Abstract
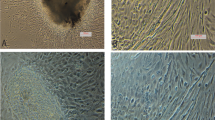
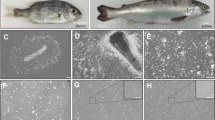
Rohu gill cell line (LRG) was established from gill tissue of Indian major carp (Labeo rohita), a freshwater fish cultivated in India. The cell line was maintained in Leibovitz's L-15 supplemented with 10 % foetal bovine serum (FBS). This cell line has been sub-cultured more than 85 passages over a period of 2 years. The LRG cell line consists of both epithelial and fibroblastic-like cells. The cells were able to grow at a wide range of temperatures from 22 to 32 °C, the optimum temperature being 28 °C. The growth rate of gill cells increased as the FBS proportion increased from 2 to 20 % at 28 °C. The plating efficiency was also high (34.37 %). The viability of the LRG cell line was 70–80 % after 6 months of storage in liquid nitrogen. The karyotype analysis revealed a diploid count of 50 chromosomes. The gill cells of rohu were successfully transfected with pEGFP-N1. Amplification of mitochondrial Cox1 gene using primers specific to L. rohita confirmed the origin of this cell line from L. rohita. The cytotoxicity of malathion was assessed in LRG cell line using multiple endpoints such as 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, Neutral Red assay, Alamar Blue assay and Coomassie Blue protein assay. Acute toxicity assay on fish was conducted by exposing L. rohita for 96 h to malathion under static conditions. Statistical analysis revealed good correlation with r 2 = 0.946–0.990 for all combinations between endpoints employed. Linear correlations between each in vitro effective concentration 50 and the in vivo lethal concentration 50 data were highly significant.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AB:
-
Alamar Blue
- CB:
-
Coomassie Blue
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulphoxide
- EC50 :
-
Effective concentration 50
- FBS:
-
Foetal bovine serum
- HBSS:
-
Hank's balanced salt solution
- L-15:
-
Leibovitz's L-15
- LC50 :
-
Lethal concentration 50
- LRG:
-
Labeo rohita Gill cell line
- MTT:
-
3-(4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NR:
-
Neutral Red
- OPs:
-
Organophosphorus
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
Anonymous. United States Environmental Protection Agency technical report. 2005.
Avella M, Berhaut J, Payan P. Primary culture of gill epithelial cells from the sea bass Dicentrarchus labrux. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1994;30:41–9.
Babich H, Rosenberg DW, Borenfreund E. In vitro cytotoxicity studies with the fish hepatoma cell line, lhc-1 (Poeciliopsis lucida). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1991;21:327–36.
Bahich H, Borenfreund E. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity assays with cultured fish cells: a review. Toxicol In Vitro. 1991;5:91–100.
Bejar J, Borrego JJ, Alvarez MC. A continuous cell line from the cultured marine fish gilt-head seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Aquaculture. 1997;150:143–53.
Borenfreund E, Babich H, Martin-Alguacil N. Comparison of two in vitro cytotoxicity assays: the neutral red and tetrazolium (MTT) tests. Toxicol in Vitro. 1988;2:1–6.
Borenfreund E, Puerner JA. Toxicity determined in vitro by morphological alterations and neutral red absorption. Toxicol Lett. 1985;24:119–24.
Castano A, Bols N, Braunbeck T, Dierickx P, Halder M, Isomaa B, Kawahara K, Lee LEJ, Mothersill C, Part P, Repetto G, Sintes JR, Rufli H, Smith R, Wood C, Segner H. The use of fish cells in ecotoxicology. Report and recommendations of the ECVAM workshop. ATLA. 2003;47(31):317–51.
Castano A, Cantarino MJ, Castillo F, Tarasona JV. Correlation between the RTG-2 cytotoxicity test EC50 and in vivo LC50 rainbow trout bioassay. Chemosphere. 1996;32:2141–57.
Chen SL, Sha ZX, Ye HQ. Establishment of a pluripotent embryonic cell line from sea perch blastula embryo. Aquaculture. 2003;218:141–51.
Chen TR. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by fluorescent Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp Cell Res. 1977;104:255–62.
Chen XY, Shao JZ, **ang L, Liu X. Involvement of apoptosis in malathion-induced cytotoxicity in a grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) cell line. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 2006;142:36–45.
Chi SC, Hu WW, Lo BJ. Establishment and characterization of a continuous cell line (GF-1) derived from grouper, Epinephelus coioides (Hamilton): a cell line susceptible to grouper nervous necrosis virus (GNNV). J Fish Dis. 1999;22:173–82.
Dayeh VR, Bols NC, Schirmer K, Lee LEJ. The use of fish-derived cell lines for investigation of environmental contaminants. Current protocols in toxicology. New York: Wiley; 2003. p. 1–17.
Fernandez-Puentes C, Novoa B, Figueras A. A new fish cell line derived from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) TV-1. B Eur Assoc Fish Pat. 1993a;13:94–6.
Fernandez-Puentes C, Novoa B, Figueras A. Initiation of a cell line from turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-An. 1993b;29:899–900.
Flano E, Lopez-Fierro P, Alvarez F, Razquin B, Villena A. Splenic cultures from rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss: establishment and characterization. Fish and Shellfish Immun. 1998;8:589–606.
Freiberg EF, Masover GK. Mycoplasma detection in cell culture by concomitant use of bisbenzamide and fluoresceinated antibody. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990;26:585–8.
Freshney RI. Culture of animal cells: a manual of basic technique. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1994.
Gulden M, Seibert H. Impact of bioavailability on the correlation between in vitro cytotoxic and in vivo acute fish toxic concentrations of chemicals. Aquat Toxicol. 2005;72:327–37.
Hessling JJ, Miller S, Levy L. A direct comparison of procedures for the detection of mycoplasma in tissue culture. J Immunol Methods. 1980;38:315–24.
Hightower LE, Renfro JL. Recent applications of fish cell culture to biomedical research. J Exp Zool. 1988;248(3):290–302.
Hunkapiller MW, Lujan E. Purification of microgram quantities of proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In: Shively J, editor. Methods of protein microcharacterization. Clifton: Humana; 1986. p. 89–101.
Ishaq Ahmed VP, Chandra V, Sudhakaran R, Rajesh Kumar S, Sarathi M, Sarath Babu V, Ramesh B, Sahul Hameed AS. Development and characterization of cell lines derived from rohu, Labeo rohita (Hamilton), and catla, Catla catla (Hamilton). J Fish Dis. 2009;32:211–8.
Isomaa B, Lilius H, Rabergh C. Aquatic toxicology in vitro: a brief review. ATLA. 1994;22:243–53.
Kang MS, Oh MJ, Kim YJ, Kawai K, Jung SJ. Establishment and characterization of two cell lines derived from flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus (Temminck & Schlegel). J Fish Dis. 2003;26:657–65.
Katiha PK, Jena JK, Pillai NGK, Chakraborty C, Dey MM. Inland aquaculture in India: past trend, present status and future prospects. Aquacul Econ Manag. 2005;9:237–64.
Knauer K, Lampert C, Valero-Gonzalez J. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo acute fish toxicity in relation to toxicant made of action. Chemosphere. 2007;68:1435–41.
Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970;227:680–5.
Lakra WS, Bhonde RR. Development of primary cell culture from the caudal fin of an Indian major carp, Labeo rohita (Ham.). Asian Fish Sci. 1996;9:149–52.
Lakra WS, Raja-Swaminathan T, Joy KP. Development, characterization, conservation and storage of fish cell lines: a review. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2011;37:1–20.
Lo CF, Leu JH, Ho CH, Chen CH, Peng SE, Chen YT, Yeh PY, Huang CJ, Wang CH, Kou GH. Detection of baculovirus associated with white spot syndrome (WSSV) in penaeid shrimps using polymerase chain reaction. Dis Aquat Org. 1996;25:133–41.
Manna M, Chakraborty P. Analysis of lactate and malate dehydrogenase enzyme profiles of selected major carps of wetland of Calcutta. J Environ Biol. 2012;33:763–7.
Matei VE. Changes in the cellular ultrastructure of the gill epithelium in Tilapia under the action of cadmium on the fish. Tsitol. 1993;35:34–41.
Mohan CV, Shankar KM. Epidemiological analysis of epizootic ulcerative syndrome of fresh and brackish water fishes of Karnataka. India Curr Sci. 1994;66:656–8.
Na N, Guo HR, Zhang SC, Li ZL, Yin LC. In vitro and in vivo acute toxicity of fenpyroximate to flounder Paralichthys olivaceus and its gill cell line FG. Aquat Toxicol. 2009;92(2):76–85.
Nicholson BL, Danner DJ, Wu JL. Three new continuous cell lines from marine fishes of Asia. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987;23:199–204.
OECD 203. OECD guideline for testing chemicals. Test no. 203: acute fish test. 1992.
Parameswaran V, Ishaq Ahmed VP, Ravi S, Bhonde RR, Sahul Hameed AS. Development and characterization of two new cell lines from milkfish (Chanos chanos) and grouper (Epinephelus coioides) for virus isolation. Mar Biotechnol. 2007;9:281–91.
Prakasam A, Sethupathy S, Lalitha S. Plasma and RBCs antioxidant status in occupational male pesticide sprayers. Clin Chim Acta. 2001;310:107–12.
Rahim SM, Delaunoy JP, Laurent P. Identification and immunocytochemical localization of two different carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes in teleostean fish erythrocytes and gill epithelia. Histochemie. 1988;89:451–9.
Rao KS, Joseph MA, Shankar KM, Mohan CV. Primary cell culture from explants of heart tissue of Indian major carps. Curr Sci. 1997;73:374–5.
Reddy ATV, Ayyanna K, Yellamma K. Cypermethrin induced modulations in lipid metabolism of fresh water teleost. Tilapia mossambica. Biochem Int. 1991;23:963–7.
Reddy ATV, Yellamma K. Cypermethrin induced changes in nitrogen metabolism of fish. Tilapia mossambica. Biochem Int. 1991;23:649–54.
Rocha A, Ruiz S, Coll JM. Improvement of transfection efficiency of epithelioma papulosum cyprinid carp cells by modification of cell cycle and use of an optimal promoter. Mar Biotechnol. 2004;6:401–10.
Sahul Hameed AS, Parameswaran V, Ravi S, Singh B, Ramesh B. Establishment and characterization of India’s first marine fish cell line (SISK) from kidney of sea bass, (Lates calcarifer). Aquaculture. 2006;257:92–103.
Sarath Babu V, Chandra V, Nambi KSN, Majeed SA, Taju G, Patole MS, Hameed ASS. Development and characterization of novel cell lines from Etroplus suratensis and their applications in virology, toxicology and gene expression. J Fish Biol. 2012;80:312–34.
Sathe PS, Basu A, Mourya DT, Marathe BA, Gogate SS, Banerjee K. A cell line from the gill tissues of Indian cyprinoid Labeo rohita. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1997;33:425–7.
Segner H. Fish cell lines as a tool in aquatic toxicology. In: Braunbeck T, Hinton DE, Streit DE, editors. Fish ecotoxicology. Basel: Birkhauser; 1998.
Sender S, Böttcher K, Cetin Y, Gros G. Carbonic anhydrase in the gills of seawater-and freshwater-acclimated flounders Platichthys flesus: purification, characterization, and immunohistochemical localization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1999;47:43–50.
Shopsis C, Eng B. Rapid cytotoxicity testing using a semi-automated protein determination on cultured cells. Toxicol Lett. 1985;26(1):1–8.
Singh S, Sahai S. Changes in gill structure induced by BHC, lindane and endosulfan in the fresh-water teleost Puntius ticto (Ham.). Folia Morphol (Praha). 1990;38:423–32.
Storm JE, Karl KR, Doull J. Occupational exposure limits for 30 organophosphate pesticides based on inhibition of red blood cell acetylcholinesterase. Toxicol. 2000;150:1–29.
Suresh A, Sivaramakrisha B, Victoriamma PC, Radhakrisshnaiah K. Shifts in protein metabolism in some organs of fresh water fish Cyprinus carpio under mercury stress. Biochem Int. 1991;24:379–89.
Taju G, Abdul Majeed S, Nambi KSN, Sarath Babu V, Vimal S, Kamatchiammal S, Sahul Hameed AS. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo acute toxicity assays in Etroplus suratensis (Bloch, 1790) and its three cell lines in relation to tannery effluent. Chemosphere. 2012;87:55–61.
Talbot PV, Knobler RL, Buchmeier M. Western and dot immunoblotting analysis of viral antigens and antibodies: application to murine hepatitis virus. J Immunol Methods. 1984;73:177–88.
Thenmozhi C, Vignesh V, Thirumurugan R, Arun S. Impacts of malathion on mortality and biochemical changes of freshwater fish Labeo rohita. Iran. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2011;8(4):325–32.
Tong SL, Lee H, Miao HZ. The establishment and partial characterization of a continuous fish cell line FG-9307 from the gill of flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture. 1997;156:327–33.
Tong SL, Miao HZ, Li H. Three new continuous fish cell lines of SPH, SPS and RSBF derived from sea perch (Lateolabrax japonicus) and red sea bream (Pagrosomus major). Aquaculture. 1998;169:143–51.
Wise Sr JP, Winn RN, Renfro JL. Generating new marine cell lines and transgenic species. J Exp Zoo. 2002;15:292–5.
Wolf K, Quimby MC. Established eurythermic line of fish cells in vitro. Science. 1962;135:1065–6.
Zhang SM, Reddy PVGK. On the comparative karyomorphology of three Indian major carps, Catla catla (Ham.), Labeo rohita (Ham.) and Cirrhinus mrigala (Ham.). Aquaculture. 1991;97:7–12.
Acknowledgments
The first author is a recipient of INSPIRE Fellowship from the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi, India. The authors thank the management of C. Abdul Hakeem College, Melvisharam, India for providing the facilities to carry out this work. This work was funded by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdul Majeed, S., Nambi, K.S.N., Taju, G. et al. Establishment and characterization of permanent cell line from gill tissue of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) and its application in gene expression and toxicology. Cell Biol Toxicol 29, 59–73 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-012-9237-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-012-9237-7