Abstract
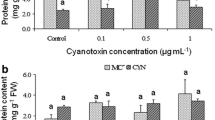
Natural toxins produced by freshwater cyanobacteria, such as cylindrospermopsin, have been regarded as an emergent environmental threat. Despite the risks for food safety, the impact of these water contaminants in agriculture is not yet fully understood. Carrots (Daucus carota) are root vegetables, extensively consumed worldwide with great importance for human nourishment and economy. It is, therefore, important to evaluate the possible effects of using water contaminated with cyanotoxins on carrot cultivation. The aim of this work was to investigate cylindrospermopsin effects on D. carota grown in soil and irrigated for 30 days, with a Chrysosporum ovalisporum extract containing environmentally relevant concentrations of cylindrospermopsin (10 and 50 μg/L). The parameters evaluated were plant growth, photosynthetic capacity, and nutritional value (mineral content) in roots of carrots, as these are the edible parts of this plant crop. The results show that, exposure to cylindrospermopsin did not have a clear negative effect on growth or photosynthesis of D. carota, even leading to an increase of both parameters. However, alterations in mineral contents were detected after exposure to crude extracts of C. ovalisporum containing cylindrospermopsin. A general decline was observed for most minerals (Ca, Mg, Na, Fe, Mn, Zn, Mo, and P), although an increase was shown in the case of K and Cu, pointing to a possible interference of the cyanobacterial extract in mineral uptake. This study is the first to evaluate the effects of C. ovalisporum extracts on a root vegetable, however, more research is necessary to understand the effects of this toxin in environmentally relevant scenarios.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azevedo CC, Azevedo J, Osório H, Vasconcelos V, Campos A (2014) Early physiological and biochemical responses of rice seedlings to low concentration of microcystin-LR. Ecotoxicology 23:107–121
Baetz U, Martinoia E (2014) Root exudates: The hidden part of plant defense. Trends Plant Sci 19:90–98
Banker R, Carmeli S, Hadas O, Teltsh B, Porat R, Sukenik A (1997) Identification of cylindrospermopsin in Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Cyanophyceae) isolated from lake Kinneret, Israel. J Phycol 33:613–616
Bazin E, Mourot A, Humpage AR, Fessard V (2010) Genotoxicity of a freshwater cyanotoxin, cylindrospermopsin, in two human cell lines: Caco-2 and HepaRG. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:251–259
Berry JP, Gibbs PD, Schmale MC, Saker ML (2009) Toxicity of cylindrospermopsin, and other apparent metabolites from Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Aphanizomenon ovalisporum, to the zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryo. Toxicon 53:289–299
Beyer D, Surányi G, Vasas G, Roszik J, Erdodi F, M-Hamvas M, Bácsi I, Bátori R, Serfozo Z, Szigeti ZM, Vereb G, Demeter Z, Gonda S, Máthé C (2009) Cylindrospermopsin induces alterations of root histology and microtubule organization in common reed (Phragmites australis) plantlets cultured in vitro. Toxicon 54:440–449
Bogialli S, Bruno M, Curini R, Di Corcia A, Fanali C, Lagana A (2006) Monitoring algal toxins in lake water by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Technol 40:2917–2923
Burns J (2008) Toxic cyanobacteria in Florida waters. Adv Exp Med Biol 619:127–137
Capelo A, Santos C, Loureiro S, Pedrosa MA (2012) Phytotoxicity of lead on Lactuca sativa: effects on growth, mineral nutrition, photosynthetic activity and oxidant metabolism. Fresen Environ Bull 21:450–459
Corbel S, Mougin C, Bouaicha N (2014) Cyanobacterial toxins: modes of actions, fate in aquatic and soil ecosystems, phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in agricultural crops. Chemosphere 96:1–5
Dai HP, Wei Y, Yang TX, Sa WQ, Wei AZ (2010) Influence of cadmium stress on chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in Populus 9 canescens. J Food Agric Environ 10:1281–1283
De la Cruz AA, Hiskia A, Kaloudis T, Chernoff N, Hill D, Antoniou MG, He X, Loftin K, O’Shea K, Zhao C, Pelaez M, Han C, Lynch TJ, Dionysiou DD (2013) A review on cylindrospermopsin: the global occurrence, detection, toxicity and degradation of a potent cyanotoxin. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:1979–2003
El Khalloufi F, Oufdou K, Lahrouni M, El Ghazali I, Saqrane S, Vasconcelos V, Oudra B (2011) Allelopatic effects of cyanobacteria extracts containing microcystins on Medicago sativa-Rhizobia symbiosis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:431–438
El Khalloufi F, El Ghazali I, Saqrane S, Oufdou K, Vasconcelos V, Oudra B (2012) Phytotoxic effects of a natural bloom extract containing microcystins on Lycopersicon esculentum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 79:199–205
Elliott JA (2012) Is the future blue-green? A review of the current model predictions of how climate change could affect pelagic freshwater cyanobacteria. Water Res 46:1364–1371
Ensafi AA, Khaloo SS (2005) Determination of traces molybdenum by catalytic adsorptive strip** voltammetry. Talanta 65:781–788
Enstone DE, Peterson CA, Ma F (2002) Root endodermis and exodermis: structure, function, and responses to the environment. J Plant Growth Regul 21:335–351
Erofeeva EA (2014) Hormesis and paradoxical effects of wheat seedling (Triticum Aestivum L.) parameters upon exposure to different pollutants in a wide range of doses. Dose Response 12:121–135
Freitas M, Azevedo J, Pinto E, Neves J, Campos A, Vasconcelos V (2015) Effects of microcystin-LR, cylindrospermopsin and a microcystin-LR/cylindrospermopsin mixture on growth, oxidative stress and mineral content in lettuce plants (Lactuca sativa L.). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 116:59–67
Froscio SM, Humpage AR, Wickramasinghe W, Shaw G, Falconer IR (2008) Interaction of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin with the eukaryotic protein synthesis system. Toxicon 5:191–198
Garda T, Riba M, Vasas G, Beyer D, M-Hamvas M, Hajdu G, Tándor I, Máthé C (2015) Cytotoxic effects of cylindrospermopsin in mitotic and non-mitotic Vicia faba cells. Chemosphere 120:145–153
Gutiérrez-Praena D, Jos A, Pichardo S, Moreno IM, Cameán AM (2013) Presence and bioaccumulation of microcystins and cylindrospermopsin in food and the effectiveness of some cooking techniques at decreasing their concentrations: a review. Food Chem Toxicol 53:136–152
Gutiérrez-Praena D, Campos A, Azevedo J, Neves J, Freitas M, Guzmán-Guillén R, Vasconcelos V (2014) Exposure of Lycopersicon Esculentum to microcystin-LR: Effects in the leaf proteome and toxin translocation from water to leaves and fruits. Toxins 6:1837–1854
Guzmán-Guillén R, Prieto AI, González AG, Soria-Díaz ME, Cameán AM (2012) Cylindrospermopsin determination in water by LC–MS/MS: Optimization and validation of the method and application to real samples. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:2233–2238
Guzmán-Guillén R, Prieto AI, Moreno I, Rios V, Vasconcelos VM, Camean AM (2014) Effects of depuration on oxidative biomarkers in Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) after subchronic exposure to cyanobacterium producing cylindrospermopsin. Aquat Toxicol 149:40–49
Havens KE (2008) Cyanobacteria blooms: effects on aquatic ecosystems. Adv Exp Med Biol 619:733–747
Hawes MC, Gunawardena U, Miyasaka S, Zhao X (2000) The role of root border cells in plant defense. Trends Plant Sci 5:128–133
Hoeger SJ, Shaw G, Hitzfeld BC, Dietrich DR (2004) Occurrence and elimination of cyanobacterial toxins in two Australian drinking water treatment plants. Toxicon 43:639–649
Humpage A (2008) Toxin types, toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics. In: Hudnel HK (ed) Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms state of the science and research needs. Springer Press, New York, pp 383–415
Humpage AR, Falconer IR (2003) Oral toxicity of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin in male Swiss albino mice: determination of no observed adverse effect level for deriving a drinking water guideline value. Environ Toxicol 18:94–103
Ibelings BW, Chorus I (2007) Accumulation of cyanobacterial toxins in freshwater “seafood” and its consequences for public health: a review. Environ Pollut 150:177–192
Jia L, Liu Z, Chen W, Ye Y, Yu S, He X (2015) Hormesis effects induced by cadmium on growth and phtotosynthetic performance in a hyperaccumulator Lonicera japonica thunb. J Plant Growth Regul 34:13–21
Kinnear S, Fabbro L, Duivenvoorden L (2008) Variable growth responses of water thyme (Hydrilla verticillata); To whole-cell extracts of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:187–194
Kinnear S (2010) Cylindrospermopsin: a decade of progress on bioaccumulation research. Mar Drugs 8:542–564
Kirkby EA, Römheld V (2007) Micronutrients in Plant Physiology: Functions, Uptake and Mobility. Proceedings 543. The International Fertilizer Society, York, United Kingdom.
Kittler K, Schreiner M, Krumbein A, Manzei S, Koch M, Rohn S, Maul R (2012) Uptake of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin in Brassica vegetables. Food Chem 133:875–879
Kosma DK, Rice A, Pollard M (2015) Analysis of aliphatic waxes associated with root periderm or exodermis from eleven plant species. Phytochemistry 117:351–362
Lahrouni M, Oufdou K, El Khalloufi F, Baz M, Lafuente A, Dary M, Pajuelo E, Oudra B (2013) Physiological and biochemical defense reactions of Vicia faba L.-Rhizobium symbiosis face to chronic exposure to cyanobacterial bloom extract containing microcystins. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5405–5415
Li TQ, Tao Q, Di ZZ, Lu F, Yang XE (2014) Effect of elevated CO2 concentration on photosynthetic characteristics of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii under cadmium stress. J Integr Plant Biol 57:653–660
M-Hamvas M, Máthé C, Vasas G, Jámbrik K, Papp M, Beyer D, Mészáros I, Borbély G (2010) Cylindrospermopsin and microcystin-LR alter the growth, development and peroxidase enzyme activity of white mustard (Sinapis alba L.) seedlings, a comparative analysis. Acta Biol Hung 61:35–48
Machado JFF (2014) Implicações do Uso de Água Contaminada com Microcistina na Qualidade de Daucus Carota (Cenoura). Dissertação de Mestrado. Universidade do Porto, Portugal
Madhana Sekhar K, Rachapudi VS, Mudalkar S, Reddy AR (2014) Persistent stimulation of photosynthesis in short rotation coppice mulberry under elevated CO2 atmosphere. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 137:21–30
Maxwell K, Johnson N (2000) Cholorophyll fluorescence – A practical guide. J Exp Bot 51:659–668
Metcalf JS, Barakate A, Codd GA (2004) Inhibition of plant protein synthesis by the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, cylindrospermopsin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 235:125–129
Mitrovic SM, Allis O, Furey A, James KJ (2005) Bioaccumulation and harmful effects of microcystin-LR in the aquatic plants Lemna minor and Wolffia arrhiza and the filamentous alga Chladophorafracta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 61:345–352
Moreira C, Azevedo J, Antunes A, Vasconcelos V (2012) Cylindrospermopsin: occurrence, methods of detection and toxicology. J Appl Microbiol 114:605–620
Nicolle C, Simon G, Rock E, Amouroux P, Rémésy C (2004) Genetic variability influences carotenoid, vitamin, phenolic, and mineral content in white, yellow, purple, orange and dark orange carrot cultivars. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 129:523–529
Pearson L, Mihali T, Moffitt M, Kellmann R, Neilan B (2010) On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin. Mar Drugs 8:1650–1680
Pflugmacher S, Jung K, Lundvall L, Neumann S, Peuthert A (2006) Effects of cyanobacterial toxins and cyanobacterial cell-free crude extract on germination of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and induction of oxidative stress. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2381–2387
Pinto E, Almeida AA, Aguiar AA, Ferreira IM (2014a) Changes in macrominerals, trace elements and pigments content during lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) growth: influence of soil composition. Food Chem 152:603–611
Pinto E, Aguiar AA, Ferreira IM (2014b) Influence of soil chemistry and plant physiology in the phytoremediation of Cu, Mn, and Zn. Crit Rev Plant Sci 33:351–373
Pinto E, Ferreira IMPLVO (2015) Cation transporters/channels in plants: tools for nutrient biofortification. J Plant Physiol 179:64–82
Prieto A, Campos A, Cameán A, Vasconcelos V (2011) Effects on growth and oxidative stress status of rice plants (Oryza sativa) exposed to two extracts of toxin-producing cyanobacteria (Aphanizomenon ovalisporum and Microcystis aeruginosa). Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 74:1973–1980
Quesada A, Moreno E, Carrasco D, Paniagua T, Wörmer L, De Hoyos C, Sukenik A (2006) Toxicity of Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Cyanobacteria) in a Spanish water reservoir. Eur J Phycol 41:39–45
Quiblier C, Susanna W, Isidora ES, Mark H, Aurélie V, Jean-François H (2013) A review of current knowledge on toxic benthic freshwater cyanobacteria - Ecology, toxin production and risk management. Water Res 47:5464–5479
Rücker J, Stüken A, Nixdorf B, Fastner J, Chorus I, Wiedne C (2007) Concentrations of particulate and disolved cylindrospermopsin in 21 Aphanizomenon-dominated temperate lakes. Toxicon 50:800–809
Saker ML, Eaglesham GK (1999) The accumulation of cylindrospermopsin from the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in tissues of the Redclaw crayfish Cherax quadricarinatus. Toxicon 37:1065–1077
Saker ML, Metcalf JS, Codd GA, Vasconcelos VM (2004) Accumulation and depuration of the cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin in the freshwater mussel Anodonta cygnea. Toxicon 43:185–194
Saqrane S, Ouahid Y, El Ghazali I, Oudra B, Bouarab L, del Campo FF (2009) Physiological changes in Triticum durum, Zea mays, Pisum sativum and Lens esculenta cultivars, caused by irrigation with water contaminated with microcystins: a laboratory experimental approach. Toxicon 53:786–796
Scherz H, Kirchhoff E (2006) Trace elements in foods: zinc contents of raw foods—A comparison of data originating from different geographical regions of the world. Critical Review. J Food Compos Anal 19:420–433
Shaw GR, Seawright AA, Moore MR, Lam PKS (2009) Cylindrospermopsin, a cyanobacterial alkaloid: evaluation of its toxicologic activity. Ther Drug Monit 22:89–92
Van Apeldoorn ME, Van Egmond HP, Speijers GJA, Bakker GJI (2007) Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:7–60
Vasas G, Gáspár A, Surányi G, Batta G, Gyémánt G, M-Hamvas M, Máthé C, Grigorszky I, Molnaár E, Borbeély G (2002) Capillary electrophoretic assay and purification of cylindrospermopsin, a cyanobacterial toxin from Aphanizomenon ovalisporum, by plant test (blue-green sinapis test). Anal Biochem 302:95–103
Warman PR, Havard KA (1997) Yield, vitamin and mineral contents of organically and conventionally grown carrots and cabbage. Agr Ecosyst Environ 61:155–162
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080
Zaccari F, Cabrera MC, Ramos A, Saadoun A (2015) In vitro bioaccessibility of β-carotene, Ca, Mg and Zn in landrace carrots (Daucus carota, L.). Food Chem 166:365–371
Žegura B, Gajski G, Štraser A, Garaj-Vrhovac V (2011) Cylindrospermopsin induced DNA damage and alteration in the expression of genes involved in the response to DNA damage, apoptosis and oxidative stress. Toxicon 58:471–479
Funding
This work was partially funded by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT), under the framework of the project UID/Multi/04423/2013, by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación of Spain under the project AGL2009-10026, and by Junta de Andalucía under the project P09-AGR-4672. Remedios Guzmán’s work is supported by the Spanish Ministerio de Educación fellowship. Alexandre Campos work is supported by a post-doctoral grant (SFRH/BPD/103683/2014) from FCT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guzmán-Guillén, R., Campos, A., Machado, J. et al. Effects of Chrysosporum (Aphanizomenon) ovalisporum extracts containing cylindrospermopsin on growth, photosynthetic capacity, and mineral content of carrots (Daucus carota). Ecotoxicology 26, 22–31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1737-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1737-4