Abstract
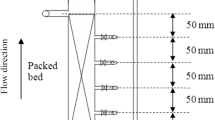
The bagasse fly ash, obtained from the local sugar industry, has been used as an inexpensive and effective adsorbent for the removal of color from pulp and paper industry. Effect of various operating variables, viz., contact time, initial concentration, adsorbent dose and particle size on the removal of color has been studied and discussed. It is found that for optimum removal of color, contact time for adsorption equilibrium equals to 60 min., at dosage of 2 g/l of baggase fly ash. The material exhibits good removal capacity (86%) and follows both the Langmuir and the Freundlich models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson, A. W. (1967). Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 2nd Edition. New York: Interscience.
Cowan, C. E., Zachara, J. M., & Resch, C. T. (1991). Cadmium adsorption on iron oxides in the presence of alkaline earth elements. Environmental Science Technology, 25, 437–446.
Dey, A., Sarkar, D., Sengupta, B., & Banerjee, S. (1991). Waste water treatment in pulp and paper industry – Trends and practices. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 11, 899–905 Dec. 1991.
Freundlich, H. (1926). Colloid and capillary chemistry. London: Mathuen and Co. Ltd., 883p.
Groffman, A., Peterson, S., & Brookins, D. (1992). Removing lead from wastewater using zeolite. Water Environment and Technology, 5, 54–59.
Gupta, V. K., & Ali, I. (2000). Utilisation of bagasse fly ash (a sugar industry waste) for the removal of copper and zinc from wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology, 18, 131–140.
Gupta, V. K., Jain, C. K., & Ali, I. (2002). Removal of lindane and malathion from wastewater using bagasse fly ash – a sugar industry waste. Water Research, 36, 2483–2490.
Gupta, V. K., Jain, C. K., & Ali, I. (2003). Removal of cadmium and nickel from wastewater using bagasse fly ash – a sugar industry waste. Water Research, 37, 4038–4044.
Kesaoul-Qukel, S., Cheeseman, C., & Perry, R. (1993). Effect of conditioning and treatment of chabazite and clinoptilolite prior to lead and cadmium removal. Environmental Science and Technology, 27, 1108–1116.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica, and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1403.
Lee, C. K., & Low, K. S. (1989). Removal of copper from solution using moss. Environmental Technology Letters, 10, 395–404.
Low, K. S., & Lee, C. K. (1991). Cadmium uptake by the moss, calymperes delessertii and besch. Biosour. Technol., 38, 1–6.
Manivasakam, N. (1987). Industrial Effluents: Origin, Characteristics, Effects, Analysis and Treatment. New Delhi: Sakthi Publications.
Rastogi, S. K. (1995). Physico-chemical Treatment of Paper Mill Black Liquor Along with Sugar Mill Waste, M.E. Dissertation. Roorkee, India: University of Roorkee.
Rodda, P. D., Johnson, B. B., & Wello, J. D. (1993). The effect of temperature and pH on the adsorption of copper (II), lead(II) and zinc(II) on geolite. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 161, 57–62.
Sastry, C. A. (1986). Color removal from pulp and paper mill waste water. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 6(2), April 1986.
Sastry, C. A., & Kamatchiammal, R. (1988). Effect of paper mill effluents on fish life. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection, 8(1), January.
Sharma, S. (1983). Color Removal from Pulp and Paper Mill Waste by Magnesium Salt, M.E. Dissertation. Roorkee, India: University of Roorkee.
Tan, T. C., Chia, C. K., & Teo, C. K. (1985). Uptake of the metal ions by chemically treated human hair. Water Research, 19, 157–162.
Vogel, A. I. (1989). Text book of Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 5th ed. London: ELBS Publications.
Weber Jr., W. J. (1972). Physico-chemical processes for water quality control pp. (pp. 208–210). New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Weber, W. J. Jr. & Moris, J. C. (1963). J. Sanit. Eng. Div., ASCE, SA2, 31, cited in Faust, S. D, Aly, O. M., 1987, Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment. Butterworth, London pp. 65–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, C.K., Kumar, A. & Hayssam Izazy, M. Color removal from paper mill effluent through adsorption technology. Environ Monit Assess 149, 343–348 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0207-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0207-8