Abstract
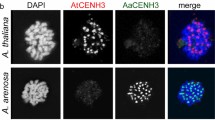
The centromere is a region utilized for spindle attachment on a eukaryotic chromosome and essential for accurate chromatid segregation. In most eukaryotes, centromeres have specific DNA sequences and are capable of assembling specific proteins to form a complex called the kinetochore. Among these proteins, centromeric histone H3 (CENH3) is one of the most fundamental, since CENH3s have been found in all investigated functional centromeres and recruits other centromeric proteins. In this study, the localization of alien CENH3s were analyzed in Arabidopsis and tobacco-cultured cells to determine the interaction between species-specific centromeric DNA and CENH3. Results showed that CENH3 of Arabidopsis and tobacco were localized on centromeres in the tobacco-cultured cells, unlike the case with CENH3 of rice and Luzula. In addition to these CENH3s, CENH3 of Luzula was partially localized in the Arabidopsis cultured cells. These data suggest that only evolutionally close CENH3s are able to target centromeres in alien species. Furthermore, the ability to target alien centromeres of histone fold domains was investigated using amino-terminal deleted CENH3s.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2, 4-D:
-
2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- Cen:
-
centromeric
- CENH3:
-
centromeric histone H3
- Disp:
-
dispersed
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- HFD:
-
histone fold domains
- HTR12:
-
centromeric histone H3 of Arabidopsis thaliana
- LnCENH3:
-
centromeric histone H3 of Luzula nivea
- LS medium:
-
Linsmaier and Skoog’s medium
- MS medium:
-
Murashige and Skoog’s medium
- NtCENH3:
-
centromeric histone H3 of Nicotiana tabaccum
- OsCENH3:
-
centromeric histone H3 of Oryza sativa
- T-DNA:
-
transfer DNA
References
Amor DJ, Kalitsis P, Sumer H, Choo KH (2004) Building the centromere: from foundation proteins to 3D organization. Trends Cell Biol 14:359–368
Ananiev EV, Phillips RL, Rines HW (1998) Chromosome-specific molecular organization of maize (Zea mays L.) centromeric regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:13073–13078
Black BE, Foltz DR, Chakravarthy S, Luger K, Woods VL Jr, Cleveland DW (2004) Structural determinants for generating centromeric chromatin. Nature 430:578–582
Cheng Z, Dong F, Langdon T, Ouyang S, Buell CR, Gu M, Blattner FR, Jiang J (2002) Functional rice centromeres are marked by a satellite repeat and a centromere-specific retrotransposon. Plant Cell 14:1691–1704
Cooper JL, Henikoff S (2004) Adaptive evolution of the histone fold domain in centromeric histones. Mol Biol Evol 21:1717–1718
Dong F, Miller JT, Jackson SA, Wang GL, Ronald PC, Jiang J (1998) Rice (Oryza sativa) centromeric regions consist of complex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:8135–8140
Henikoff S, Ahmad K, Malik HS (2001) The centromere paradox: stable inheritance with rapidly evolving DNA. Science 293:1098–1102
Heun P, Erhardt S, Blower MD, Weiss S, Skora AD, Karpen GH (2006) Mislocalization of the Drosophila centromere-specific histone CID promotes formation of functional ectopic kinetochores. Dev Cell 10:303–315
** W, Melo JR, Nagaki K, Talbert PB, Henikoff S, Dawe RK, Jiang J (2004) Maize centromeres: organization and functional adaptation in the genetic background of oat. Plant Cell 16:571–581
Karimi M, Inze D, Depicker A (2002) Gateway vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Trends Plant Sci 7:193–195
Kato K, Matsumoto T, Koiwai A, Mizusaki S, Nishida K, Noguchi M, Tamaki E (1972) Liquid suspension culture of tobacco cells. Proc IV IFS: Ferment Technol 680–695
Kawabe A, Nasuda S (2005) Structure and genomic organization of centromeric repeats in Arabidopsis species. Mol Gen Genomics 272:593–602
Kondo K, Lavarack PS (1984) A cytotaxonomic study of some Australian species of Drosera L. (Droseraceae). Botanical J Linnean Soc 88:317–333
Kumekawa N, Hosouchi T, Tsuruoka H, Kotani H (2000) The size and sequence organization of the centromeric region of Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 5. DNA Res 7:315–321
Kumekawa N, Hosouchi T, Tsuruoka H, Kotani H (2001) The size and sequence organization of the centromeric region of Arabidopsis thaliana chromosome 4. DNA Res 8:285–290
Lee H, Zhang W, Langdon T, ** W, Yan H, Cheng Z, Jiang J (2005) Chromatin immunoprecipitation cloning reveals rapid evolutionary patterns of centromeric DNA in Oryza species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:11793–11798
Lermontova I, Schubert V, Fuchs J, Klatte S, Macas J, Schubert I (2006) Loading of Arabidopsis centromeric histone CENH3 occurs mainly during G2 and requires the presence of the histone fold domain. Plant Cell 18:2442–2451
Malik HS, Henikoff S (2001) Adaptive evolution of Cid, a centromere-specific histone in Drosophila. Genetics 157:1293–1298
Mathur J, Szabados L, Schaefer S, Grunenberg B, Lossow A, Jonas-Straube E, Schell J, Konez C, Konez-Kalman Z (1998) Gene identification with sequenced T-DNA tags generated by transformation of Arabidopsis cell suspension. Plant J 13:707–716
Nagaki K, Tsujimoto H, Sasakuma T (1998) A novel repetitive sequence of sugar cane, SCEN family, locating on centromeric regions. Chromosome Res 6:295–302
Nagaki K, Cheng Z, Ouyang S, Talbert PB, Kim M, Jones KM, Henikoff S, Buell CR, Jiang J (2004) Sequencing of a rice centromere uncovers active genes. Nat Genet 36:138–145
Nagaki K, Kashihara K, Murata M (2005) Visualization of diffuse centromeres with centromere-specific histone H3 in the holocentric plant Luzula nivea. Plant Cell 17:1886–1893
Nagaki K, Kashihara K, Murata M (2009a) A centromeric DNA sequence colocalized with a centromere-specific histone H3 in tobacco. Chromosoma 118:249–257
Nagaki K, Kashihara K, Murata M (2009b) Characterization of the two centromeric proteins CENP-C and MIS12 in Nicotiana species. Chromosome Res 17:719–726
Pimpinelli S, Goday C (1989) Unusual kinetochores and chromatin diminution in Parascaris. Trends Genet 5:310–315
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sato H, Shibata F, Murata M (2005) Characterization of a Mis 12 homologue in Arabidopsis thaliana. Chromosome Res 13:827–834
Talbert PB, Masuelli R, Tyagi AP, Comai L, Henikoff S (2002) Centromeric localization and adaptive evolution of an Arabidopsis histone H3 variant. Plant Cell 14:1053–1066
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Vermaak D, Hayden HS, Henikoff S (2002) Centromere targeting element within the histone fold domain of Cid. Mol Cell Biol 22:7553–7561
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Wesco Scientific Promotion Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans de Jong.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaki, K., Terada, K., Wakimoto, M. et al. Centromere targeting of alien CENH3s in Arabidopsis and tobacco cells. Chromosome Res 18, 203–211 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-009-9108-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-009-9108-0