Abstract
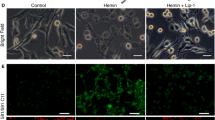
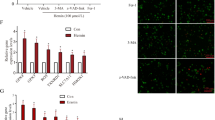
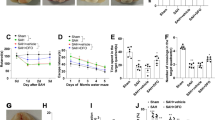
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a serious cerebrovascular disease with high mortality, and the mean age at morbidity is younger than in other types of stroke. Early brain injury (EBI) plays a key role in the poor prognoses of SAH. In EBI, multiple forms of cell death have been identified and well studied; however, the role of ferroptosis has not been elucidated. Hence, in this study, we developed an in vivo (SAH rat model) and in vitro model (SH-SY5Y oxyhemoglobin injury model) to understand the role of ferroptosis in EBI, then explored the protective mechanism of ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1). Firstly, we found that neurological scores, blood–brain barrier permeability, brain edema deteriorated after SAH in the in vivo model, cell viability was decreased after SAH in both cortex and SH-SY5Y cells. Further, iron content in cortex was increased after SAH, while transferrin receptor 1 and ferroportin (Fpn) were increased in oxyhemoglobin-treated in vitro model. Additionally, glutathione content and glutathione peroxidase 4 activity were reduced in SAH rats, and lipid peroxides were increased in the oxyhemoglobin-treated cells. Finally, administration of Fer-1 upregulated Fpn and decreased the iron content, then improved the lipid peroxidation and EBI. However, Fer-1 had no effect on the apoptosis. Our study indicated that the ferroptosis was involved in EBI of SAH, and the inhibitor Fer-1 provided neuroprotection against EBI by alleviating ferroptosis, the potential protective mechanism might be via suppressing lipid peroxidation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BBB:
-
Blood–brain barrier
- CCA:
-
Common carotid artery
- DMT1:
-
Divalent metal transporter 1
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- EBI:
-
Early brain injury
- ECA:
-
External carotid artery
- Fer-1:
-
Ferrostatin-1
- FJC:
-
Fluoro-Jade C
- Fpn:
-
Ferroportin
- GPx4:
-
Glutathione peroxidase 4
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- Hb:
-
Oxyhemoglobin
- ICH:
-
Intracranial hematoma
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- IRP1/2:
-
Iron regulatory proteins 1/2
- OD:
-
Optical density
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer solution
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SAH:
-
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
- TfR1:
-
Transferrin receptor 1
- WW:
-
Wet weight
References
Bayeva M, Khechaduri A, Puig S, Chang HC, Patial S, Blackshear PJ, Ardehali H (2012) mTOR regulates cellular iron homeostasis through tristetraprolin. Cell Metab 16(5):645–657
Cao JY, Dixon SJ (2016) Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(11–12):2195–2209
D’Arcy M (2019) Cell death. A review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int 43(6):582–592
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS, Morrison B 3rd, Stockwell BR (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072
Drakesmith H, Nemeth E, Ganz T (2015) Ironing out ferroportin. Cell Metab 22(5):777–787
Edebali NTI, Açıkgöz B, Açıkgöz S, Barut F, Sevinç N, Sümbüloğlu V (2014) Apoptosis and necrosis in the circumventricular organs after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage as detected with annexin V and caspase 3 immunostaining. Neurol Res 36(12):1114–1120
Fuchs Y, Steller H (2011) Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 147(4):742–758
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R, Jiang X (2015) Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol Cell 59(2):298–308
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ (1995) Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation. Stroke 26(4):627–634
Geng N, Shi BJ, Li SL, Zhong ZY, Li YC, Xua WL, Zhou H, Cai JH (2018) Knockdown of ferroportin accelerates erastin-induced ferroptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Eur Rev Med Pharm Sci 22(12):3826–3836
Guiney SJ, Adlard PA, Bush AI, Finkelstein DI, Ayton S (2017) Ferroptosis and cell death mechanisms in Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Int 104:34–48
Hansen-Schwartz J, Vajkoczy P, Macdonald RL, Pluta RM, Zhang JH (2007) Cerebral vasospasm: looking beyond vasoconstriction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28(6):252–256
Hong SH, Lee DH, Lee YS, Jo MJ, Jeong YA, Kwon WT, Choudry HA, Bartlett DL, Lee YJ (2017) Molecular crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis: emerging role of ER stress-induced p53-independent PUMA expression. Oncotarget 8(70):115164–115178
Hou W, **e Y, Song X, Sun X, Lotze MT, Zeh HJ 3rd, Kang R, Tang D (2016) Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 12(8):1425–1428
Imai H, Matsuoka M, Kumagai T, Sakamoto T, Koumura T (2017) Lipid peroxidation-dependent cell death regulated by GPx4 and ferroptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 403:143–170
Li XHQ, Lan X, Gao Y, Wan J, Durham F, Cheng T, Yang J, Wang Z, Jiang C, Ying M, Koehler RC, Stockwell BR, Wang J (2017) Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis protects hemorrhagic brain. JCI Insight 2(7):1–19
Li Y, Wu P, Dai J, Zhang T, Bihl J, Wang C, Liu Y, Shi H (2019) Inhibition of mTOR alleviates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via relieving excessive mitochondrial fission. Cell Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00760
Liu L, Kawakita F, Fujimoto M, Nakano F, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Suzuki H (2017) Role of periostin in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in mice. Stroke 48(4):1108–1111
Liu W, Li R, Yin J, Guo S, Chen Y, Fan H, Li G, Li Z, Li X, Zhang X, He X, Duan C (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate the early brain injury of subarachnoid hemorrhage partly by suppression of Notch1-dependent neuroinflammation: involvement of Botch. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):8
Ma S, Henson ES, Chen Y, Gibson SB (2016) Ferroptosis is induced following siramesine and lapatinib treatment of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 7:e2307
Ma X, Wang J, Li J, Ma C, Chen S, Lei W, Yang Y, Liu S, Bihl J, Chen C (2018) Loading MiR-210 in endothelial progenitor cells derived exosomes boosts their beneficial effects on hypoxia/reoxygeneation-injured human endothelial cells via protecting mitochondrial function. Cell Physiol Biochem 46(2):664–675
MacKenzie EL, Iwasaki K, Tsuji Y (2008) Intracellular iron transport and storage: from molecular mechanisms to health implications. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(6):997–1030
Masaldan S, Clatworthy SAS, Gamell C, Meggyesy PM, Rigopoulos A-T, Haupt S, Haupt Y, Denoyer D, Adlard PA, Bush AI, Cater MA (2018) Iron accumulation in senescent cells is coupled with impaired ferritinophagy and inhibition of ferroptosis. Redox Biol 14:100–115
Morris G, Berk M, Carvalho AF, Maes M, Walker AJ, Puri BK (2018) Why should neuroscientists worry about iron? The emerging role of ferroptosis in the pathophysiology of neuroprogressive diseases. Behav Brain Res 341:154–175
Musci G, Polticelli F, Bonaccorsi di Patti MC (2014) Ceruloplasmin-ferroportin system of iron traffic in vertebrates. World J Biol Chem 5(2):204–215
Neitemeier S, Jelinek A, Laino V, Hoffmann L, Eisenbach I, Eying R, Ganjam GK, Dolga AM, Oppermann S, Culmsee C (2017) BID links ferroptosis to mitochondrial cell death pathways. Redox Biol 12:558–570
Ooko E, Saeed ME, Kadioglu O, Sarvi S, Colak M, Elmasaoudi K, Janah R, Greten HJ, Efferth T (2015) Artemisinin derivatives induce iron-dependent cell death (ferroptosis) in tumor cells. Phytomedicine 22(11):1045–1054
Peng Y, ** J, Fan L, Xu H, He P, Li J, Chen T, Ruan W, Chen G (2018) Rolipram attenuates early brain injury following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats: possibly via regulating the SIRT1/NF-kappaB pathway. Neurochem Res 43(4):785–795
Sakai O, Uchida T, Imai H, Ueta T (2016) Glutathione peroxidase 4 plays an important role in oxidative homeostasis and wound repair in corneal epithelial cells. FEBS Open Biol 6(12):1238–1247
Savarraj J, Parsha K, Hergenroeder G, Ahn S, Chang TR, Kim DH, Choi HA (2018) Early brain injury associated with systemic inflammation after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 28(2):203–211
Shao J, Wu Q, Lv SY, Zhou XM, Zhang XS, Wen LL, Xue J, Zhang X (2019) Allicin attenuates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Clin Neurosci 63:202–208
Shaw AT, Winslow MM, Magendantz M, Ouyang C, Dowdle J, Subramanian A, Lewis TA, Maglathin RL, Tolliday N, Jacks T (2011) Selective killing of K-ras mutant cancer cells by small molecule inducers of oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(21):8773–8778
Shi L, Liang F, Zheng J, Zhou K, Chen S, Yu J, Zhang J (2018) Melatonin regulates apoptosis and autophagy via ROS-MST1 pathway in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Front Mol Neurosci 11:93
Skouta R, Dixon SJ, Wang J, Dunn DE, Orman M, Shimada K, Rosenberg PA, Lo DC, Weinberg JM, Linkermann A, Stockwell BR (2014) Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J Am Chem Soc 136(12):4551–4556
Sugawara T, Ayer R, Jadhav V, Zhang JH (2008) A new grading system evaluating bleeding scale in filament perforation subarachnoid hemorrhage rat model. J Neurosci Methods 167(2):327–334
Sun Q, Wu W, Hu YC, Li H, Zhang D, Li S, Li W, Li WD, Ma B, Zhu JH, Zhou ML, Hang CH (2014) Early release of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) from neurons in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in vivo and in vitro. J Neuroinflammation 11:106
Suzuki H (2015) What is early brain injury? Transl Stroke Res 6(1):1–3
Wang Z, Ding Y, Wang X, Lu S, Wang C, He C, Wang L, Piao M, Chi G, Luo Y, Ge P (2018) Pseudolaric acid B triggers ferroptosis in glioma cells via activation of Nox4 and inhibition of xCT. Cancer Lett 428:21–33
Wenz C, Faust D, Linz B, Turmann C, Nikolova T, Bertin J, Gough P, Wipf P, Schroder AS, Krautwald S, Dietrich C (2018) t-BuOOH induces ferroptosis in human and murine cell lines. Arch Toxicol 92(2):759–775
Wenzel SE, Tyurina YY, Zhao J, St. Croix CM, Dar HH, Mao G, Tyurin VA, Anthonymuthu TS, Kapralov AA, Amoscato AA, Mikulska-Ruminska K, Shrivastava IH, Kenny EM, Yang Q, Rosenbaum JC, Sparvero LJ, Emlet DR, Wen X, Minami Y, Qu F, Watkins SC, Holman TR, VanDemark AP, Kellum JA, Bahar I, Bayır H, Kagan VE (2017) PEBP1 wardens ferroptosis by enabling lipoxygenase generation of lipid death signals. Cell 171(3):628.e626–641.e626
Wu P, Li Y, Zhu S, Wang C, Dai J, Zhang G, Zheng B, Xu S, Wang L, Zhang T, Zhou P, Zhang JH, Shi H (2017) Mdivi-1 alleviates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats, possibly via inhibition of Drp1-activated mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress. Neurochem Res 42(5):1449–1458
Yang WS, Stockwell BR (2016) Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol 26(3):165–176
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji AF, Clish CB, Brown LM, Girotti AW, Cornish VW, Schreiber SL, Stockwell BR (2014) Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156(1–2):317–331
Yang S, Chen X, Li S, Sun B, Hang C (2018) Melatonin treatment regulates SIRT3 expression in early brain injury (EBI) due to reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). Med Sci Monit 24:3804–3814
Zhang T, Wu P, Zhang JH, Li Y, Xu S, Wang C, Wang L, Zhang G, Dai J, Zhu S, Liu Y, Liu B, Reis C, Shi H (2018) Docosahexaenoic acid alleviates oxidative stress-based apoptosis via improving mitochondrial dynamics in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(7):1413–1423
Zille M, Karuppagounder SS, Chen Y, Gough PJ, Bertin J, Finger J, Milner TA, Jonas EA, Ratan RR (2017) Neuronal death after hemorrhagic stroke in vitro and in vivo shares features of ferroptosis and necroptosis. Stroke 48(4):1033–1043
Funding
This work is supported by the American Heart Association, USA (16SDG26420078), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, China (ZD2018018) and Innovation Fund of Harbin Medical University, China (YTSKYCX2018-38HYD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exists.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Wu, P. et al. Inhibition of Ferroptosis Alleviates Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage In Vitro and In Vivo via Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41, 263–278 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00850-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00850-1