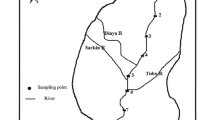
Abstract
Principal component analysis (PCA) is capable of handling large sets of data. However, lack of consistent method in data pre-treatment and its importance are the limitations in PCA applications. This study examined pre-treatments methods (log (x + 1) transformation, outlier removal, and granulometric and geochemical normalization) on dataset of Mengkabong Lagoon, Sabah, mangrove surface sediment at high and low tides. The study revealed that geochemical normalization using Al with outliers removal resulted in a better classification of the mangrove surface sediment than that outliers removal, granulometric normalization using clay and log (x + 1) transformation. PCA output using geochemical normalization with outliers removal demonstrated associations between environmental variables and tides of mangrove surface sediment, Mengkabong Lagoon, Sabah. The PCA outputs at high and low tides also provided to better interpret information about the sediment and its controlling factors in the intertidal zone. The study showed data pre-treatment method to be a useful procedure to standardize the datasets and reducing the influence of outliers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aris, A. Z., Abdullah, M. H., Ahmed, A., & Woong, K. K. (2007). Controlling factors of groundwater hydrochemistry in a small island’s aquifer. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4, 441–450.
APHA. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (19th ed.). Washington: Amer Public Health Assn.
Barcelo, D., & Petrovic, M. (2011). The Ebro River Basin. Berlin: Springer.
Chidambaram, S., Senthil Kumar, G., Prasanna, M. V., John Peter, A., Ramanathan, A. L., & Srinivasamoorthy, K. (2009). A study on the hydrogeology and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater from different depths in a coastal aquifer: Annamalai Nagar, Tamilnadu, India. Environmental Geology, 57, 59–73.
Church, A. H. (1989). The ionic of the sea. The Phytologist, 68, 239–247.
Deng, Z., Sato, Y., & Jia, H. (2008). Map** land cover patterns of Gunma Prefecture, Japan, by using remote sensing. Remote Sensing, 5, 1–15.
El Nemr, A., Khaled, A., & Sikaily, A. E. (2006). Distribution and statistical analysis of leachable and total heavy metals in the sediments of the Suez Gulf. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 89–112.
Environmental Impact Assessment. (1992). Proposed mangrove paradise resort complex on LA 91040377 Tuaran, Sabah. Sabah: Perunding Sekitar.
Gargouri, D., Azri, C., Serbaji, M. M., Jedoui, Y., & Montacer, M. (2011). Heavy metal concentrations in the surface marine sediments of Sfax Coast, Tunisia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 175, 519–530.
Grande, J. A., Borrego, J., Morales, J. A., & Torre, M. L. (2003). A description of how metal pollution occurs in the Tinto-Odiel Rias (Huelva-Spain) through the application of cluster analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46, 475–480.
Heiri, O., Lotter, A. F., & Lemcke, G. (2001). Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology, 25, 101–110.
Hirosawa, Y., Marsh, S. E., & Kliman, D. H. (1996). Application of standardized principal component analysis to land-cover characterization using multitemporal AVHRR data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 58, 267–281.
Hsue, Z. Y., & Chen, Z. S. (2000). Monitoring the changes of redox potential, ph and electrical conductivity of the mangrove soils in Northern Taiwan. Proceeding of Natural Science Council, 24, 143–150.
Huang, K., & Lin, S. (2003). Consequences and implications of heavy metal spatial variations in sediments of the Keelung River drainage basin, Taiwan. Chemosphere, 53, 1113–1121.
Hussein, A. H., & Rabenhorst, M. C. (2001). Tidal inundation of transgressive coastal areas: pedogenesis of salinization and alkalinization. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 65, 536–544.
Iyengar, R. N. (1991). Application of principal component analysis to understand variability of rainfall. Proceeding of Indian Academy Science (Earth Planet. Sci.), 100, 105–126.
Koterba, M. T., Wilde, F. D., & Lapham, W. W. (1995). Ground-water data-collection protocols and procedures for the National Water-Quality Assessment Program—Collection and documentation of water-quality samples and related data. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 95-399.
Leardi, R., Armanino, C., Lanteri, S., & Alberotanza, L. (2001). Three-mode principal component analysis of monitoring data from Venice lagoon. Journal of Chemometrics, 14, 187–195.
Ma, H., Liu, L., & Chen, T. (2010). Water security assessment in Haihe River Basin using principal component analysis based on Kendall τ. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 163, 539–544.
McNabola, A., Broderick, B. M., & Gill, L. W. (2009). A principal components analysis of the factors effecting personal exposure to air pollution in urban commuters in Dublin, Ireland. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A. Toxic / Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 44, 1219–1226.
Morad, S. (1998). Carbonate cementation in sandstones: Distribution patterns and geochemical evolution. London: Blackwell Science Limited.
Neto, J. A. B., Gingele, F. X., Leipe, G., & Brehme, I. (2006). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in surficial sediments from Guanabara Bay: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Environmental Geology, 49, 1051–1063.
Parra, G. A., Mouchot, M.-C., & Roux, C. (1996). A multitemporal land cover change analysis tool using change vector and principal component analysis. Proceeding of Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. 27–31 May 1996. Lincoln, USA.
Peré-Trepat, E., Petrovic, M., Barcelo, D., & Tauler, R. (2004). Application of chemometric methods to the investigation of main microcontaminant sources of endocrine disruptors in coastal and harbour waters and sediments. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 378, 642–654.
Pineiro, A. M., Marcos, A., Fisher, A., & Hill, S. J. (2001). Evaluation of the effect of data pre-treatment procedures on classical pattern recognition and principal component analysis: a case study for the geographical classification of tea. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 3, 352–360.
Praveena, S. M., Ahmed, A., Radojevic, M., Abdullah, M. H., & Aris, A. Z. (2008a). Multivariate and geo-accumulation index evaluation in mangrove surface sediment of Mengkabong. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 81, 52–63.
Praveena, S. M., Ahmed, A., Radojevic, M., Abdullah, M. H., & Aris, A. Z. (2008b). Heavy metals in mangrove surface sediment of Mengkabong Lagoon, Sabah: multivariate and geo-accumulation index approaches. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2, 139–148.
Preda, M., & Cox, M. E. (2000). Sediment-water interaction, acidity and other water quality parameters in a subtropical setting, Pimpama river, Southeast Queensland. Environmental Geology, 39, 319–329.
Radojevic, M., & Bashkin, V. N. (1999). Practical environmental analysis. Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry.
Ramanathan, A. L., Subramaniam, V., Ramesh, R., Chidambaram, S., & James, A. (1999). Environmental geochemistry of the Pichavaram mangrove ecosystem (tropical), Southeast Coast of India. Environmental Geology, 37, 223–233.
Reid, M. K., & Spencer, K. L. (2009). Use of principal components analysis (PCA) on estuarine sediment datasets: the effect of data pre-treatment. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2275–2281.
Roberts, S., & Martin, M. A. (2006). Using supervised principal components analysis to assess multiple pollutant effects. Environmental Health Perspectives, 114, 1877–1882.
Rodrigo, A. G. (1989). Surficial sediment heavy metal associations in the Avon-Heathcote Estuary, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 23, 255–262.
Shrestha, S., Kazama, F., & Nakamura, T. (2008). Use of principal component analysis, factor analysis and discriminant analysis to evaluate spatial and temporal variations in water quality of the Mekong River. Journal of Hydroinformatics, 10, 43–56.
Singh, K. K., & Singh, S. V. (1996). Space-time variation and regionalization of seasonal and monthly summer monsoon rainfall of the sub-Himalayan region and Gangetic plain of India. Climate Research, 6, 251–262.
Town and Regional Planning Department. (2003). Project Sabah, 2003. Kota Kinabalu: Environmental Local Planning (ELP).
Webster, R. (2001). Statistics to support soil research and their presentation. European Journal of Soil Science, 52, 331–340.
Yongming, H., Peixuan, D., Junji, C., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metals contamination in urban dusts of **’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355, 176–186.
Zhou, H., Peng, X., & Pan, J. (2004). Distribution, source and enrichment of some chemical elements in sediments of the Pearl river estuary, China. Continental Shelf Research, 24, 1857–1875.
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Mr. Asram and Mr. Neldin Jeoffrey for assisting with the field sampling. The primary author gratefully acknowledges her Universiti Malaysia Sabah Scholarship (YTL Foundation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Praveena, S.M., Kwan, O.W. & Aris, A.Z. Effect of data pre-treatment procedures on principal component analysis: a case study for mangrove surface sediment datasets. Environ Monit Assess 184, 6855–6868 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2463-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2463-2