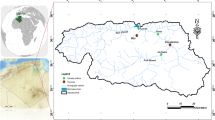
Abstract
Water quality assessment is crucial for assessment of marine eutrophication, prediction of harmful algal blooms, and environment protection. Previous studies have developed many numeric modeling methods and data driven approaches for water quality assessment. The cluster analysis, an approach widely used for grou** data, has also been employed. However, there are complex correlations between water quality variables, which play important roles in water quality assessment but have always been overlooked. In this paper, we analyze correlations between water quality variables and propose an alternative method for water quality assessment with hierarchical cluster analysis based on Mahalanobis distance. Further, we cluster water quality data collected form coastal water of Bohai Sea and North Yellow Sea of China, and apply clustering results to evaluate its water quality. To evaluate the validity, we also cluster the water quality data with cluster analysis based on Euclidean distance, which are widely adopted by previous studies. The results show that our method is more suitable for water quality assessment with many correlated water quality variables. To our knowledge, it is the first attempt to apply Mahalanobis distance for coastal water quality assessment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alameddine, I., Kenney, M. A., Gosnell, R. J., & Reckhow, K. H. (2010). Robust multivariate outlier detection methods for environmental data. Journal of environmental engineering, 136(11), 1299–1304.
An, F., & Tao, J. (2008). Method of two-grade fuzzy synthesis assessment of seawater eutrophication and its application in Bohai bay. Marine environmental science, 27, 366–369.
Barhillel, A., Hertz, T., Shental, N., & Weinshall, D. (2005). Learning a Mahalanobis metric from equivalence constraints. Journal of machine learning research, 937–965.
Cao, Y., Bark, A. W., & Williams, W. P. (1997). A comparison of clustering methods for river benthic community analysis. Hydrobiologia, 347(1), 24–40.
Chang, F., Tsai, Y., Chen, P., Coynel, A., & Vachaud, G. (2015). Modeling water quality in an urban river using hydrological factors—Data driven approaches. Journal of environmental management, 151, 87–96.
Chau, K. (2006). A review on integration of artificial intelligence into water quality modelling. Marine pollution bulletin, 52(7), 726–733.
Chaves, P. H., Tsukatani, T., & Kojiri, T. (2004). Operation of storage reservoir for water quality by using optimization and artificial intelligence techniques. Mathematics and computers in simulation, 67, 419–432.
Du, X., **ng, C., Shao, F., & Sun, R. (2015). A novel marine big data analysis framework based on complex network theory. International conference on communication technology. 186–191.
Dwarakish, G. S., Sarkar, A., & Pandey, P. (2015). River water quality modelling using artificial neural network technique. Aquatic Procedia, 4, 1070–1077.
Everitt, B. S., Landau, S., & Leese, M. (2001). Cluster analysis. London: Arnold press.
Farber, O., & Kadmon, R. (2003). Assessment of alternative approaches for bioclimatic modeling with special emphasis on the Mahalanobis distance. Ecological modelling, 160(1), 115–130.
Ferreira, J. G., Andersen, J. H., Borja, A., Bricker, S. B., Camp, J., Silva, M. C. D., Garces, E., Heiskanen, A., Humborg, C., & Ignatiades, L. (2011). Overview of eutrophication indicators to assess environmental status within the European marine strategy framework directive. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 93(2), 117–131.
Forio, M. A., Landuyt, D., Bennetsen, E., Lock, K., Nguyen, T. H., Ambarita, M. N., Musonge, Peace, L. S., Boets, P., Everaert, G., & Dominguezgranda, L. (2015). Bayesian belief network models to analyze and predict ecological water quality in rivers. Ecological modelling, 312, 222–238.
Goes, J. I., Saino, T., Oaku, H., Ishizaka, J., Wong, C. S., & Nojiri, Y. (2000). Basin scale estimates of sea surface nitrate and new production from remotely sensed sea surface temperature and chlorophyll. Geophysical research letters, 27(9), 1263–1266.
Gower, J., & Legendre, P. (1986). Metric and Euclidean properties of dissimilarity coefficients. Journal of classification, 3(1), 5–48.
de Amorim, R. C., & Hennig, C. (2015). Recovering the number of clusters in data sets with noise features using feature rescaling factors. Information sciences, 324, 126–145.
Kamble, S. R., & Vijay, R. (2010). Assessment of water quality using cluster analysis in coastal region of Mumbai, India. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 178, 321–332.
Karydis, M. (1992). Scaling methods in assessing environmental quality: a methodological approach to eutrophication. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 22(2), 123–136.
Karydis, M., & Kitsiou, D. (2013). Marine water quality monitoring: A review. Marine pollution bulletin, 77, 23–36.
Kitsiou, D., & Karydis, M. (2011). Coastal marine eutrophication assessment: a review on data analysis. Environment international, 37(4), 778–801.
Kong, X., & Ye, S. (2014). The impact of water temperature on water quality indexes in north of Liaodong Bay. Marine pollution bulletin, 80(1), 245–249.
Kuo, J., Hsieh, M., Lung, W., & She, N. (2007). Using artificial neural network for reservoir eutrophication prediction. Ecological modelling, 200(1), 171–177.
Kuo, J., Lung, W., Yang, C., Liu, W., Yang, M., & Tang, T. (2006). Eutrophication modelling of reservoirs in Taiwan. Environmental modelling and software, 21(6), 829–844.
Liang, S., Han, S., & Sun, Z. (2015). Parameter optimization method for the water quality dynamic model based on data-driven theory. Marine pollution bulletin, 98(1), 137–147.
Liu, S., Lou, S., Kuang, C., Huang, W., Chen, W., Zhang, J., & Zhong, G. (2011). Water quality assessment by pollution-index method in the coastal waters of Hebei Province in western Bohai Sea, China. Marine pollution bulletin, 62(10), 2220–2229.
Liu, H., & Yin, B. (2010). Numerical investigation of nutrient limitations in the Bohai Sea. Marine environmental research, 70(3), 308–317.
Lobato, T. D., Hauserdavis, R. A., De Oliveira, T. F., Silveira, A. M., Silva, H. J., Tavares, M., & Saraiva, A. (2015). Construction of a novel water quality index and quality indicator for reservoir water quality evaluation: a case study in the Amazon region. Journal of hydrology, 522, 674–683.
Ludwig, J. A., & Reynolds, J. F. (1988). Statistical ecology: a primer on methods and computing. Journal of applied ecology, 26(3), 1099–1100.
Magurran, A. E. (2004). Measuring biological diversity. Hoboken: Blackwell Science Ltd..
Mahalanobis, P. C. (1936). On the generalized distance in statistics. Proceedings of the National Institute of Science of India, 2, 49–55.
Mao, X., Jiang, W., Zhao, P., & Gao, H. (2008). A 3-D numerical study of salinity variations in the Bohai Sea during the recent years. Continental shelf research, 28(19), 2689–2699.
McLachlan, G. (1999). Mahalanobis distance. Resonance, 4(6), 20–26.
Melesse, A. M., Krishnaswamy, J., & Zhang, K. (2008). Modeling coastal eutrophication at Florida bay using neural networks. Journal of coastal research, 24, 190–196.
Palani, S., Liong, S., & Tkalich, P. (2008). An ANN application for water quality forecasting. Marine pollution bulletin, 56(9), 1586–1597.
Panda, U. C., Sundaray, S. K., Rath, P., Nayak, B. B., & Bhatta, D. (2006). Application of factor and cluster analysis for characterization of river and estuarine water systems—a case study: Mahanadi River (India). Journal of hydrology, 331(3), 434–445.
Peter, J. R. (1987). Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. Journal of computational and applied mathematics, 20, 53–65.
Primpas, I., Karydis, M., & Tsirtsis, G. (2008). Assessment of clustering algorithms in discriminating eutrophic levels in coastal waters. Glob Nest Journal, 10, 359–365.
Primpas, I., Tsirtsis, G., Karydis, M., & Kokkoris, G. D. (2010). Principal component analysis: Development of a multivariate index for assessing eutrophication according to the European water framework directive. Ecological indicators, 10(2), 178–183.
Rajar, R., & Cetina, M. (1997). Hydrodynamic and water quality modelling: an experience. Ecological modelling, 101(2), 195–207.
Robinson, R., Cox, C. D., & Odom, K. R. (2005). Identifying outliers in correlated water quality data. Journal of environmental engineering, 131(4), 651–657.
Romesburg, H. C. (2004). Cluster analysis for researchers. North Carolina: Lulu Press.
Salah, E., Turki, A. M., & Alothman, E. M. (2012). Assessment of water quality of Euphrates River using cluster analysis. Journal of environmental protection, 3(12), 1629–1633.
Seiler, L. M., Fernandes, E. H., Martins, F., & Abreu, P. C. (2015). Evaluation of hydrologic influence on water quality variation in a coastal lagoon through numerical modeling. Ecological Modelling, 314, 44–61.
Singh, K. P., Basant, A., Malik, A., & Jain, G. (2009). Artificial neural network modeling of the river water quality—a case study. Ecological modelling, 220(6), 888–895.
Sundermann, J., & Feng, S. (2004). Analysis and modelling of the Bohai sea ecosystem—a joint German–Chinese study. Journal of marine systems, 44(3), 127–140.
Tan, P.-N., Steinbach, M., & Kumar, V. (2005). Introduction to data mining. Boston: Addison-Wesley press.
Tan, G., Yan, J., Gao, C., & Yang, S. (2012). Prediction of water quality time series data based on least squares support vector machine. Procedia Engineering, 31, 1194–1199.
Wang, C., Li, X., & Lv, X. (2012). Adjoint assimilation of SeaWiFS data into a marine ecosystem dynamical model of the Bohai Sea and the North Yellow Sea. Procedia environmental sciences, 13, 2045–2061.
Wang, X., Zou, Z., & Zou, H. (2013). Water quality evaluation of Haihe River with fuzzy similarity measure methods. Journal of Environmental Sciences China, 25(10), 2041–2046.
Wu, S., Shao, F., Wang, Y., Sun, R., & Sui, Y. (2013). Red tide forecast with semi-supervised clustering. International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering. 81–86.
Wu, M., Wang, Y., Sun, C., Wang, H., Dong, J., Yin, J., & Han, S. (2010). Identification of coastal water quality by statistical analysis methods in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Marine pollution bulletin, 60(6), 852–860.
**ang, S., Nie, F., & Zhang, C. (2008). Learning a Mahalanobis distance metric for data clustering and classification. Pattern recognition, 41(12), 3600–3612.
**ong, H., Wu, J., & Chen, J. (2009). K-means clustering versus validation measures: a data-distribution perspective. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics., 3, 318–331.
Xu, H., Xu, Z., Wu, W., & Tang, F. (2012). Assessment and spatiotemporal variation analysis of water quality in the Zhangweinan River Basin, China. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 1641–1652.
Yang, S., Dong, S., Dou, M., Xu, Z., Li, F., & Wu, Y. (2007). Study on ecological environment in the Bohai BayII. Assessment of coastal eutrophication. Marine environmental science, 26, 541–545.
Yang, J., Li, H., Liu, Q. Z., He, E., & Ren, X. X. (2012). Environmental factors affecting chlorophyll-a concentration in the Bohai bay. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 43, 1023–1029.
Zhang, Y., Huang, D., Ji, M., & **e, F. (2011). Image segmentation using PSO and PCM with Mahalanobis distance. Expert systems with applications, 38(7), 9036–9040.
Zhang, J., Yu, Z., Raabe, T., Liu, S., Starke, A., Zou, L., Gao, H., & Brockmann, U. H. (2004). Dynamics of inorganic nutrient species in the Bohai seawaters. Journal of marine systems, 44(3), 189–212.
Zhang, Z., Zhu, M., Wang, Z., & Wang, J. (2006). Monitoring and managing pollution load in Bohai Sea, PR China. Ocean & Coastal Management, 49(9), 706–716.
Zou, J., Dong, L., & Qin, B. (1985). Preliminary studies on eutrophication and red tide problems in Bohai Bay. Hydrobiologia, 127(1), 27–30.
Zou, H., Zou, Z., & Wang, X. (2015). An enhanced K-means algorithm for water quality analysis of the Haihe River in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 12, 14400–14413.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [NO. 41476101], and we also thank North China Sea Branch of State Oceanic Administration for providing water quality monitoring data. In addition, we would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Shao, F., Wu, S. et al. Water quality assessment with hierarchical cluster analysis based on Mahalanobis distance. Environ Monit Assess 189, 335 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6035-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6035-y