Abstract
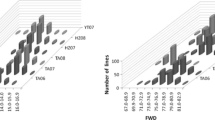
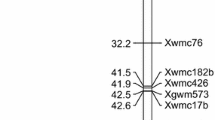
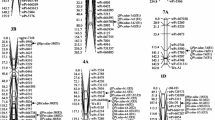
Grain protein content (GPC) and gluten quality are the most important factors determining the end-use quality of wheat for pasta-making. Both GPC and gluten quality are considered to be polygenic traits influenced by environmental factors and other agricultural practices. Two related F8:9 recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations were generated to localise genetic factors controlling seven quality traits: GPC, wet gluten content (WGC), flour whiteness (FW), kernel hardness (KH), water absorption (Abs), dough development time (DDT) and dough stability time (DST). These lines were derived by crossing Weimai 8 and Jimai 20 (WJ) and by crossing Weimai 8 and Yannong 19 (WY). In total, WJ comprised 485 lines, while WY comprised 229 lines. Data on these seven quality traits were collected from each line in five different environments. Up to 85 putative QTLs for the seven traits were detected in WJ and 65 putative QTLs were detected in WY. Of these QTLs, 31 QTLs (36.47%) were detected in at least two trials in WJ, while 24 QTLs (36.92%) were detected in at least two trials in WY. Three QTLs from WJ and 25 from WY accounted for more than 10% of the phenotypic variance. The total 150 QTLs were spread throughout all 21 wheat chromosomes. Of these, at least thirteen pairwise were common to both populations, accounting for 20.00 and 15.29% of the total QTLs in WJ and WY, respectively. A major QTL for GPC, accounting for 53.04% of the phenotypic variation, was detected on chromosome 5A. A major QTL for WGC also shared this interval, explained more than 36% of the phenotypic variation, and was significant in two environments. Though co-located QTLs were common, every trait had its unique control mechanism, even for two closely related traits. Due to the different sizes of the two line populations, we also assessed the effects of population size on the efficiency and precision of QTL detection. In sum, this study will enhance our understanding of the genetic basis of these seven pivotal quality traits and facilitate the breeding of improved wheat varieties.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken KS (1993) Genetic analysis of grain protein content in wheat. PhD Thesis, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK
Autran JC, Abecassis J, Feillet P (1996) Statistical evaluation of different technological and biochemical tests for quality assessment in durum wheat. Cereal Chem 63:390–394
Beavis WB (1998) QTL analyses: power, precision, and accuracy. In: Patterson AH (ed) Molecular dissection of complex traits. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Blanco A, De Giovanni C, Laddomada B, Sciancalepore A, Simeone R, Devos KM, Gale MD (1996) Quantitative trait loci influencing grain protein content in tetraploid wheats. Plant Breed 115:10–316
Blanco A, Pasqualone A, Troccoli A, DiFonzo N, Simeone R (2002) Detection of grain protein content QTL across environments in tetraploid wheats. Plant Mol Biol 48:615–623
Blanco A, Simeone R, Gadaleta A (2006) Detection of QTL for grain protein content in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 112:1195–1204
Branlard G, Bernard S, Boeuf C, Bernard M (1999) Detection of QTL for bread making quality in wheat using molecular markers. In: Scarascia Mugnozza GT, Porceddu E, Pagnotta MA (eds) Genetics and breeding for crop quality and resistance. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 361–366
Buckler ES, Holland JB, Acharya CB, Brown PJ, Browne C, Ersoz E, Flint-Garcia S, Garcia A, Glaubitz JC, Goodman MM, Harjes C, Guill K, Kroom DE, Larsson S, Lepak NK, Li HH, Mitchell SE, Pressoin G, Peiffer JA, Rosas MO, Rocheford TR, Romay MC, Romero S, Salvo S, Villeda HS, Sliva HSD, Sun Q, Tian F, Upadyayula N, Ware D, Yates H, Yu J, Zhang Z, Kresovich S, McMullen MD (2009) The genetic architecture of maize flowering time. Science 325:714–718
Cantrell RG, Joppa LR (1991) Genetic analysis of quantitative traits in wild emmer (Triticum turgidum L. var dicoccoides). Crop Sci 31:645–649
Chantret N, Cenci A, Sabot F, Anderson O (2004) Sequencing of the Triticum monococcum hardness locus reveals good microcolinearity with rice. Mol Genet Genomics 271:377–386
Chantret N, Salse J, Sabot F, Rahman S, Bellec A, Laubin B, Dubois I, Dossat C, Sourdille P, Joudrier P, Gautier MF, Cattolico L, Bechert M, Aubourg S, Weissenbach J, Caboche M, Bernard M, Leroy P, Chalhoub B (2005) Molecular basis of evolutionary events that shaped the hardness locus in diploid and polyploidy wheat species (Triticum and Aegilops). Plant Cell 17:1033–1045
Chee PW, Elias EM, Anderson JA, Kianian SF (2001) Evaluaion of a high protein QTL from Triticum turgidum L.v ar. dicoccoides in an adapted durum wheat background. Crop Sci 41:295–301
Doerge RW (2002) Multifactorial genetics: map** and analysis of quantitative trait locus in experimental populations. Nat Rev 3:43–52
Dohlman E, Hoffman L (2000) The new agricultural trade negotiations: background and issues for the U.S. wheat sector. Wheat yearbook. Economic Research Service, USDA
Gao LF, **g RL, Huo NX, Li Y, Li XP, Zhou RH, Chang XP, Tang JF, Ma ZY, Jia JZ (2004) One hundred and one new microsatellite loci derived from ESTs (EST-SSR) in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 108:1392–1400
Hao YF, Liu AF, Wang YH, Feng DS, Gao JR, Li XF, Liu SB, Wang HG (2008) Pm23: a new allele of Pm4 located on chromosome 2AL in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 117:1205–1212
Harjit-Singh Prasad M, Varshney RK, Roy KJ, Balyan HS, Dhaliwal HS, Gupta PK (2001) STMS markers for grain protein content and their validation using near-isogenic lines in bread wheat. Plant Breed 120:273–278
Joppa LR, Cantrell RG (1990) Chromosomal location of genes for grain protein content of wild tetraploid wheat. Crop Sci 30:1059–1064
Joppa LR, Du C, Hart GE, Hareland GA (1997) Map** a QTL for grain protein in tetraploid wheat (Triticum turgidum L.) using a population of recombinant inbred chromosome lines. Crop Sci 37:1586–1589
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Annu Eugen 12:172–175
Kuchel H, Landridge P, Mosinek L, Williams K, Jefferies SP (2006) The genetic control of milling yield, dough rheology and baking quality of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 112:1487–1495
Kulwal P, Kumar N, Kumar A, Gupta RK, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2005) Gene networks in hexaploid wheat: interacting quantitative trait loci for grain protein content. Funct Integr Genomics 5:254–259
Kumar N, Kulwal PL, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2007) QTL map** for yield and yield contributing traits in two map** populations of bread wheat. Mol Breeding 19:163–177
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Law CN, Young CF, Brown JWS, Snape JW, Worland AJ (1978) The study of grain protein control in wheat using whole chromosome substitution lines. In: Seed protein improvement by nuclear techniques. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 483–502
Li SS, Jia JZ, Wei XY, Zhang XC, Li LZ, Chen HM, Fan YD, Sun HY, Zhao XH, Lei TD, Xu YF, Jiang FS, Wang HG, Li LH (2007) A intervarietal genetic map and QTL analysis for yield traits in wheat. Mol Breeding 20:167–178
Li Y, Song Y, Zhou R, Branland Jia J (2009) Detection of QTLs for bread-making quality in wheat using a recombinant inbred line population. Plant Breed 128:235–243
Liang D, Tang JW, Peña RJ, Singh R, He XY, Shen XY, Yao DN, **a XH, He ZH (2010) Characterization of CIMMYT bread wheats for highand low-molecular weight glutenin subunits and other quality-related genes with SDS-PAGE, RP-HPLC and molecular markers. Euphytica 172:235–250
Liu SX, Chao SM, Anderson JA (2008) New DNA markers for high molecular weight glutenin subunits in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 118:177–185
Ma ZQ, Zhao DM, Zhang CQ, Zhang ZZ, Xue SL, Lin F, Kong ZX, Tian DG, Luo QY (2007) Molecular genetic analysis of five spike-related traits in wheat using RIL and immortalized F2 populations. Mol Gen Genomics 277:31–42
Mackay TFC (2001) The genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Annu Rev Genet 35:303–339
Mann G, Diffey S, Cullis B, Azanza F, Martin D, Kelly A, McIntyre L, Schmidt A, Ma WJ, Nath Z, Kutty I, Leyne PE, Rampling L, Quail KJ, Morell MK (2009) Genetic control of wheat quality: interactions between chromosomal regions determining protein content and composition, dough rheology, and sponge and dough baking properties. Theor Appl Genet 118:1519–1537
Matsuo RR, Dexter JE, Kosmolak FG, Leisle D (1982) Statistical evaluation of tests for assessing paghetti-making quality of durum wheat. Cereal Chem 59:222–228
Morris CF (2002) Puroindolines: the molecular genetic basis of wheat grain hardness. Plant Mol Biol 48:633–647
Mullan DJ, Platteter A, Teakle NL, Appels R, Colmer TD, Anderson JM, Francki MG (2005) EST-derived SSR markers from defined regions of the wheat genome to identify Lophopyrum elongatum specific loci. Genome 48:811–822
Nagaoka T, Ogihara Y (1997) Applicability of inter-simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in wheat for use as DNA markers in comparison to RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 94:597–602
Nelson JC, Andreescu C, Breseghello F, Finney PL, Gualberto DG, Bergman CJ, Peña RJ, Perretant MR, Leroy P, Qualset CO, Sorrells ME (2006) Quantitative trait locus analysis of wheat quality traits. Euphytica 149:145–159
Olmos S, Distelfeld A, Chicaiza O, Schlatter AR, Fahima T, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2003) Precise map** of a locus affecting grain protein content in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 107:1243–1251
Peng JH, Lapitan NLV (2005) Characterization of EST-derived microsatellites in the wheat genome and development of eSSR markers. Funct Integr Genomics 5:80–96
Perretant MR, Cadalen T, Charmet G, Sourdlle P, Nicolas P, Boeuf C, Tixier MH, Branlard G, Bernard S, Bernard M (2000) QTL analysis of bread-making quality in wheat using a doubled haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 100:1167–1175
Pomeranz Y, Williams PC (1990) Wheat hardness: its genetic, structural and biochemical background, measurement and significance. In: Pomeranz Y (ed) Advances in cereal science and technology, vol 10. American Association of Cereal Chemists, St Paul, pp 471–544
Prasad M, Kumar N, Kulwal PL, Röder MS, Balyan HS, Dhaliwal HS, Gupta PK (2003) QTL analysis for grain protein content using SSR markers and validation studies using NILs in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 106:659–667
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier M-H, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Schön CC, Utz HF, Groh S, Truberg B, Openshaw S, Melchinger AE (2004) Quantitative trait locus map** based on resampling in a vast maize testcross experiment and its relevance to quantitative genetics for complex traits. Genetics 167:485–498
Singh NK, Shepherd KW (1991) A simplified SDS-PAGE procedure for separation LMW subunits of glutenin. J Cereal Sci 14:203–208
Sourdille P, Perretant MR, Charmet G, Leroy P, Gautier MF, Joudrier P, Nelson JC, Sorrells ME, Bernard M (1996) Linkage between RFLP markers and gene affecting kernel hardness in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 93:580–586
Sourdille P, Perretant MR, Charmet G, Cadalen T, Tixier MH, Joudrier P, Gautier MF, Branlard G, Bernard S, Boeuf C, Bernard M (1999) Detection of QTL for bread making quality in wheat using molecular markers. In: Scarascia Mugnozza GT, Porceddu E, Pagnotta MA (eds) Genetics and breeding for crop quality and resistance. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 361–366
Stein N, Herren G, Keller B (2001) A new DNA extraction method for high-throughout marker analysis in a large-genome species such as Triticum aestivum. Plant Breed 120:354–356
Suenaga K, Khairallah M, William HM, Hoisington DA (2005) A new intervarietal linkage map and its application for quantitative trait locus analysis of ‘‘gigas’’ features in bread wheat. Genome 48:65–75
Sun XC, Marza F, Ma HX, Carver Brett F, Bai GH (2010) Map** quantitative trait loci for quality factors in an inter-class cross of US and Chinese wheat. Theor Appl Genet 120:1041–1051
Suprayogi Y, Pozniak CJ, Clarke FR, Clarke JM, Knox RE, Singh AK (2009) Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for grain protein concentration in adapted Canadian durum wheat populations. Theor Appl Genet 119:437–448
Turner AS, Bradburne RP, Fish L, Snap JW (2004) New quantitative trait loci influencing grain texture and protein content in bread wheat. J Cereal Sci 40:51–60
Uga Y, Siangliw M, Nagamine T, Ohsama R, Fujimura T, Fukuta Y (2010) Comparative map** of QTLs determining glume, pistil and stamen sizes in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Breed 129:657–669
Vales MI, Schön CC, Capettini F, Chen XM, Corey AE, Mather DE, Mundt CC, Richardson KL, Sandoval-Islas JS, Utz HF, Hayes PM (2005) Effect of population size on the estimation of QTL: a test using resistance to barley stripe rust. Theor Appl Genet 111:1260–1270
Zanetti S, Keller M, Winzeler M, Saurer W, Keller B, Messmer M (1999) QTL for quality parameters for bread-making quality in a segregating wheat by spelt population. In: Scarascia Mugnozza GT, Porceddu E, Pagnotta MA (eds) Genetics and breeding for crop quality and resistance. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 357–360
Zhao CH, Cui F, Zong H, Wang YH, Bao YG, Hao YF, Du B, Wang HG (2009) Transmission of the Chromosome 1R in winter wheat germplasm Aimengniu and its derivatives revealed by molecular markers. Agric Sci China 8(6):652–657
Zou F, Gelfond JAL, Airey DC, Lu L, Manly KF, Williams RW, hreadgill DW (2005) Quantitative trait locus analysis using ecombinant inbred intercross (RIX): theoretical and empirical considerations. Genetics 170:1299–1311
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2006CB101700). The author thanks Sishen Li, College of Agronomy, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, China, for kindly providing EST-SSR markers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. Li, F. Cui, A. Ding and C. Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Cui, F., Ding, Am. et al. QTL detection of seven quality traits in wheat using two related recombinant inbred line populations. Euphytica 183, 207–226 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0448-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0448-4