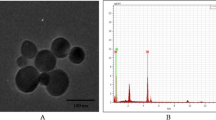
Abstract
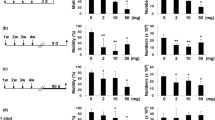
As a new type of nanomaterials, nickel nanoparticles (Ni NPs) have been widely used by human beings, whose exposure probability was greatly increasing. Many studies have shown that Ni NPs can induce apoptosis, oxidative stress and DNA damage. Nowadays, male reproductive health is an important public health problem, which is a hot topic in toxicological research. In the present study, to protect reproductive health, the effect of Ni NPs exposure on spermatogenesis injury was assessed, understanding the toxicity and safety of Ni NPs. Sixty ICR male mice with 20 ± 2 g were randomly divided into five groups. The experimental groups were treated with 5 mg/kg, 15 mg/kg and 45 mg/kg Ni NPs. The reproductive toxicity of Ni NPs on male mice was evaluated by the indexes of testicular organ coefficient, testicular marker enzyme, sperm motility and histopathology. As a result, the somatic index of testis and epididymis increased in each group. Compared with the control group, the activity of testicular markers increased and the sperm motility index decreased in the low-, middle- and high-dose groups. Pathological results indicated that various cell apoptosis and disordered arrangement of cells occurred in the seminiferous tubules of the exposed groups. In conclusion, the findings of this study suggest that Ni NPs have certain damage to spermatogenesis in mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, A., Mulgund, A., Hamada, A., & Chyatte, M. R. (2015). A unique view on male infertility around the globe. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology,13, 37.
Ahamed, M., & Alhadlaq, H. A. (2014). Nickel nanoparticle-induced dose-dependent cyto-genotoxicity in human breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells. Onco Targets and Therapy,7, 269–280.
Caporali, M., Serrano-Ruiz, M., Telesio, F., Heun, S., Nicotra, G., Spinella, C., et al. (2017). Decoration of exfoliated black phosphorus with nickel nanoparticles and its application in catalysis. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England),53, 10946–10949.
Carmona, E. R., Garcia-Rodriguez, A., & Marcos, R. (2018). Genotoxicity of copper and nickel nanoparticles in somatic cells of drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Toxicology,2018, 7278036.
Chemes, H. E., & Alvarez, Sedo C. (2012). Tales of the tail and sperm head aches: Changing concepts on the prognostic significance of sperm pathologies affecting the head, neck and tail. Asian Journal of Andrology,14, 14–23.
Choi, J. H., & Oh, B. K. (2014). Development of two-component nanorod complex for dual-fluorescence imaging and sirna delivery. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,24, 1291–1299.
Duty, S. M., Calafat, A. M., Silva, M. J., Brock, J. W., Ryan, L., Chen, Z., et al. (2004). The relationship between environmental exposure to phthalates and computer-aided sperm analysis motion parameters. Journal of Andrology,25, 293–302.
Ferlin, A., Raicu, F., Gatta, V., Zuccarello, D., Palka, G., & Foresta, C. (2007). Male infertility: Role of genetic background. Reproductive Biomedicine Online,14, 734–745.
Fourati, E., Vogel-Mikuš, K., Bettaieb, T., Kavčič, A., Kelemen, M., Vavpetič, P., et al. (2019). Physiological response and mineral elements accumulation pattern in sesuvium portulacastrum L. Subjected in vitro to nickel. Chemosphere,219, 463–471.
Fratila, R. M., Rivera-Fernandez, S., & de la Fuente, J. M. (2015). Shape matters: Synthesis and biomedical applications of high aspect ratio magnetic nanomaterials. Nanoscale,7, 8233–8260.
Gallo, A., Boni, R., Buttino, I., & Tosti, E. (2016). Spermiotoxicity of nickel nanoparticles in the marine invertebrate ciona intestinalis (ascidians). Nanotoxicology,10, 1096–1104.
Geng, X., Shao, H., Zhang, Z., Ng, J. C., & Peng, C. (2015). Malathion-induced testicular toxicity is associated with spermatogenic apoptosis and alterations in testicular enzymes and hormone levels in male wistar rats. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,39, 659–667.
Glista-Baker, E. E., Taylor, A. J., Sayers, B. C., Thompson, E. A., & Bonner, J. C. (2014). Nickel nanoparticles cause exaggerated lung and airway remodeling in mice lacking the T-box transcription factor, TBX21 (T-bet). Particle and Fibre Toxicology,11, 7.
Ju-Nam, Y., & Lead, J. R. (2008). Manufactured nanoparticles: An overview of their chemistry, interactions and potential environmental implications. Science of the Total Environment,400, 396–414.
Kang, G. S., Gillespie, P. A., Gunnison, A., Moreira, A. L., Tchou-Wong, K. M., & Chen, L. C. (2011). Long-term inhalation exposure to nickel nanoparticles exacerbated atherosclerosis in a susceptible mouse model. Environmental Health Perspectives,119, 176–181.
Kazama, M., Sato, T., & Hino, A. (2014). Spontaneous generation of reactive oxygen species and effect on motility and fertilizability of sea urchin spermatozoa. Zygote,22, 246–258.
Kong, L., Gao, X., Zhu, J., Zhang, T., Xue, Y., & Tang, M. (2017). Reproductive toxicity induced by nickel nanoparticles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environmental Toxicology,32, 1530–1538.
Kong, L., Hu, W., Lu, C., Cheng, K., & Tang, M. (2019). Mechanisms underlying nickel nanoparticle induced reproductive toxicity and chemo-protective effects of vitamin c in male rats. Chemosphere,218, 259–265.
Kong, L., Tang, M., Zhang, T., Wang, D., Hu, K., Lu, W., et al. (2014). Nickel nanoparticles exposure and reproductive toxicity in healthy adult rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,15, 21253–21269.
Koroglu, K. M., Cevik, O., Sener, G., & Ercan, F. (2019). Apocynin alleviates cisplatin-induced testicular cytotoxicity by regulating oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats. Andrologia, 51, e13227.
Latvala, S., Vare, D., Karlsson, H. L., & Elihn, K. (2017). In vitro genotoxicity of airborne ni-np in air-liquid interface. Journal of Applied Toxicology,37, 1420–1427.
Li, X., Yi, H., & Wang, H. (2018). Sulphur dioxide and arsenic affect male reproduction via interfering with spermatogenesis in mice. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,165, 164–173.
Liu, X., Jia, Y., Chong, L., Jiang, J., Yang, Y., Li, L., et al. (2018). Effects of oral cimetidine on the reproductive system of male rats. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine,15, 4643–4650.
Long, M., Yang, S., Dong, S., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., & He, J. (2017). Characterization of semen quality, testicular marker enzyme activities and gene expression changes in the blood testis barrier of kunming mice following acute exposure to zearalenone. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,24, 27235–27243.
McKinley, K., McLellan, I., Gagne, F., & Quinn, B. (2019). The toxicity of potentially toxic elements (cu, fe, mn, zn and ni) to the cnidarian hydra attenuata at environmentally relevant concentrations. Science of the Total Environment,665, 848–854.
Moore, H. D., & Akhondi, M. A. (1996). Fertilizing capacity of rat spermatozoa is correlated with decline in straight-line velocity measured by continuous computer-aided sperm analysis: Epididymal rat spermatozoa from the proximal cauda have a greater fertilizing capacity in vitro than those from the distal cauda or vas deferens. Journal of Andrology,17, 50–60.
Muthuviveganandavel, V., Muthuraman, P., Muthu, S., & Srikumar, K. (2008). A study on low dose cypermethrin induced histopathology, lipid peroxidation and marker enzyme changes in male rat. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology,91, 12–16.
Oleszczuk, K., Giwercman, A., & Bungum, M. (2016). Sperm chromatin structure assay in prediction of in vitro fertilization outcome. Andrology,4, 290–296.
Pereira, C. M. S., Blust, R., & De Schamphelaere, K. A. C. (2019). Effect of temperature on nickel uptake and elimination indaphnia magna. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry,38, 784–793.
Peters, A., Merrington, G., Leverett, D., Wilson, I., Schlekat, C., & Garman, E. (2019). Comparison of the chronic toxicity of nickel to temperate and tropical freshwater species. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 38, 1211–1220.
Qin, F., Shen, T., Li, J., Qian, J., Zhang, J., Zhou, G., et al. (2019). SF-1 mediates reproductive toxicity induced by cerium oxide nanoparticles in male mice. Journal of Nanobiotechnology,17, 41.
Reck, B. K., Muller, D. B., Rostkowski, K., & Graedel, T. E. (2008). Anthropogenic nickel cycle: Insights into use, trade, and recycling. Environmental Science and Technology,42, 3394–3400.
Salem, A. K., Searson, P. C., & Leong, K. W. (2003). Multifunctional nanorods for gene delivery. Nature Materials,2, 668–671.
Santos, F. C. F., Gomes, S. I. L., Scott-Fordsmand, J. J., & Amorim, M. J. B. (2017). Hazard assessment of nickel nanoparticles in soil-the use of a full life cycle test with enchytraeus crypticus. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry,36, 2934–2941.
Sleiman, H. K., Romano, R. M., Oliveira, C. A., & Romano, M. A. (2013). Effects of prepubertal exposure to silver nanoparticles on reproductive parameters in adult male wistar rats. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A,76, 1023–1032.
Song, Y., Jia, Z. C., Chen, J. Y., Hu, J. X., & Zhang, L. S. (2014). Toxic effects of atrazine on reproductive system of male rats. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences,27, 281–288.
Su, F., Qiu, X., Liang, F., Tanaka, M., Qu, T., Yao, Y., et al. (2018). Preparation of nickel nanoparticles by direct current arc discharge method and their catalytic application in hybrid na-air battery. Nanomaterials (Basel),8, 684.
Valverde, A., Madrigal-Valverde, M., Lotz, J., Bompart, D., & Soler, C. (2019). Effect of video capture time on sperm kinematic parameters in breeding boars. Livestock Science,220, 52–56.
Wang, L., Zhang, L., Song, X. H., Zhang, H. B., Xu, C. Y., & Chen, Z. J. (2017). Decline of semen quality among chinese sperm bank donors within 7 years (2008-2014). Asian Journal of Andrology,19, 521–525.
Weissig, V., Pettinger, T. K., & Murdock, N. (2014). Nanopharmaceuticals (part 1): Products on the market. International Journal of Nanomedicine,9, 4357–4373.
Yang, Y., Doudrick, K., Bi, X., Hristovski, K., Herckes, P., Westerhoff, P., et al. (2014). Characterization of food-grade titanium dioxide: The presence of nanosized particles. Environmental Science and Technology,48, 6391–6400.
Yang, J., Qiu, Z., Zhao, C., Wei, W., Chen, W., Li, Z., et al. (2018). In situ thermal atomization to convert supported nickel nanoparticles into surface-bound nickel single-atom catalysts. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,57, 14095–14100.
Yuan, C., Wang, C., Gao, S. Q., Kong, T. T., Chen, L., Li, X. F., et al. (2010). Effects of permethrin, cypermethrin and 3-phenoxybenzoic acid on rat sperm motility in vitro evaluated with computer-assisted sperm analysis. Toxicology in Vitro,24, 382–386.
Zhou, C., Carotenuto, Y., Vitiello, V., Wu, C., Zhang, J., & Buttino, I. (2018). De novo transcriptome assembly and differential gene expression analysis of the calanoid copepod acartia tonsa exposed to nickel nanoparticles. Chemosphere,209, 163–172.
Zhou, L., Zhuang, W., Wang, X., Yu, K., Yang, S., & **a, S. (2017). Potential acute effects of suspended aluminum nitride (ALN) nanoparticles on soluble microbial products (SMP) of activated sludge. 3,57, 284–292.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the support from the National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 81502783, 21876026, 31671034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, W., Yu, Z., Gao, X. et al. Study on the damage of sperm induced by nickel nanoparticle exposure. Environ Geochem Health 42, 1715–1724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00364-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00364-w