Abstract
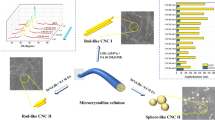
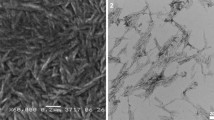
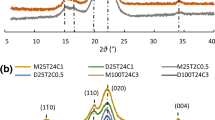
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) have drawn tremendous attention because of their extraordinary physical and chemical properties as well as renewability and sustainability. In this work, after a range of pretreatments, such as freeze-drying, ball-milling, mercerization, N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide dissolution and ionic liquid dissolution, various CNCs with different crystalline properties and morphologies were obtained by hydrolysis or oxidation. XRD and AFM were used to determine the influences of pretreatments on the crystalline properties and morphologies of CNCs. New methods, i.e., specific pretreatments followed by sulfuric acid hydrolysis or 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl radical (TEMPO) oxidation, were developed to obtain sphere-like CNCs. It was found that sphere-like CNCs were more likely to be obtained from cellulose materials possessing high accessibility. Pretreatments produced cellulose with various crystallinities and polymorphs, and therefore changed the yields of CNCs and influenced their morphology. CNCs prepared by TEMPO oxidation generally had smaller size than the corresponding products obtained by sulfuric acid hydrolysis. In addition, for the dissolved/regenerated cellulose, TEMPO oxidation was a better method to yield sphere-like CNCs than sulfuric acid hydrolysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ago M, Endo T, Hirotsu T (2004) Crystalline transformation of native cellulose from cellulose I to cellulose II polymorph by a ball-milling method with a specific amount of water. Cellulose 11:163–167. doi:10.1023/B:CELL.0000025423.32330.fa
Araki J, Wada M, Kuga S, Okano T (2000) Birefringent glassy phase of a cellulose microcrystal suspension. Langmuir 16(6):2413–2415. doi:10.1021/la9911180
Aulin C, Ahola S, Josefsson P, Nishino T, Hirose Y, Österberg M, Wågberg L (2009) Nanoscale cellulose films with different crystallinities and mesostructures—Their surface properties and interaction with water. Langmuir 25(13):7675–7685. doi:10.1021/la900323n
Azizi Samir MAS, Alloin F, Sanchez J-Y, El Kissi N, Dufresne A (2004) Preparation of cellulose whiskers reinforced nanocomposites from an organic medium suspension. Macromolecules 37(4):1386–1393. doi:10.1021/ma030532a
Beck-Candanedo S, Roman M, Gray DG (2005) Effect of reaction conditions on the properties and behavior of wood cellulose nanocrystal suspensions. Biomacromolecules 6(2):1048–1054. doi:10.1021/bm049300p
Bondeson D, Mathew A, Oksman K (2006) Optimization of the isolation of nanocrystals from microcrystalline cellulose by acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 13(2):171–180. doi:10.1007/s10570-006-9061-4
Driemeier C, Calligaris GA (2011) Theoretical and experimental developments for accurate determination of crystallinity of cellulose I materials. J Appl Crystallogr 44(1):184–192. doi:10.1107/S0021889810043955
Elazzouzi-Hafraoui S, Nishiyama Y, Putaux J-L, Heux L, Dubreuil F, Rochas C (2007) The shape and size distribution of crystalline nanoparticles prepared by acid hydrolysis of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 9(1):57–65. doi:10.1021/bm700769p
Esteghlalian AR, Bilodeau M, Mansfield SD, Saddler JN (2001) do enzymatic hydrolyzability and Simons’ stain reflect the changes in the accessibility of lignocellulosic substrates to cellulase enzymes? Biotechnol Prog 17(6):1049–1054. doi:10.1021/bp0101177
Fan LT, Lee YH, Beardmore DR (1981) The influence of major structural features of cellulose on rate of enzymatic hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 23(2):419–424. doi:10.1002/bit.260230215
French AD, Santiago Cintrón M (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the segal crystallinity index. Cellulose 20:583–588. doi:10.1007/s10570-012-9833-y
Gao Q, Shen X, Lu X (2011) Regenerated bacterial cellulose fibers prepared by the NMMO H2O process. Carbohydr Polym 83(3):1253–1256. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.09.029
Goetz L, Mathew A, Oksman K, Gatenholm P, Ragauskas AJ (2009) A novel nanocomposite film prepared from crosslinked cellulosic whiskers. Carbohydr Polym 75(1):85–89. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.06.017
Habibi Y, Chanzy H, Vignon M (2006) TEMPO-mediated surface oxidation of cellulose whiskers. Cellulose 13(6):679–687. doi:10.1007/s10570-006-9075-y
Habibi Y, Lucia LA, Rojas OJ (2010) Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Rev 110(6):3479–3500. doi:10.1021/cr900339w
Hirota M, Tamura N, Saito T, Isogai A (2010) Water dispersion of cellulose II nanocrystals prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of mercerized cellulose at pH 4.8. Cellulose 17(2):279–288. doi:10.1007/s10570-009-9381-2
Isogai T, Yanagisawa M, Isogai A (2008) Degrees of polymerization (DP) and DP distribution of dilute acid-hydrolyzed products of alkali-treated native and regenerated celluloses. Cellulose 15(6):815–823. doi:10.1007/s10570-008-9231-7
Isogai T, Yanagisawa M, Isogai A (2009) Degrees of polymerization (DP) and DP distribution of cellouronic acids prepared from alkali-treated celluloses and ball-milled native celluloses by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Cellulose 16(1):117–127. doi:10.1007/s10570-008-9245-1
Klemm D, Kramer F, Moritz S, Lindström T, Ankerfors M, Gray D, Dorris A (2011) Nanocelluloses: a new family of nature-based materials. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(24):5438–5466. doi:10.1002/anie.201001273
Langan P, Nishiyama Y, Chanzy H (2001) X-ray structure of mercerized cellulose II at 1 Å resolution. Biomacromolecules 2:410–416. doi:10.1021/bm005612q
Liu Y, Hu H (2008) X-ray diffraction study of bamboo fibers treated with NaOH. Fiber Polym 9(6):735–739. doi:10.1007/s12221-008-0115-0
Nishiyama Y, Langan P, Chanzy H (2002) Crystal structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose Iβ from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J Am Chem Soc 124(31):9074–9082. doi:10.1021/ja0257319
Revol JF, Dietrich A, Goring DAI (1987) Effect of mercerization on the crystallite size and crystallinity index in cellulose from different sources. Can J Chem 65(8):1724–1725. doi:10.1139/v87-288
Saito T, Isogai A (2004) TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose. The effect of oxidation conditions on chemical and crystal structures of the water-insoluble fractions. Biomacromolecules 5(5):1983–1989. doi:10.1021/bm0497769
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-Ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794. doi:10.1177/004051755902901003
Siqueira G, Bras J, Dufresne A (2008) Cellulose whiskers versus microfibrils: influence of the nature of the nanoparticle and its surface functionalization on the thermal and mechanical properties of nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 10(2):425–432. doi:10.1021/bm801193d
Terech P, Chazeau L, Cavaille JY (1999) A small-angle scattering study of cellulose whiskers in aqueous suspensions. Macromolecules 32(6):1872–1875. doi:10.1021/ma9810621
van den Berg O, Schroeter M, Capadona JR, Weder C (2007) Nanocomposites based on cellulose whiskers and (semi) conducting conjugated polymers. J Mater Chem 17(26):2746–2753
Wada M, Heux L, Sugiyama J (2004) Polymorphism of cellulose I family: reinvestigation of cellulose IV. Biomacromolecules 5:1385–1391. doi:10.1021/bm0345357
Wang N, Ding E, Cheng R (2007a) Preparation and liquid crystalline properties of spherical cellulose nanocrystals. Langmuir 24(1):5–8. doi:10.1021/la702923w
Wang N, Ding E, Cheng R (2007b) Thermal degradation behaviors of spherical cellulose nanocrystals with sulfate groups. Polymer 48(12):3486–3493. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2007.03.062
Zhang H, Wu J, Zhang J, He J (2005) 1-Allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride room temperature ionic liquid: a new and powerful nonderivatizing solvent for cellulose. Macromolecules 38(20):8272–8277. doi:10.1021/ma0505676
Zhang J, Elder TJ, Pu Y, Ragauskas AJ (2007) Facile synthesis of spherical cellulose nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 69(3):607–611. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.01.019
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude for financial support from the State Forestry Administration (201204803), Ministry of Science and Technology (973 project, 2010CB732204), and the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30930073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D., Peng, XW., Zhong, LX. et al. Effects of pretreatments on crystalline properties and morphology of cellulose nanocrystals. Cellulose 20, 2427–2437 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9997-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9997-0