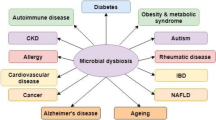
Abstract
The gut microbiota is a vast ensemble of microorganisms inhabiting the mammalian gastrointestinal tract that can impact physiologic and pathologic processes. However, our understanding of the underlying mechanism for the dynamic interaction between host and gut microbiota is still in its infancy. The highly evolved epigenetic modifications allow hosts to reprogram the genome in response to environmental stimuli, which may play a key role in triggering multiple human diseases. In spite of increasing studies in gut microbiota and epigenetic modifications, the correlation between them has not been well elaborated. Here, we review current knowledge of gut microbiota impacts on epigenetic modifications, the major evidence of which centers on DNA methylation and histone modification of the immune system.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walsh CJ, Guinane CM, Hill C, Ross RP, O’Toole PW, Cotter PD. In silico identification of bacteriocin gene clusters in the gastrointestinal tract, based on the Human Microbiome Project’s reference genome database. BMC Microbiol. 2015;15:183.
Browne HP, Forster SC, Anonye BO, et al. Culturing of ‘unculturable’ human microbiota reveals novel taxa and extensive sporulation. Nature. 2016;533:543–546.
Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I, et al. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature. 2013;498:99–103.
Dobson AJ, Chaston JM, Douglas AE. The Drosophila transcriptional network is structured by microbiota. BMC Genom. 2016;17:975.
Zargar A, Quan DN, Carter KK, et al. Bacterial secretions of nonpathogenic Escherichia coli elicit inflammatory pathways: a closer investigation of interkingdom signaling. MBio. 2015;6:e00025.
Parhar K, Baer KA, Parker K, Ropeleski MJ. Short-chain fatty acid mediated phosphorylation of heat shock protein 25: effects on camptothecin-induced apoptosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;291:G178–G188.
Rakyan VK, Down TA, Balding DJ, Beck S. Epigenome-wide association studies for common human diseases. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:529–541.
Holland ML, Lowe R, Caton PW, et al. Early-life nutrition modulates the epigenetic state of specific rDNA genetic variants in mice. Science. 2016;353:495–498.
Noble D. Conrad Waddington and the origin of epigenetics. J Exp Biol. 2015;218:816–818.
Kucharski R, Maleszka J, Foret S, Maleszka R. Nutritional control of reproductive status in honeybees via DNA methylation. Science. 2008;319:1827–1830.
Patisaul HB, Adewale HB. Long-term effects of environmental endocrine disruptors on reproductive physiology and behavior. Front Behav Neurosci. 2009;3:10.
Blaschke K, Ebata KT, Karimi MM, et al. Vitamin C induces Tet-dependent DNA demethylation and a blastocyst-like state in ES cells. Nature. 2013;500:222–226.
Lou S, Lee HM, Qin H, et al. Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing of multiple individuals reveals complementary roles of promoter and gene body methylation in transcriptional regulation. Genome Biol. 2014;15:408.
Thomson JP, Skene PJ, Selfridge J, et al. CpG islands influence chromatin structure via the CpG-binding protein Cfp1. Nature. 2010;464:1082–1086.
Portela A, Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28:1057–1068.
Herman JG, Baylin SB. Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2042–2054.
Maunakea AK, Nagarajan RP, Bilenky M, et al. Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature. 2010;466:253–257.
Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, et al. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000;408:740–745.
Quinonez-Silva G, Davalos-Salas M, Recillas-Targa F, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Aranda DA, Benitez-Bribiesca L. Monoallelic germline methylation and sequence variant in the promoter of the RB1 gene: a possible constitutive epimutation in hereditary retinoblastoma. Clin Epigenetics. 2016;8:1.
J**go D, Conley AB, Yi SV, Lunyak VV, Jordan IK. On the presence and role of human gene-body DNA methylation. Oncotarget. 2012;3:462–474.
Savio AJ, Lemire M, Mrkonjic M, et al. MLH1 region polymorphisms show a significant association with CpG island shore methylation in a large cohort of healthy individuals. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e51531.
Irizarry RA, Ladd-Acosta C, Wen B, et al. The human colon cancer methylome shows similar hypo- and hypermethylation at conserved tissue-specific CpG island shores. Nat Genet. 2009;41:178–186.
Liu X, Wang C, Liu W, et al. Distinct features of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 chromatin domains in pre-implantation embryos. Nature. 2016;537:558–562.
Banks DD, Gloss LM. Equilibrium folding of the core histones: the H3–H4 tetramer is less stable than the H2A–H2B dimer. Biochemistry. 2003;42:6827–6839.
Daujat S, Zeissler U, Waldmann T, Happel N, Schneider R. HP1 binds specifically to Lys26-methylated histone H1.4, whereas simultaneous Ser27 phosphorylation blocks HP1 binding. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:38090–38095.
Bhasin M, Reinherz EL, Reche PA. Recognition and classification of histones using support vector machine. J Comput Biol. 2006;13:102–112.
Chen ZJ, Pikaard CS. Epigenetic silencing of RNA polymerase I transcription: a role for DNA methylation and histone modification in nucleolar dominance. Genes Dev. 1997;11:2124–2136.
Earley K, Lawrence RJ, Pontes O, et al. Erasure of histone acetylation by Arabidopsis HDA6 mediates large-scale gene silencing in nucleolar dominance. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1283–1293.
Lawrence RJ, Earley K, Pontes O, et al. A concerted DNA methylation/histone methylation switch regulates rRNA gene dosage control and nucleolar dominance. Mol Cell. 2004;13:599–609.
Li X, Qian W, Zhao Y, et al. Antisilencing role of the RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway and a histone acetyltransferase in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:11425–11430.
Dose A, Liokatis S, Theillet FX, Selenko P, Schwarzer D. NMR profiling of histone deacetylase and acetyl-transferase activities in real time. ACS Chem Biol. 2011;6:419–424.
Mahgoub M, Monteggia LM. A role for histone deacetylases in the cellular and behavioral mechanisms underlying learning and memory. Learn Mem. 2014;21:564–568.
** K, Li S, Li X, Zhang J, Xu W. Design, synthesis and preliminary biological evaluation of indoline-2,3-dione derivatives as novel HDAC inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015;23:4728–4736.
Zhang Z, Shi L, Dawany N, Kelsen J, Petri MA, Sullivan KE. H3K4 tri-methylation breadth at transcription start sites impacts the transcriptome of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Epigenetics. 2016;8:14.
Gavin DP, Kusumo H, Zhang H, Guidotti A, Pandey SC. Role of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible, beta in alcohol-drinking behaviors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016;40:263–272.
Hou YJ, Zhu CC, Duan X, Liu HL, Wang Q, Sun SC. Both diet and gene mutation induced obesity affect oocyte quality in mice. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18858.
Poulin MB, Schneck JL, Matico RE, et al. Transition state for the NSD2-catalyzed methylation of histone H3 lysine 36. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:1197–1201.
Zhou L, Holt MT, Ohashi N, et al. Evidence that ubiquitylated H2B corrals hDot1L on the nucleosomal surface to induce H3K79 methylation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:10589.
Sundar IK, Yao H, Rahman I. Oxidative stress and chromatin remodeling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and smoking-related diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18:1956–1971.
Huang Y, Chen D, Liu C, Shen W, Ruan Y. Evolution and conservation of JmjC domain proteins in the green lineage. Mol Genet Genomics. 2016;291:33–49.
Chen H, Zhang C, Sheng Y, Yao S, Liu Z, Zhang T. Frequent SOCS3 and 3OST2 promoter methylation and their epigenetic regulation in endometrial carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:180–190.
Kim JK, Lim Y, Lee JO, et al. PRMT4 is involved in insulin secretion via the methylation of histone H3 in pancreatic beta cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015;54:315–324.
Guertin MJ, Zhang X, Anguish L, et al. Targeted H3R26 deimination specifically facilitates estrogen receptor binding by modifying nucleosome structure. PLoS Genet. 2014;10:e1004613.
Wang CM, Tsai SN, Yew TW, Kwan YW, Ngai SM. Identification of histone methylation multiplicities patterns in the brain of senescence-accelerated prone mouse 8. Biogerontology. 2010;11:87–102.
Pal S, Sif S. Interplay between chromatin remodelers and protein arginine methyltransferases. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:306–315.
Karkhanis V, Wang L, Tae S, Hu YJ, Imbalzano AN, Sif S. Protein arginine methyltransferase 7 regulates cellular response to DNA damage by methylating promoter histones H2A and H4 of the polymerase delta catalytic subunit gene, POLD1. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:29801–29814.
Obata Y, Furusawa Y, Endo TA, et al. The epigenetic regulator Uhrf1 facilitates the proliferation and maturation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:571–579.
Dimitriu PA, Boyce G, Samarakoon A, Hartmann M, Johnson P, Mohn WW. Temporal stability of the mouse gut microbiota in relation to innate and adaptive immunity. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2013;5:200–210.
Khosravi A, Yanez A, Price JG, et al. Gut microbiota promote hematopoiesis to control bacterial infection. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:374–381.
Natoli G. Maintaining cell identity through global control of genomic organization. Immunity. 2010;33:12–24.
O’Shea JJ, Lahesmaa R, Vahedi G, Laurence A, Kanno Y. Genomic views of STAT function in CD4 + T helper cell differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:239–250.
Peng D, Kryczek I, Nagarsheth N, et al. Epigenetic silencing of TH1-type chemokines shapes tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nature. 2015;527:249–253.
Allan RS, Zueva E, Cammas F, et al. An epigenetic silencing pathway controlling T helper 2 cell lineage commitment. Nature. 2012;487:249–253.
Yu DH, Gadkari M, Zhou Q, et al. Postnatal epigenetic regulation of intestinal stem cells requires DNA methylation and is guided by the microbiome. Genome Biol. 2015;16:211.
Smallwood T, Allayee H, Bennett BJ. Choline metabolites: gene by diet interactions. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2016;27:33–39.
German AJ, Holden SL, Serisier S, Queau Y, Biourge V. Assessing the adequacy of essential nutrient intake in obese dogs undergoing energy restriction for weight loss: a cohort study. BMC Vet Res. 2015;11:253.
Paul B, Barnes S, Demark-Wahnefried W, et al. Influences of diet and the gut microbiome on epigenetic modulation in cancer and other diseases. Clin Epigenetics. 2015;7:112.
Choi KC, Jung MG, Lee YH, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, inhibits EBV-induced B lymphocyte transformation via suppression of RelA acetylation. Cancer Res. 2009;69:583–592.
Lee YH, Kwak J, Choi HK, et al. EGCG suppresses prostate cancer cell growth modulating acetylation of androgen receptor by anti-histone acetyltransferase activity. Int J Mol Med. 2012;30:69–74.
Le Roy T, Llopis M, Lepage P, et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut. 2013;62:1787–1794.
Macfarlane S, Macfarlane GT. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc Nutr Soc. 2003;62:67–72.
Remely M, Aumueller E, Merold C, et al. Effects of short chain fatty acid producing bacteria on epigenetic regulation of FFAR3 in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Gene. 2014;537:85–92.
Canani RB, Costanzo MD, Leone L, Pedata M, Meli R, Calignano A. Potential beneficial effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1519–1528.
Walker AK, Jacobs RL, Watts JL, et al. A conserved SREBP-1/phosphatidylcholine feedback circuit regulates lipogenesis in metazoans. Cell. 2011;147:840–852.
Oster M, Nuchchanart W, Trakooljul N, et al. Methylating micronutrient supplementation during pregnancy influences foetal hepatic gene expression and IGF signalling and increases foetal weight. Eur J Nutr. 2016;55:1717–1727.
Yamada K, Gherasim C, Banerjee R, Koutmos M. Structure of human B12 trafficking protein CblD reveals molecular mimicry and identifies a new subfamily of nitro-FMN reductases. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:29155–29166.
Mischke M, Plosch T. More than just a gut instinct-the potential interplay between a baby’s nutrition, its gut microbiome, and the epigenome. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;304:R1065–R1069.
Kellermayer R, Dowd SE, Harris RA, et al. Colonic mucosal DNA methylation, immune response, and microbiome patterns in Toll-like receptor 2-knockout mice. FASEB J. 2011;25:1449–1460.
Takahashi K. Influence of bacteria on epigenetic gene control. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71:1045–1054.
Takahashi K, Sugi Y, Nakano K, et al. Epigenetic control of the host gene by commensal bacteria in large intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:35755–35762.
Dapito DH, Mencin A, Gwak GY, et al. Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:504–516.
Kumar H, Lund R, Laiho A, et al. Gut microbiota as an epigenetic regulator: pilot study based on whole-genome methylation analysis. MBio. 2014;5:e02113–e02114.
Nakajima T, Enomoto S, Yamashita S, et al. Persistence of a component of DNA methylation in gastric mucosae after Helicobacter pylori eradication. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:37–44.
Kiga K, Mimuro H, Suzuki M, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-210 increases the proliferation of gastric epithelium during chronic Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4497.
Maekita T, Nakazawa K, Mihara M, et al. High levels of aberrant DNA methylation in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosae and its possible association with gastric cancer risk. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:989–995.
Cortese R, Lu L, Yu Y, Ruden D, Claud EC. Epigenome-microbiome crosstalk: a potential new paradigm influencing neonatal susceptibility to disease. Epigenetics. 2016;11:205–215.
van’t Slot G, Humpf HU. Degradation and metabolism of catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), and related compounds by the intestinal microbiota in the pig cecum model. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:8041–8048.
Rungapamestry V, Rabot S, Fuller Z, Ratcliffe B, Duncan AJ. Influence of cooking duration of cabbage and presence of colonic microbiota on the excretion of N-acetylcysteine conjugates of allyl isothiocyanate and bioactivity of phase 2 enzymes in F344 rats. Br J Nutr. 2008;99:773–781.
Ciarlo E, Heinonen T, Herderschee J, et al. Impact of the microbial derived short chain fatty acid propionate on host susceptibility to bacterial and fungal infections in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37944.
Hichino A, Okamoto M, Taga S, et al. Down-regulation of claudin-2 expression and proliferation by epigenetic inhibitors in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. J Biol Chem. 2017;292:2411–2421.
Haldar S, Dru C, Mishra R, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors mediate DNA damage repair in ameliorating hemorrhagic cystitis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39257.
Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 2013;504:451–455.
Wostmann BS, Larkin C, Moriarty A, Bruckner-Kardoss E. Dietary intake, energy metabolism, and excretory losses of adult male germfree Wistar rats. Lab Anim Sci. 1983;33:46–50.
Schwiertz A, Taras D, Schafer K, et al. Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010;18:190–195.
Li G, Su H, Zhou Z, Yao W. Identification of the porcine G protein-coupled receptor 41 and 43 genes and their expression pattern in different tissues and development stages. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e97342.
Andrade-Oliveira V, Amano MT, Correa-Costa M, et al. Gut bacteria products prevent AKI induced by ischemia–reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:1877–1888.
Singh N, Thangaraju M, Prasad PD, et al. Blockade of dendritic cell development by bacterial fermentation products butyrate and propionate through a transporter (Slc5a8)-dependent inhibition of histone deacetylases. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:27601–27608.
Davie JR. Inhibition of histone deacetylase activity by butyrate. J Nutr. 2003;133:2485S–2493S.
Cousens LS, Gallwitz D, Alberts BM. Different accessibilities in chromatin to histone acetylase. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:1716–1723.
Bernhard D, Ausserlechner MJ, Tonko M, et al. Apoptosis induced by the histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate in human leukemic lymphoblasts. FASEB J. 1999;13:1991–2001.
Gozzini A, Rovida E, Dello Sbarba P, Galimberti S, Santini V. Butyrates, as a single drug, induce histone acetylation and granulocytic maturation: possible selectivity on core binding factor-acute myeloid leukemia blasts. Cancer Res. 2003;63:8955–8961.
Finzer P, Stohr M, Seibert N, Rosl F. Phenylbutyrate inhibits growth of cervical carcinoma cells independent of HPV type and copy number. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003;129:107–113.
Kuefer R, Hofer MD, Altug V, et al. Sodium butyrate and tributyrin induce in vivo growth inhibition and apoptosis in human prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:535–541.
Yu C, Subler M, Rahmani M, et al. Induction of apoptosis in BCR/ABL + cells by histone deacetylase inhibitors involves reciprocal effects on the RAF/MEK/ERK and JNK pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003;2:544–551.
Wei W, Sun W, Yu S, Yang Y, Ai L. Butyrate production from high-fiber diet protects against lymphoma tumor. Leuk Lymphoma. 2016;57:2401–2408.
Chang PV, Hao L, Offermanns S, Medzhitov R. The microbial metabolite butyrate regulates intestinal macrophage function via histone deacetylase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:2247–2252.
Yu DC, Waby JS, Chirakkal H, Staton CA, Corfe BM. Butyrate suppresses expression of neuropilin I in colorectal cell lines through inhibition of Sp1 transactivation. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:276.
Khan S, Jena G. The role of butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor in diabetes mellitus: experimental evidence for therapeutic intervention. Epigenomics. 2015;7:669–680.
Rao P, Hayden MS, Long M, et al. IkappaBbeta acts to inhibit and activate gene expression during the inflammatory response. Nature. 2010;466:1115–1119.
Tay S, Hughey JJ, Lee TK, Lipniacki T, Quake SR, Covert MW. Single-cell NF-kappaB dynamics reveal digital activation and analogue information processing. Nature. 2010;466:267–271.
Wang KS, Li J, Wang Z, et al. Artemisinin inhibits inflammatory response via regulating NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2017;39:28–36.
Liu W, Sun Y, He Y, et al. IL-1beta impedes the chondrogenic differentiation of synovial fluid mesenchymal stem cells in the human temporomandibular joint. Int J Mol Med. 2016;39:317–326.
Wang B, Liao PP, Liu LH, Fang X, Li W, Guan SM. Baicalin and geniposide inhibit the development of atherosclerosis by increasing Wnt1 and inhibiting dickkopf-related protein-1 expression. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2016;13:846–854.
Yang JX, Pan YY, Ge JH, et al. Tanshinone II A attenuates TNF-alpha-induced expression of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 in endothelial progenitor cells by blocking activation of NF-kappaB. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40:195–206.
Chang X, Zhu A, Liu F, et al. Role of NF-kappaB activation and Th1/Th2 imbalance in pulmonary toxicity induced by nano NiO. Environ Toxicol. 2016;32:1354–1362.
Deng QW, Yang H, Yan FL, et al. Blocking sympathetic nervous system reverses partially stroke-induced immunosuppression but does not aggravate functional outcome after experimental stroke in rats. Neurochem Res. 2016;41:1877–1886.
He YW, Wang HS, Zeng J, et al. Sodium butyrate inhibits interferon-gamma induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression via STAT1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Life Sci. 2013;93:509–515.
Gao Z, He Q, Peng B, Chiao PJ, Ye J. Regulation of nuclear translocation of HDAC3 by IkappaBalpha is required for tumor necrosis factor inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma function. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:4540–4547.
Hase K, Murakami M, Iimura M, et al. Expression of LL-37 by human gastric epithelial cells as a potential host defense mechanism against Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1613–1625.
Schauber J, Svanholm C, Termen S, et al. Expression of the cathelicidin LL-37 is modulated by short chain fatty acids in colonocytes: relevance of signalling pathways. Gut. 2003;52:735–741.
Steinmann J, Halldorsson S, Agerberth B, Gudmundsson GH. Phenylbutyrate induces antimicrobial peptide expression. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009;53:5127–5133.
Imai K, Ochiai K, Okamoto T. Reactivation of latent HIV-1 infection by the periodontopathic bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis involves histone modification. J Immunol. 2009;182:3688–3695.
Haller D, Holt L, Kim SC, Schwabe RF, Sartor RB, Jobin C. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibits non-pathogenic Gram negative bacteria-induced NF-kappa B recruitment to the interleukin-6 gene promoter in intestinal epithelial cells through modulation of histone acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:23851–23860.
Ghadimi D, Helwig U, Schrezenmeir J, Heller KJ, de Vrese M. Epigenetic imprinting by commensal probiotics inhibits the IL-23/IL-17 axis in an in vitro model of the intestinal mucosal immune system. J Leukoc Biol. 2012;92:895–911.
Schmeck B, Beermann W, van Laak V, et al. Intracellular bacteria differentially regulated endothelial cytokine release by MAPK-dependent histone modification. J Immunol. 2005;175:2843–2850.
Opitz B, Puschel A, Beermann W, et al. Listeria monocytogenes activated p38 MAPK and induced IL-8 secretion in a nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1-dependent manner in endothelial cells. J Immunol. 2006;176:484–490.
Hamon MA, Cossart P. K+ efflux is required for histone H3 dephosphorylation by Listeria monocytogenes listeriolysin O and other pore-forming toxins. Infect Immun. 2011;79:2839–2846.
**a G, Schneider-Stock R, Diestel A, et al. Helicobacter pylori regulates p21(WAF1) by histone H4 acetylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;369:526–531.
Acknowledgments
We thank Haiyang Hu for figure preparation. This study was supported by the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81330011) and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2013CB531401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, J., Wu, W., Li, Y. et al. Influences of the Gut Microbiota on DNA Methylation and Histone Modification. Dig Dis Sci 62, 1155–1164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4538-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-017-4538-6