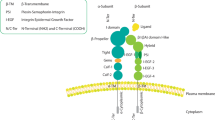
Abstract
Enhanced levels of expression of certain integrins, and a consequent increase in specific integrin signals, have been linked to cancer cell progression. Dysfunctional integrin signaling is thought to be involved, at least in part, in mediating the detachment of tumor cells from neighboring cells while providing enhanced survival and proliferative capabilities which allow such disseminating tumor cells to grow in new, foreign, microenvironments. Cell biologists have known for some time that integrin heterodimers are endocytosed from the plasma membrane in to the cytoplasm with some of this receptor later being exocytosed back to the cell surface; a cellular mechanism referred to as ‘trafficking– Although extensive research within the integrin field has elucidated key signal transduction pathways as being involved in integrin-mediated cellular behavior, both in normal and transformed cells, it is only relatively recently that the importance of integrin trafficking in modulating cellular function has been demonstrated. This review aims to identify the major trafficking molecules found to play a functional role in cancer cell behavior with special emphasis on the importance of integrin trafficking during neoplastic cell migration and invasion; vital components of the metastatic process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 100, 57–0.
Munshi, H. G., & Stack, M. S. (2006). Reciprocal interactions between adhesion receptor signaling and MMP regulation. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 25, 45–6.
Wu, X., Gan, B., Yoo, Y., & Guan, J. L. (2005). FAK-mediated src phosphorylation of endophilin A2 inhibits endocytosis of MT1-MMP and promotes ECM degradation. Developmental Cell, 9, 185–96.
Hood, J. D., & Cheresh, D. A. (2002). Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2, 91–00.
Hynes, R. O. (2002). Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell, 110, 673–87.
Aplin, A. E., Howe, A. K., & Juliano, R. L. (1999). Cell adhesion molecules, signal transduction and cell growth. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 11, 737–44.
Naylor, M. J., Li, N., Cheung, J., Lowe, E. T., Lambert, E., Marlow, R., & Wang, P., et al. (2005). Ablation of beta1 integrin in mammary epithelium reveals a key role for integrin in glandular morphogenesis and differentiation. Journal of Cell Biology, 171, 717–28.
Reddig, P. J., & Juliano, R. L. (2005). Clinging to life: cell to matrix adhesion and cell survival. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 24, 425–39.
Nikolopoulos, S. N., Blaikie, P., Yoshioka, T., Guo, W., & Giancotti, F. G. (2004). Integrin beta4 signaling promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell, 6, 471–83.
Guo, W., & Giancotti, F. G. (2004). Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 5, 816–26.
Guo, W., Pylayeva, Y., Pepe, A., Yoshioka, T., Muller, W. J., Inghirami, G., et al. (2006). Beta 4 integrin amplifies ErbB2 signaling to promote mammary tumorigenesis. Cell, 126, 489–02.
Brooks, P. C., Clark, R. A., & Cheresh, D. A. (1994). Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science, 264, 569–71.
Thomas, G. J., Lewis, M. P., Whawell, S. A., Russell, A., Sheppard, D., Hart, I. R., et al. (2001). Expression of the alphavbeta6 integrin promotes migration and invasion in squamous carcinoma cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 117, 67–3.
Caswell, P. T., & Norman, J. C. (2006). Integrin trafficking and the control of cell migration. Traffic, 7, 14–1.
Le Roy, C., & Wrana, J. L. (2005). Clathrin- and non-clathrin-mediated endocytic regulation of cell signalling. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 6, 112–26.
Maldonado-Baez, L., & Wendland, B. (2006). Endocytic adaptors: recruiters, coordinators and regulators. Trends in Cell Biology, 16, 505–13.
Nesterov, A., Carter, R. E., Sorkina, T., Gill, G. N., & Sorkin, A. (1999). Inhibition of the receptor-binding function of clathrin adaptor protein AP-2 by dominant-negative mutant mu2 subunit and its effects on endocytosis. EMBO Journal, 18, 2489–499.
de Melker, A. A., van der Horst, G., & Borst, J. (2004). c-Cbl directs EGF receptors into an endocytic pathway that involves the ubiquitin-interacting motif of Eps15. Journal of Cell Science, 117, 5001–012.
Nichols, B. J., & Lippincott-Schwartz, J. (2001). Endocytosis without clathrin coats. Trends in Cell Biology, 11, 406–12.
Cheng, Z. J., Singh, R. D., Sharma, D. K., Holicky, E. L., Hanada, K., Marks, D. L., et al. (2006). Distinct mechanisms of clathrin-independent endocytosis have unique sphingolipid requirements. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 17, 3197–210.
Nabi, I. R., & Le, P. U. (2003). Caveolae/raft-dependent endocytosis. Journal of Cell Biology, 161, 673–77.
Polo, S., & Di Fiore, P. P. (2006). Endocytosis conducts the cell signaling orchestra. Cell, 124, 897–00.
Nichols, B. (2003). Caveosomes and endocytosis of lipid rafts. Journal of Cell Science, 116, 4707–714.
Pelkmans, L., Kartenbeck, J., & Helenius, A. (2001). Caveolar endocytosis of simian virus 40 reveals a new two-step vesicular-transport pathway to the ER. Nature Cell Biology, 3, 473–83.
Nichols, B. J. A. (2002). Distinct class of endosome mediates clathrin-independent endocytosis to the Golgi complex. Nature Cell Biology, 4, 374–78.
Sabharanjak, S., Sharma, P., Parton, R. G., & Mayor, S. (2002). GPI-anchored proteins are delivered to recycling endosomes via a distinct cdc42-regulated, clathrin-independent pinocytic pathway. Developmental Cell, 2, 411–23.
Pelkmans, L., Burli, T., Zerial, M., & Helenius, A. (2004). Caveolin-stabilized membrane domains as multifunctional transport and sorting devices in endocytic membrane traffic. Cell, 118, 767–80.
Lamaze, C., Dujeancourt, A., Baba, T., Lo, C. G., Benmerah, A., & Dautry-Varsat, A. (2001). Interleukin 2 receptors and detergent-resistant membrane domains define a clathrin-independent endocytic pathway. Molecular Cell, 7, 661–71.
Sauvonnet, N., Dujeancourt, A., & Dautry-Varsat, A. (2005). Cortactin and dynamin are required for the clathrin-independent endocytosis of gammac cytokine receptor. Journal of Cell Biology, 168, 155–63.
Di Guglielmo, G. M., Le Roy, C., Goodfellow, A. F., & Wrana, J. L. (2003). Distinct endocytic pathways regulate TGF-beta receptor signalling and turnover. Nature Cell Biology, 5, 410–21.
Zerial, M., & McBride, H. (2001). Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 2, 107–17.
Pellinen, T., Arjonen, A., Vuoriluoto, K., Kallio, K., Fransen, J. A., & Ivaska, J. (2006). Small GTPase Rab21 regulates cell adhesion and controls endosomal traffic of beta1-integrins. Journal of Cell Biology, 173, 767–80.
Mohrmann, K., & van der Sluijs, P. (1999). Regulation of membrane transport through the endocytic pathway by rabGTPases. Molecular Membrane Biology, 16, 81–7.
Roberts, M., Barry, S., Woods, A., van der Sluijs, P., & Norman, J. (2001). PDGF-regulated rab4-dependent recycling of alphavbeta3 integrin from early endosomes is necessary for cell adhesion and spreading. Current Biology, 11, 1392–402.
Roberts, M. S., Woods, A. J., Dale, T. C., Van Der Sluijs, P., & Norman, J. C. (2004). Protein kinase B/Akt acts via glycogen synthase kinase 3 to regulate recycling of alpha v beta 3 and alpha 5 beta 1 integrins. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 24, 1505–515.
Reszka, A. A., Hayashi, Y., & Horwitz, A. F. (1992). Identification of amino acid sequences in the integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain implicated in cytoskeletal association. Journal of Cell Biology, 117, 1321–330.
De Deyne, P. G., O’Neill, A., Resneck, W. G., Dmytrenko, G. M., Pumplin, D. W., & Bloch, R. J. (1998). The vitronectin receptor associates with clathrin-coated membrane domains via the cytoplasmic domain of its beta5 subunit. Journal of Cell Science, 111(Pt 18), 2729–740.
Memmo, L. M., & McKeown-Longo, P. (1998). The alphavbeta5 integrin functions as an endocytic receptor for vitronectin. Journal of Cell Science, 111(Pt 4), 425–33.
Pellinen, T., & Ivaska, J. (2006). Integrin traffic. Journal of Cell Science, 119, 3723–731.
Berryman, S., Clark, S., Monaghan, P., & Jackson, T. (2005). Early events in integrin alphavbeta6-mediated cell entry of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Journal of Virology, 79, 8519–534.
Altankov, G., & Grinnell, F. (1995). Fibronectin receptor internalization and AP-2 complex reorganization in potassium-depleted fibroblasts. Experimental Cell Research, 216, 299–09.
Ng, T., Shima, D., Squire, A., Bastiaens, P. I., Gschmeissner, S., Humphries, M. J., et al. (1999). PKCalpha regulates beta1 integrin-dependent cell motility through association and control of integrin traffic. EMBO Journal, 18, 3909–923.
Upla, P., Marjomaki, V., Kankaanpaa, P., Ivaska, J., Hyypia, T., Van Der Goot, F. G., et al. (2004). Clustering induces a lateral redistribution of alpha 2 beta 1 integrin from membrane rafts to caveolae and subsequent protein kinase C-dependent internalization. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 15, 625–36.
Wary, K. K., Mainiero, F., Isakoff, S. J., Marcantonio, E. E., & Giancotti, F. G. (1996). The daptor protein Shc couples a class of integrins to the control of cell cycle progression. Cell, 87, 733–43.
Wary, K. K., Mariotti, A., Zurzolo, C., & Giancotti, F. G. (1998). A requirement for caveolin-1 and associated kinase Fyn in integrin signaling and anchorage-dependent cell growth. Cell, 94, 625–34.
Panicker, A. K., Buhusi, M., Erickson, A., & Maness, P. F. (2006). Endocytosis of beta1 integrins is an early event in migration promoted by the cell adhesion molecule L1. Experimental Cell Research, 312, 299–07.
Laukaitis, C. M., Webb, D. J., Donais, K., & Horwitz, A. F. (2001). Differential dynamics of alpha 5 integrin, paxillin, and alpha-actinin during formation and disassembly of adhesions in migrating cells. Journal of Cell Biology, 153, 1427–440.
Liu, G., Swihart, M. T., & Neelamegham, S. (2005). Sensitivity, principal component and flux analysis applied to signal transduction: the case of epidermal growth factor mediated signaling. Bioinformatics, 21, 1194–202.
del Pozo, M. A., Balasubramanian, N., Alderson, N. B., Kiosses, W. B., Grande-Garcia, A., Anderson, R. G., et al. (2005). Phospho-caveolin-1 mediates integrin-regulated membrane domain internalization. Nature Cell Biology, 7, 901–08.
Bretscher, M. S. (1996). Moving membrane up to the front of migrating cells. Cell, 85, 465–67.
Rappoport, J. Z., & Simon, S. M. (2003). Real-time analysis of clathrin-mediated endocytosis during cell migration. Journal of Cell Science, 116, 847–55.
Jones, M. C., Caswell, P. T., & Norman, J. C. (2006). Endocytic recycling pathways: emerging regulators of cell migration. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 18, 549–57.
Fabbri, M., Di Meglio, S., Gagliani, M. C., Consonni, E., Molteni, R., Bender, J. R., et al. (2005). Dynamic partitioning into lipid rafts controls the endo-exocytic cycle of the alphaL/beta2 integrin, LFA-1, during leukocyte chemotaxis. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 16, 5793–803.
Ivaska, J., Whelan, R. D., Watson, R., & Parker, P. J. (2002). PKC epsilon controls the traffic of beta1 integrins in motile cells. EMBO Journal, 21, 3608–619.
Woods, A. J., White, D. P., Caswell, P. T., & Norman, J. C. (2004). PKD1/PKCmu promotes alphavbeta3 integrin recycling and delivery to nascent focal adhesions. EMBO Journal, 23, 2531–543.
Ivaska, J., Vuoriluoto, K., Huovinen, T., Izawa, I., Inagaki, M., & Parker, P. J. (2005). PKCepsilon-mediated phosphorylation of vimentin controls integrin recycling and motility. EMBO Journal, 24, 3834–845.
Naslavsky, N., & Caplan, S. (2005). C-terminal EH-domain-containing proteins: consensus for a role in endocytic trafficking, EH. Journal of Cell Science, 118, 4093–101.
Chuang, Y. Y., Tran, N. L., Rusk, N., Nakada, M., Berens, M. E., & Symons, M. (2004). Role of synaptojanin 2 in glioma cell migration and invasion. Cancer Research, 64, 8271–275.
Silletti, S., Kessler, T., Goldberg, J., Boger, D. L., & Cheresh, D. A. (2001). Disruption of matrix metalloproteinase 2 binding to integrin alpha vbeta 3 by an organic molecule inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 119–24.
Echarri, A., & Del Pozo, M. A. (2006). Caveolae internalization regulates integrin-dependent signaling pathways. Cell Cycle, 5, 2179–182.
Schwartz, M. A. (1997). Integrins, oncogenes, and anchorage independence. Journal of Cell Biology, 139, 575–78.
Koleske, A. J., Baltimore, D., & Lisanti, M. P. (1995). Reduction of caveolin and caveolae in oncogenically transformed cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 92, 1381–385.
Lee, H., Park, D. S., Razani, B., Russell, R. G., Pestell, R. G., & Lisanti, M. P. (2002). Caveolin-1 mutations (P132L and null) and the pathogenesis of breast cancer: caveolin-1 (P132L) behaves in a dominant-negative manner and caveolin-1 (. -. /. -. ) null mice show mammary epithelial cell hyperplasia. American Journal of Pathology, 161, 1357–369.
Williams, T. M., Medina, F., Badano, I., Hazan, R. B., Hutchinson, J., Muller, W. J., et al. (2004). Caveolin-1 gene disruption promotes mammary tumorigenesis and dramatically enhances lung metastasis in vivo. Role of Cav-1 in cell invasiveness and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2/9) secretion. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 51630–1646.
Engelman, J. A., Wykoff, C. C., Yasuhara, S., Song, K. S., Okamoto, T., & Lisanti, M. P. (1997). Recombinant expression of caveolin-1 in oncogenically transformed cells abrogates anchorage-independent growth. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 16374–6381.
Sahai, E., & Marshall, C. J. (2002). RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer, 2, 133–42.
Ning, Y., Zeineldin, R., Liu, Y., Rosenberg, M., Stack, M. S., & Hudson, L. G. (2005). Down-regulation of integrin alpha2 surface expression by mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII) induces aberrant cell spreading and focal adhesion formation. Cancer Research, 65, 9280–286.
Ning, Y., Buranda, T., & Hudson, L. G. (2007). Activated EGF receptor induces integrin alpha 2 internalization via caveolae/raft-dependent endocytic pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry (in press).
Ramsay, A. G., Keppler, M. D., Jazayeri, M., Thomas, G. J., Parsons, M., Violette, S. M., et al. (2007). HSI-associated protein X-1 regulates carcinoma cell migration and invasion via clathrin-mediated endocytosis of integrin alpha v beta 6. Cancer Research, 67, 5275–284.
Bates, R. C., Bellovin, D. I., Brown, C., Maynard, E., Wu, B., Kawakatsu, H., et al. (2005). Transcriptional activation of integrin beta6 during the epithelial-mesenchymal transition defines a novel prognostic indicator of aggressive colon carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115, 339–47.
Nystrom, M. L., Thomas, G. J., Stone, M., Mackenzie, I. C., Hart, I. R., & Marshall, J. F. (2005). Development of a quantitative method to analyse tumour cell invasion in organotypic culture. Journal of Pathology, 205, 468–75.
Jekely, G., Sung, H. H., Luque, C. M., & Rorth, P. (2005). Regulators of endocytosis maintain localized receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in guided migration. Developmental Cell, 9, 197–07.
Orth, J. D., & McNiven, M. A. (2006). Get off my back! Rapid receptor internalization through circular dorsal ruffles. Cancer Research, 66, 11094–1096.
Orth, J. D., Krueger, E. W., Weller, S. G., & McNiven, M. A. (2006). A novel endocytic mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor sequestration and internalization. Cancer Research, 66, 3603–610.
Yamaguchi, H., & Condeelis, J. (2006). Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta, 1773(5), 642–52.
Yoon, S. O., Shin, S., & Mercurio, A. M. (2005). Hypoxia stimulates carcinoma invasion by stabilizing microtubules and promoting the Rab11 trafficking of the alpha6beta4 integrin. Cancer Research, 65, 2761–769.
Cheng, K. W., Lahad, J. P., Kuo, W. L., Lapuk, A., Yamada, K., Auersperg, N., et al. (2004). The RAB25 small GTPase determines aggressiveness of ovarian and breast cancers. Nature Medicine, 10, 1251–256.
Miaczynska, M., Pelkmans, L., & Zerial, M. (2004). Not just a sink: endosomes in control of signal transduction. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 16, 400–06.
Kermorgant, S., & Parker, P. J. (2005). c-Met signalling: spatio-temporal decisions. Cell Cycle, 4, 352–55.
Kermorgant, S., Zicha, D., & Parker, P. J. (2004). PKC controls HGF-dependent c-Met traffic, signalling and cell migration. EMBO Journal, 23, 3721–734.
Tucker, G. C. (2006). Integrins: Molecular targets in cancer therapy. Current Oncology Reports, 80, 96–03.
Dicara, D., Rapisarda, C., Sutclifffe, J. L., Violette, S. M., Weinreb, P. H., Hart, I. R., et al. (2007). Structure-function analysis of RGD-helix motifs in alpha vbeta 6 integrin ligands. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 282, 9657–665.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramsay, A.G., Marshall, J.F. & Hart, I.R. Integrin trafficking and its role in cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26, 567–578 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9078-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9078-7