Abstract
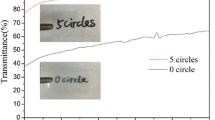
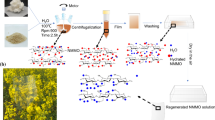
Transparent and water repellent gas barrier cellulose films were fabricated by surface modification of alkali/urea regenerated cellulose (AUC) films by soaking in cationic alkylketene dimer (AKD) dispersion, drying, and heating. Highly water repellent and excellent gas barrier properties were obtained for AKD-treated and heated AUC films due to covering of the film surfaces by hydrophobic AKD components. The maximum AKD content of the films was 0.2 %. Oxygen transmission rates for AKD-treated AUC films at 0 % relative humidity (RH) were less than 0.0005 mL m−2 day−1 kPa−1, the lowest detection limit of the instrument. Water contact angles on the AUC film increased from 50 to 110° after AKD treatment, and water uptake (immersion in water for 6 days) decreased from 92 to 20 %. Moreover, oxygen permeability decreased from 0.56 and 5.8 to 0.13 and 2.1 mL μm m−2 day−1 kPa−1 at 50 and 75 % RH, respectively, when the AKD content of the film was increased from 0 to 0.2 %. The present AKD-treated AUC film also had high light transparency (88 % at 600 nm), tensile strength (168 MPa), elongation at break (29 %), and work of fracture (37 MJ m−3). FT–IR analysis showed that AKD components were still present as major species on the AKD-treated film surfaces without hydrolysis at 2 months after conditioning the films at 23 °C and 50 % RH, indicating that such AKD molecules contributed to the hydrophobic nature of the AKD-treated AUC films.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakura K, Iwamoto M, Isogai A (2006) The effects of AKD oligomers present in AKD wax on dispersion stability and paper sizing performance. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 2006:245–252
Balu B, Breedveld V, Hess DW (2008) Fabrication of “roll-off” and “sticky” superhydrophobic cellulose surfaces via plasma processing. Langmuir 24:4785–4790
Bras J, Vaca-Garcia C, Borredon ME, Glasser W (2007) Oxygen and water vapor permeability of fully substituted long chain cellulose esters (LCCE). Cellulose 14:367–374
Edlund U, Zhu Ryberg YZ, Albertsson AC (2010) Barrier films from renewable forestry waste. Biomacromolecules 11:2532–2538
Fujisawa S, Saito T, Isogai A (2012) Nano-dispersion of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose/aliphatic amine salts in isopropyl alcohol. Cellulose 19:459–466
Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Iwata T, Kumamoto Y, Isogai A (2009) Transparent and high gas barrier films of cellulose nanofibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. Biomacromolecules 10:162–165
Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Iwamoto S, Kumamoto Y, Ohdaira T, Suzuki R, Isogai A (2011) Pore size determination of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril films by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 12:4057–4062
Gross RA, Kalra B (2002) Biodegradable polymers for the environment. Science 297:803–807
Hartman J, Albertsson AC, Sjöberg J (2006) Surface-and bulk-modified galactoglucomannan hemicellulose films and film laminates for versatile oxygen barriers. Biomacromolecules 7:1983–1989
Isogai A (1999) Mechanism of paper sizing by alkylketene dimer. J Pulp Paper Sci 25:251–255
Isogai A, Onabe F, Usuda M (1992a) Changes in zeta potentials of amorphous cellulose particles with aluminum sulfate. Sen’i Gakkaishi 48:649–654
Isogai A, Taniguchi R, Onabe F, Usuda M (1992b) Sizing mechanism of alkylketene dimers, part 2. Deterioration of alkylketene dimer emulsion. Nord Pulp Paper Res J 6:205–211
Isogai A, Kitaoka C, Onabe F (1997) Effects of carboxyl groups in pulp on retention of alkylketene dimer. J Pulp Paper Sci 23:J215–J219
Kannangara D, Shen W (2008) Roughness effects of cellulose and paper substrates on water drop impact and recoil. Colloids Surf A 330:151–160
Klemm D, Heubletin B, Fink HP, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:3358–3393
Liu A, Walther A, Ikkala O, Belova L, Berglund LA (2011) Clay nanopaper with tough cellulose nanofiber matrix for fire retardancy and gas barrier functions. Biomacromolecules 12:633–641
Miller KS, Krochta JM (1997) Oxygen and aroma barrier properties of edible films: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 8:228–237
Obokata T, Isogai A (2007) The mechanism of wet-strength development of cellulose sheets prepared with polyamideamine–epichlorohydrin (PAE) resin. Colloids Surf A 302:525–531
Revell KM (1991) High barrier metallized film. US Patent 5021298
Roberts JC (1996) Paper Chemistry, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall, London
Sehaqui H, Liu A, Zhou Q, Berglund LA (2010) Fast preparation procedure for large, flat cellulose and cellulose/inorganic nanopaper structures. Biomacromolecules 11:2195–2198
Siró I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17:459–494
Yang Q, Lue A, Qi H, Sun Y, Zhang X, Zhang L (2009) Properties and bioapplications of blended cellulose and corn protein films. Macromol Biosci 9:849–856
Yang Q, Lue A, Zhang L (2010) Reinforcement of ramie fibers on regenerated cellulose films. Compos Sci Technol 70:2319–2324
Yang Q, Fukuzumi H, Saito T, Isogai A, Zhang L (2011a) Transparent cellulose films with high gas barrier properties fabricated from aqueous alkali/urea solutions. Biomacromolecules 12:2766–2771
Yang Q, Qin X, Zhang L (2011b) Properties of cellulose films prepared from NaOH/urea/zincate aqueous solution at low temperature. Cellulose 18:681–688
Yang Q, Fujisawa S, Saito T, Isogai A (2012) Improvement of mechanical and oxygen barrier properties of cellulose films by controlling drying conditions of regenerated cellulose hydrogels. Cellulose 19:695–703
Yoshida Y, Yanagisawa M, Isogai A, Suguri N, Sumikawa N (2005) Preparation of polymer brush-type cellulose β-ketoesters using LiCl/1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone as a solvent. Polymer 46:2548–2557
Yu L, Dean K, Li L (2006) Polymer blends and composites from renewable resources. Prog Polym Sci 31:576–602
Zhang L, Zhou Q (1997) Water-resistant film from polyurethane/nitrocellulose coating to regenerated cellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 36:2651–2656
Zhu Ryberg YZ, Edlund U, Albertsson AC (2011) Conceptual approach to renewable barrier film design based on wood hydrolysate. Biomacromolecules 12:1355–1362
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS): Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research S (21228007), and Research Fellowships for Young Scientists (24-7663).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Saito, T. & Isogai, A. Facile fabrication of transparent cellulose films with high water repellency and gas barrier properties. Cellulose 19, 1913–1921 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9790-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9790-5