Abstract
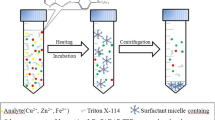
A novel improved preconcentration method known as rapidly synergistic cloud point extraction (RS-CPE) was established for nickel preconcentration and determination prior to its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. In this work, the traditional CPE pattern was changed and greatly simplified in order to be applicable in metal extraction and detection. This method was accomplished in room temperature in 1 min. Non-ionic surfactant Triton X-114 was used as extractant. Octanol worked as cloud point revulsant and synergic reagent. The various parameters affecting the extraction and preconcentration of nickel such as sample pH, 2,2′-Furildioxime concentration, amounts of octanol, amounts of Triton X-114, type of diluting solvent, extraction time, and ionic strength were investigated and optimized. Under optimal conditions, the calibration curve showed an excellent linearity in the concentration range of 2–200 μg L−1, and the limit of detection was 0.6 μg L−1 for nickel. The developed method was successfully applied for the determination of nickel in food and water samples. The results showed that, the proposed method can be used as a cheap, rapid, and efficient method for the extraction and preconcentration of nickel from real samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amais, R. S., Ribeiro, J. S., Segatelli, M. G., Yoshida, I. V. P., Luccas, P. O., & Tarley, C. R. T. (2007). Assessment of nanocomposite alumina supported on multi-wall carbon nanotubes as sorbent for on-line nickel preconcentration in water samples. Sep Purif Technol, 58, 122–128.
Arslan, Z., & Paulson, A. J. (2002). Analysis of biogenic carbonates by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry (ICP–MS). Flow injection on-line solid-phase preconcentration for trace element determination in fish otoliths. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 372, 776–785.
Aydin, F. A., & Soylak, M. (2007). A novel multi-element coprecipitation technique for separation and enrichment of metal ions in environmental samples. Talanta, 73, 134–141.
Azevedo Lemos, V., Selis Santos, M., Teixeira David, G., Vasconcelos Maciel, M., & Almeida Bezerra, M. D. (2008). Development of a cloud-point extraction method for copper and nickel determination in food samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 159, 245–251.
Baytak, S. (2007). Solid-phase extractor with ram horn powder for lead and cadmium determination in environmental samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 54, 385–391.
Beiraghi, A., Babaee, S., & Roshdi, M. (2012). Simultaneous preconcentration of cadmium, cobalt and nickel in water samples by cationic micellar precipitation and their determination by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 100, 66–71.
Bhaskara Sarma, P. V. R., & Reddy, B. R. (2002). Liquid–liquid extraction of nickel at macro-level concentration from sulphate/chloride solutions using phosphoric acid based extractants. Minerals Engineering, 15, 461–464.
Çimen, G., Tokalıoğlu, Ş., Özentürk, İ., & Soykan, C. (2013). Speciation and preconcentration of chromium from water and food samples by synthesized chelating resin. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 24, 856–864.
Citak, D., Tuzen, M., & Soylak, M. (2009). Simultaneous coprecipitation of lead, cobalt, copper, cadmium, iron and nickel in food samples with zirconium(IV) hydroxide prior to their flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 47, 2302–2307.
Dadfarnia, S., Haji Shabani, A. M., Shirani Bidabadi, M., & Jafari, A. A. (2010). A novel ionic liquid/micro-volume back extraction procedure combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry for determination of trace nickel in samples of nutritional interest. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 534–538.
Dean, J. A., & Rains, T. C. (1975). Flame emission and atomic absorption spectrometry. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Divrikli, U., Kartal, A. A., Soylak, M., & Elci, L. (2007). Preconcentration of Pb(II), Cr(III), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Cd(II) ions in environmental samples by membrane filtration prior to their flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 145, 459–464.
Dobrowolski, R., & Otto, M. (2012). Determination of nickel and cobalt in reference plant materials by carbon slurry sampling GFAAS technique after their simultaneous preconcentration onto modified activated carbon. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 26, 58–65.
Ferreira, S. L. C., Santos, W. N. L. D., & Lemos, V. A. (2001). On-line preconcentration system for nickel determination in food samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 445, 145–151.
Ghaedi, M., Ahmadi, F., & Soylak, M. (2007). Preconcentration and separation of nickel, copper and cobalt using solid phase extraction and their determination in some real samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 226–231.
Ghaedi, M., Niknam, K., Taheri, K., Hossainian, H., & Soylak, M. (2010). Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of copper, zinc and manganese after solid-phase extraction using 2,6-dichlorophenyl-3,3-bis(indolyl)methane loaded on Amberlite XAD-16. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 48, 891–897.
Hashemi, O. R., Kargar, M. R., Raoufi, F., Moghimi, A., Aghabozorg, H., & Ganjali, M. R. (2001). Separation and preconcentration of trace amounts of lead on octadecyl silica membrane disks modified with a new S-containing Schiff’s base and its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Microchemical Journal, 69, 1–6.
Karimi, H., Ghaedi, M., Shokrollahi, A., Rajabi, H. R., Soylak, M., & Karami, B. (2008). Development of a selective and sensitive flotation method for determination of trace amounts of cobalt, nickel, copper and iron in environmental samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 151, 26–32.
Kong, X., Jia, Q., & Zhou, W. (2007). Coupling on-line preconcentration by ion-exchange with microwave plasma torch-atomic emission spectrometry for the determination of cobalt and nickel. Microchemical Journal, 87, 132–138.
Kristiansen, J., Christensen, J. M., Henriksen, T., Nielsen, N. H., & Menne, T. (2000). Determination of nickel in fingernails and forearm skin (stratum corneum). Analytica Chimica Acta, 403, 265–272.
Lertlapwasin, R., Bhawawet, N., Imyim, A., & Fuangswasdi, S. (2010). Ionic liquid extraction of heavy metal ions by 2-aminothiophenol in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate and their association constants. Separation and Purification Technology, 72, 70–76.
Moawed, E. A., & El-Shahat, M. F. (2006). Preparation, characterization and application of polyurethane foam functionalized with α-naphthol for preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of nickel and copper in cast iron and granite. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 66, 720–727.
Park, Y. J., & Fray, D. J. (2009). Separation of zinc and nickel ions in a strong acid through liquid–liquid extraction. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163, 259–265.
Rahnama, R., Chamani Jojadeh, Z., & Jamali, M. R. (2012). Spectrophotometric determination of trace levels of nickel in water samples after dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using 2,2-Furildioxime as the complexing agent. Acta Chimica Slovenica, 59, 641–647.
Safavi, A., Abdollahi, H., Hormozi Nezhad, M. R., & Kamali, R. (2004). Cloud point extraction, preconcentration and simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of nickel and cobalt in water samples. Spectrochimica Acta, Part A, 60, 2897–2901.
Sahin, C. A., Efecinar, M., & Satiroglu, N. (2010). Combination of cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry for preconcentration and determination of nickel and manganese ions in water and food samples. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176, 672–677.
Schick, M. J. (Ed.). (1987). Non-ionic surfactants. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Shirani Bidabadi, M., Dadfarnia, S., & Haji Shabani, A. M. (2009). Solidified floating organic drop microextraction (SFODME) for simultaneous separation/preconcentration and determination of cobalt and nickel by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 291–296.
Silva, E. L., Santos Roldan, P., & Fernanda Gine, M. (2009). Simultaneous preconcentration of copper, zinc, cadmium, and nickel in water samples by cloud point extraction using 4-(2-pyridylazo)-resorcinol and their determination by inductively coupled plasma optic emission spectrometry. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 1133–1138.
Soylak, M., & Aydin, A. (2011). Determination of some heavy metals in food and environmental samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after coprecipitation. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 49, 1242–1248.
Soylak, M., Kars, A., & Narin, I. (2008). Coprecipitation of Ni2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ for preconcentration in environmental samples prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 159, 435–439.
Templeton, D. (1990). Biological monitoring of chemical exposure in the workplace. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wen, X. D., Deng, Q. W., Ji, S. L., Yang, S. C., & Peng, L. (2012). Design of rapidly synergistic cloud point extraction of ultra-trace lead combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry determination. Microchemical Journal, 100, 31–35.
Wen, X. D., Wu, P., Chen, L., & Hou, X. D. (2009). Determination of cadmium in rice and water by tungsten coil electrothermal vaporization-atomic fluorescence spectrometry and tungsten coil electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Analytica Chimica Acta, 650, 33–38.
Wen, X. D., Ye, L. Q., Deng, Q. W., & Peng, L. (2011). Investigation of analytical performance for rapidly synergistic cloud point extraction of trace amounts of copper combined with spectrophotometric determination. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 83, 259–264.
Zendelovska, D., Pavlovska, G., Cundeva, K., & Stafilov, T. (2001). Electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometric determination of cobalt, copper, lead and nickel traces in aragonite following flotation and extraction separation. Talanta, 54, 139–146.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks the research council at Payame Noor University for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahnama, R., Najafi, M. The use of rapidly synergistic cloud point extraction for the separation and preconcentration of trace amounts of Ni (II) ions from food and water samples coupling with flame atomic absorption spectrometry determination. Environ Monit Assess 188, 150 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5146-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5146-1