Abstract
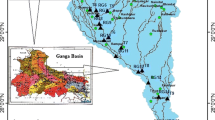
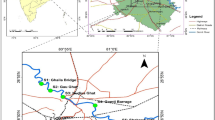
Seven representative sampling stations were selected from Indus Delta comprising of (1) Keti Bander, (2) Darya Peer, (3) Kharo Chanr, (4) Jati, (5) Shah Bander, (6) Nariri Dhand and (7) Left Bank Outfall Drain (LBOD) near Rupa Mari. The sampling scheme was repeated seven times during 2014–2015 for 1 year. The samples were analysed for temperature, conductivity, pH, hardness, chloride, alkalinity, dissolved oxygen, biological oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand, sulphate, orthophosphate-P, nitrite-N, nitrate-N, Na, K, Fe, Ni, Cr, Co, Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb and As. The analysis was carried out using standard analytical procedures. A number of parameters crossed the WHO permissible limits and water quality guidelines for aquatic life and indicated pollution within coastal region. Coefficient of correlation (r) among physicochemical parameters and metal ions were examined and a number of parameters did not correlate positively and did not indicate natural origin and may indicate their presence due to human activity. The samples were examined for cluster analysis, and principal component analysis. The samples also indicated the presence of Presumptive Coliform, Faecal coliform and E. coli.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamgir, A., Khan, M. A., Schilling, J., Shaukat, S. S., & Shahab, S. (2016). Assessment of groundwater quality in the coastal area of Sindh province, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 78–90.
Alamgir, A., Khan, M. A., Shaukat, S. S., Shahab, S., Khan, T. M. A., & Zubair, S. (2017). Water quality appraisal of Keti Bander and Shah Bander creeks of Indus Delta, Sindh, Pakistan. Desalination and Water Treatment, 70, 95–105.
Alkarkhi, F. M. A., Ismail, N., & Easa, A. M. (2008). Assessment of arsenic and heavy metal contents in cockles (Anadara granosa) using multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazardous Materials, 150, 783–789.
APHA (1998), Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater,
Azizullah, A., Khattak, M. N. K., Richter, P., & Hader, D.-P. (2011). Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—A review. Environmental International, 37, 479–497.
Chanpiwat, P., Stiannopkao, S., & Kim, K. W. (2010). Metal content variation in wastewater and biosuludge from Bangkok’s central wastewater treatment plants. Microchemical Journal, 95, 326–332.
Chen, K., Jiao, J. J., Huang, J., & Huang, R. (2007). Multivariate statically evaluation of trace elements in groundwater in a coastal area in Shenzhen. China, Environmental Pollution, 147(3), 771–780.
Danielsson, A., Cato, I., Carman, R., & Rahm, L. (1999). Spatial clustering of metals in the sediments of the Skagerrak/Kattegat. Applied Geochemistry, 14, 689–706.
Giosan, L., Constantinescu, S., Clift, P. D., Danish, M., & Inam, A. (2006). Recent morphodynamics of the Indus Delta shore and shelf. Continental Shelf Rearch, 26(14), 1668–1684.
Gelenn, E. P., Lee, C., Felger, R., & Zengel, S. (1996). Effect of water management on wetlands of the Colorado river delta, Mexico. Conservation Biology, 10(4), 1175–1186.
Hug, B. U., (1990), Past, present and future of the Indus Delta, the Indus River, biodiversity, resources, humankind, (Meadows, A., Meadows, P. S.,) The Linnaean Society of London, Oxford University Press, Oxford, U.K., pp 231–248.
Inam, A., Khan, A. T. M., Amjad, S., Danish, M., & Tabrez, A. R. (2004). Natural and man made stresses on the stability of Indus deltaic ecoregion. Extended Abstract. In The Fifth International Conference on Asian Marine Geology, Bangkok, Thailand (IGCP475/APN).http://www.megadelta.ecnu.edu.cn/main/upload/Asifpaper1.pdf.
Kalhoro, N. A., He, Z., Xu, D., Faiz, M., Yafei, L. V., Sohoo, N., & Bhutto, A. H. (2016). Vulnerability of the Indus River Delta of the north Arabian Sea, Pakistan. Global NEST Journal, 18(3), 599–610.
Khan, S. H., Saleem, M., (1988), A preliminary study of pollution in Karachi harbour. In Marine Science of the Arabian Sea, (Eds. Thompson, M. F., Timizi, W. M.), American Institute of Biology Science, Washington, D.C.
Khattak, M. I., & Mohibullah, M. (2012). Study of heavy metal pollution in mangrove sediments reference to marine environment along the coastal area of Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 44, 373–378.
Kim, J. H., Kim, R. H., Lee, J., Cheong, T. J., Yam, B. W., & Chang, H. W. (2005). Multivariate statistical analysis to identify the major factors governing groundwater quality in the coastal area of Kimje, South Korea. Hydrology Process, 19, 1261–1276.
Klavins, M., Brieda, A., Rodinov, V., Kokorite, L., Parele, E., & Klavina, I. (2000). Heavy metals in rivers of Laliva. Science of Total Envirnment, 262, 175–183.
Leichenko, B. M., & Wescoat Jr., J. L. (1993). Environmental impacts of climate change and water development in the Indus Delta Region. Water Resources Development, 9(3), 247–261.
Li, R., Dong, M., Zhao, Y., Cui, Q., & He, W. (2007). Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution source of Plateau lake in Yunnan (China). J. Environ. Quality., 36, 291–297.
Marine Pollution Base Line Survey in Korangi Pakistan, Final Report of IUCN Contract no OD/CDC/201/IAEA–(1987), Pakistan base line survey project 9128, prepared by the IAEA- Marine Environmental Studies Laboritories, International Laboratory of Marine Radioactivity IAEA Oceanographic Museum, Mc 98000, Monaco.
Martaza, G., (2014), Review article, Pollution status of Pakistan. A respective review on heavy metal contamination of water, soil and vegetables, Bio Med. Research International, Article ID 813206, 29 pages, https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/813206.
Memon, J. A., & Thapa, G. B. (2011). The Indus irrigation system, natural resources, and community occupational quality in the delta region of Pakistan. Environmental management, 47(2), 173-187.
Milliman, J. D., & Meade, R. H. (1983). Worldwide delivery of sediment to the oceans. Journal of Geology, 91(1), 1–21.
Ouyang, Y., Higman, J., Thompson, J., O’Toole, T., & Campbell, D. (2002). Characterisation and spatial distribution of heavy metals in sediments from cedar and Ortega rivers sub-basin. J. Contaminant Hydrology, 54, 19–35.
Planning and Development Department, Governemnt of Sindh, (2008–2009), Indus Delta, Sindh Development Reviews, 211–214.
Qureshi, R. M., Mashiatullah, A., Abram, M., Sajad, M. I., Shafiq, M., Javed, T., Aslam, M., (1999), Radiological assessment of coastal marine sedimentsand water samples, Karachi coast, Pakistan, radiation and isotope application division, Pakistan Institute of Nuclear Science & Technology, P. O. Nilore, Islamabad, Pakistan.
Raza, R., & Singh, G. (2010). Heavy metal contamination and its indexing approach for river water. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 7, 785–792.
Reghunath, R., Murthy, T. R. S., & Raghavan, B. R. (2002). The utility of multivariate statistical technique in hydrochemical studies: an example from Karnalaka, India. Water Research, 36, 2437–2443.
Saifullah, S. M., & Mahera, S. (2004). Insect herbivory in polluted mangroves of Indus Delta. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 36, 127–131.
Simeonov, V., Stratis, J. A., Samara, C., Zachariadis, G., Voutsa, D., & Anthemidis, A. (2003). Assessment of the surface water quality in Northern Greece. Water Research, 37, 4119–4124.
Storelli, M. M., Storelli, A., D’Addabbo, R., Marano, C., Burno, R., & Marcotrigiano, G. O. (2005). Trace elements in loggerhead turtle (Caretta caretta) from eastern Mediterranean Sea, overview and evaluation. Environmental Pollution, 135, 163–170.
Strachan, S., (2010), Trace elements, Trends in Anaesthesia & Critical Care, 21, 44–48. Twentieth ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, D. C.
Vorosmatry, C. J., Sharma, K. P., Kekete, B. M., Copeland, A. H., Holden, J., Marble, J., & Lough, J. A. (1997). The storage and ageing of continental run off in large reservoir system of the world. Ambio, 26, 26–219.
Walling, D. E., & Fang, D. (2003). Recent trends in suspended sediment loads of the world rivers. Global and Planetary Change, 39(1–2), 111–126.
Wells, J. T., Colman, J. M., (1984), Deltaic morphology and sedimentology , with special reference to Indus River Delta, Marine Geology and Occenography of Arabian Sea and Coastal Pakistan, (Haq, B. U., Milliman, J. D.), Van Nostrand Reinhold, NewYork, pp 85–100.
Zaqoot, H. A., Khan, S. H., Ansari, A. K., & Qureshi, K. (2009). Assessment of water quality in the coastal environment of Karachi bordering northern Arabian Sea. Journal of Flood Engineering, 1(1), 5–19.
Zia, I., Zafar, H., Shahzad, M., Meraj, M., & Kazmi, J. H. (2017). Assessment of sea water inundation along Daboo Creek area in Indus Delta Region, Pakistan. Journal of Ocean University of China, 16(6), 1055–1060.
Acknowledgements
The assistance of department of Fesheries and Livestock, and Sindh coastal department Authority Karachi is acknowledged for their help in selecting locations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khuhawar, M.Y., Zaman Brohi, R.O., Jahangir, T.M. et al. Water quality assessment of Ramser site, Indus Delta, Sindh, Pakistan. Environ Monit Assess 190, 492 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6756-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6756-6