gene function. Biol Reprod 52:246–257
Chen SL, Ye H, Sha Q, Shi CY (2003) Derivation of a pluripotent embryonic cell line from red sea bream blastulas. J Fish Biol 63:795–805
Chen SL, Sha ZX, Ye HQ, Liu Y, Tian YS, Hong Y, Tang QS (2007) Pluripotency and chimera competence of an embryonic stem cell line from the sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus). Mar Biotechnol 9:82–91
Chen W, Jia W, Wang K, Zhou Q, Leng Y, Duan T, Kang J (2012) Retinoic acid regulates germ cell differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cells through a Smad-dependent pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 418:571–577
Cho YS, Lee SY, Kim YK, Kim DS, Nam YK (2011) Functional ability of cytoskeletal β-actin regulator to drive constitutive and ubiquitous expression of a fluorescent reporter throughout the life cycle of transgenic marine medaka Oryzias dancena. Transgenic Res 20:1333–1355
Dash C, Routray P, Tripathy S, Verma DK, Guru BC, Meher PK, Nandi S, Eknath AE (2010) Derivation and characterization of embryonic stem-like cells of Indian major carp Catla catla. J Fish Biol 77:1096–1113
Doss MX, Koehler CI, Gissel C, Hescheler J, Sachinidis A (2004) Embryonic stem cells: a promising tool for cell replacement therapy. J Cell Mol Med 8:465–473
Evans MJ, Kaufman MH (1981) Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292:154–156
Gong SP, Kim B, Kwon HS, Yang WS, Jeong JW, Ahn J, Lim JM (2014) The co-injection of somatic cells with embryonic stem cells affects teratoma formation and the properties of teratoma-derived stem cell-like cells. PLoS ONE 9:e105975
Hayashi K, Lopes SM, Tang F, Surani MA (2008) Dynamic equilibrium and heterogeneity of mouse pluripotent stem cells with distinct functional and epigenetic states. Cell Stem Cell 3:391–401
Ho SY, Goh CW, Gan JY, Lee YS, Lam MK, Hong N, Hong Y, Chan WK, Shu-Chien AC (2014) Derivation and long-term culture of an embryonic stem cell-like line from zebrafish blastomeres under feeder-free condition. Zebrafish 11:407–420
Holen E, Hamre K (2003) Towards obtaining long term embryonic stem cell like cultures from a marine flatfish, Scophtalmus maximus. Fish Physiol Biochem 29:245–252
Hong Y, Winkler C, Schartl M (1996) Pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines from the medakafish (Oryzias latipes). Mech Dev 60:33–44
Hong SH, Rampalli S, Lee JB, McNicol J, Collins T, Draper JS, Bhatia M (2011) Cell fate potential of human pluripotent stem cells is encoded by histone modifications. Cell Stem Cell 9:24–36
Inoue K, Takei Y (2002) Diverse adaptability in Oryzias species to high environmental salinity. Zool Sci 19:727–734
Inoue K, Takei Y (2003) Asian medaka fishes offer new models for studying mechanisms of seawater adaptation. Comp Biochem Physiol B 136:635–645
Kennedy KA, Porter T, Mehta V, Ryan SD, Price F, Peshdary V, Karamboulas C, Savage J, Drysdale TA, Li SC, Bennett SA, Skerjanc IS (2009) Retinoic acid enhances skeletal muscle progenitor formation and bypasses inhibition by bone morphogenetic protein 4 but not dominant negative β-catenin. BMC Biol 7:67. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-7-67
Kim M, Habiba A, Doherty JM, Mills JC, Mercer RW, Huettner JE (2009) Regulation of mouse embryonic stem cell neural differentiation by retinoic acid. Dev Biol 328:456–471
Kim MS, Lee ST, Lim JM, Gong SP (2014) Medium composition for effective slow freezing of embryonic cell lines derived from marine medaka (Oryzias dancena). Cytotechnology. doi:10.1007/s10616-014-9749-5
Lee D, Kim MS, Nam YK, Kim DS, Gong SP (2013) Establishment and characterization of permanent cell lines from Oryzias dancena embryos. Fish Aquat Sci 16:177–185
Metallo CM, Ji L, de Pablo JJ, Palecek SP (2008) Retinoic acid and bone morphogenetic protein signaling synergize to efficiently direct epithelial differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 26:372–380
Parameswaran V, Shukla R, Bhonde R, Hameed AS (2007) Development of a pluripotent ES-like cell line from Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer)—an oviparous stem cell line mimicking viviparous ES cells. Mar Biotechnol 9:766–775
Shim JH, Kim SE, Woo DH, Kim SK, Oh CH, McKay R, Kim JH (2007) Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells towards a pancreatic cell fate. Diabetologia 50:1228–1238
Stewart MH, Bosse M, Chadwick K, Menendez P, Bendall SC, Bhatia M (2006) Clonal isolation of hESCs reveals heterogeneity within the pluripotent stem cell compartment. Nat Methods 3:807–815
Torres J, Prieto J, Durupt FC, Broad S, Watt FM (2012) Efficient differentiation of embryonic stem cells into mesodermal precursors by BMP, retinoic acid and notch signaling. PLoS ONE 7:e36405. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036405
Wichterle H, Lieberam I, Porter JA, Jessell TM (2002) Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into motor neurons. Cell 110:385–397
Wobus AM, Boheler KR (2005) Embryonic stem cells: prospects for developmental biology and cell therapy. Physiol Rev 85:635–678
Yi M, Hong N, Hong Y (2009) Generation of medaka fish haploid embryonic stem cells. Science 326:430–433
Yi M, Hong N, Hong Y (2010) Derivation and characterization of haploid embryonic stem cell cultures in medaka fish. Nat Protoc 5:1418–1430
Zhao W, Ji X, Zhang F, Li L, Ma L (2012) Embryonic stem cell markers. Molecules 17:6196–6236
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2012R1A1A1011572).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D., Ryu, J.H., Lee, S.T. et al. Identification of embryonic stem cell activities in an embryonic cell line derived from marine medaka (Oryzias dancena). Fish Physiol Biochem 41, 1569–1576 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0108-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0108-z