Abstract
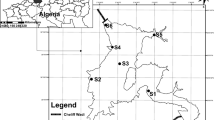
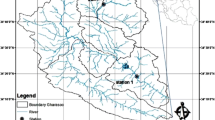
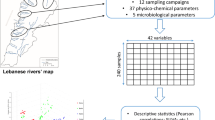
Surface water quality monitoring constitutes a crucial and important step in any water quality management system. Twenty-three physicochemical and microbiological parameters were assessed in surface water samples collected from the Arka River located in the Akkar District, north of Lebanon. Eight sampling locations were considered along the river and seven sampling campaigns were performed in order to evaluate spatial and temporal influences. The extraction of relevant information from this relatively large data set was done using principal component analysis (PCA), being a very well established chemometric tool in this field. In a first step, extracted PCA loadings revealed the implication of several physicochemical parameters in the discriminations and trends highlighted by PCA scores, mainly due to soil leaching and seawater intrusion. However, further investigations showed the implication of organic and bacterial parameters in the discrimination of stations in the Akkar flatland. These discriminations probably refer to anthropogenic pollution coming from the agricultural area and the surrounding villages. Specific ultraviolet absorption (SUVA) indices confirmed these findings since values decreased for samples collected across the villages and the flatland, indicating an increase in anthropogenic dissolved organic matter. This study will hopefully help the national and local authorities to ameliorate the surface water quality management, enabling its proper use for irrigation purposes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ates, N., Kitis, M., & Yetis, U. (2007). Formation of chlorination by-products in waters with low SUVA-correlations with SUVA and differential UV spectroscopy. Water Research, 41(18), 4139–4148. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.05.042.
Bazrafshan, E., Biglari, H., & Kord Mostafapour, F. (2012). Determination of hydrophobic and hydrophilic fractions of natural organic matter in raw water of Zahedan water treatment plant. Journal of Health Scope, 1(1), 25–28. doi:10.5812/jhs.4535.
Cordella, C. B. Y., Tekye, T., Rutledge, D. N., & Leardi, R. (2012). A multiway chemometric and kinetic study for evaluating the thermal stability of edible oils by 1H NMR analysis: comparison of methods. Talanta, 88, 358–368. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2011.11.001.
Daou, C., Salloum, M., Mouneimne, A. H., Legube, B., & Ouaini, N. (2013). Multidimensionnal analysis of two Lebanese surface water quality: Ibrahim and el-Kalb rivers. Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 9(4), 2777–2787.
Dimitri, X. (2010). Project UTF/LEB/019/LEB, wastewater reuse and sludge valorisation and reuse: proposition for Lebanese wastewater reuse guidelines. Rome: United nations-Food and Agricultural Organisation (FAO).
ECODIT Liban. (2015). Final SEA report: strategic environmental assessment for the new water sector strategy for Lebanon. Plan Bleu and the Lebanese Ministry of Energy and Water.
El Moujabber, M., Bou Samra, B., Darwish, T., & Atallah, T. (2006). Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese coast. Water Resources Management, 20(2), 161–180. doi:10.1007/s11269-006-7376-4.
Fan, X., Cui, B., Zhao, H., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, H. (2010). Assessment of river water quality in Pearl River Delta using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2(5), 1220–1234. doi:10.1016/j.proenv.2010.10.133.
Gazzaz, N. M., Yusoff, M. K., Ramli, M. F., Aris, A. Z., & Juahir, H. (2012). Characterization of spatial patterns in river water quality using chemometric pattern recognition techniques. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(4), 688–698. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.01.032.
Haddad, M., & Lindner, K. (2001). Sustainable water demand management versus develo** new and additional water in the Middle East: a critical review. Water Policy, 3, 143–163. doi:10.1016/S1366-7017(01)00006-X.
Hua, G., Reckhow, D. A., & Abusallout, I. (2015). Correlation between SUVA and DBP formation during chlorination and chloramination of NOM fractions from different sources. Chemosphere, 130, 82–89. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.03.039.
Mohammad Rusan, M. J., Hinnawi, S., & Rousan, L. (2007). Long term effect of wastewater irrigation of forage crops on soil and plant quality parameters. Desalination, 215(1–3), 143–152. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2006.10.032.
OCHA. (2014). Lebanon: Akkar Governorate Profile (as of 11 August 2014).
Olsen, R. L., Chappell, R. W., & Loftis, J. C. (2012). Water quality sample collection, data treatment and results presentation for principal components analysis— literature review and Illinois River watershed case study. Water Research, 46(9), 3110–3122. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.028.
Ouyang, Y. (2005). Evaluation of river water quality monitoring stations by principal component analysis. Water Research, 39, 2621–2635. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.024.
Rattan, R. K., Datta, S. P., Chhonkar, P. K., Suribabu, K., & Singh, A. K. (2005). Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater - a case study. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 109(3–4), 310–322. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2005.02.025.
Razmkhah, H., Abrishamchi, A., & Torkian, A. (2010). Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in water quality by pattern recognition techniques: a case study on Jajrood River (Tehran, Iran). Journal of Environmental Management, 91(4), 852–860. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.11.001.
Shin, E.-C., Craft, B. D., Pegg, R. B., Phillips, R. D., & Eitenmiller, R. R. (2010). Chemometric approach to fatty acid profiles in runner-type peanut cultivars by principal component analysis (PCA). Food Chemistry, 119(3), 1262–1270. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.07.058.
Shrestha, S., & Kazama, F. (2007). Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22(4), 464–475. doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2006.02.001.
Sun, Y., Cui, X., & Liu, F. (2015). Effect of irrigation regimes and phosphorus rates on water and phosphorus use efficiencies in potato. Scientia Horticulturae, 190, 64–69. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2015.04.017.
Varol, M., Gökot, B., Bekleyen, A., & Şen, B. (2012). Spatial and temporal variations in surface water quality of the dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Catena, 92, 11–21. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2011.11.013.
Walker, D., Jakovljević, D., Savić, D., & Radovanović, M. (2015). Multi-criterion water quality analysis of the Danube River in Serbia: a visualisation approach. Water Research, 79(1983), 158–172. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2015.03.020.
Wang, Y., Wang, P., Bai, Y., Tian, Z., Li, J., Shao, X., et al. (2013). Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. Journal of Hydro-Environment Research, 7(1), 30–40. doi:10.1016/j.jher.2012.10.003.
Wilbers, G.-J., Becker, M., Nga, L. T., Sebesvari, Z., & Renaud, F. G. (2014). Spatial and temporal variability of surface water pollution in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. The Science of the Total Environment, 485-486, 653–665. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.03.049.
Xu, J., Wu, L., Chang, A. C., & Zhang, Y. (2010). Impact of long-term reclaimed wastewater irrigation on agricultural soils: a preliminary assessment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1–3), 780–786. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.094.
Zhao, Y., **a, X. H., Yang, Z. F., & Wang, F. (2012). Assessment of water quality in Baiyangdian Lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13(2011), 1213–1226. doi:10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.115.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Michel Afram, PDG of the Lebanese Agricultural Research Institute (LARI) and Mr. Michel Issa El Khoury, responsible of LARI, Abdeh station, for their valuable help in accomplishing this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daou, C., Nabbout, R. & Kassouf, A. Spatial and temporal assessment of surface water quality in the Arka River, Akkar, Lebanon. Environ Monit Assess 188, 684 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5686-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5686-4