Abstract
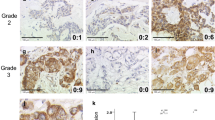
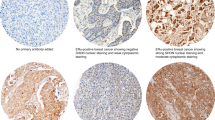
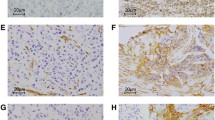
Cytoplasmic HuR is associated with reduced survival in invasive breast cancer. We designed this study to determine the predictive and prognostic value of HuR expression in women with breast cancer who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgical resection. We immunohistochemically analyzed cytoplasmic HuR expression in tumor biopsy cores obtained from 139 patients with invasive breast cancers who received paclitaxel and anthracycline-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy. We evaluated the relationship of HuR expression level with pathologic complete response (pCR), local recurrence-free survival (LRFS), distant recurrence-free survival (DRFS), recurrence-free survival (RFS), and overall survival (OS). Cytoplasmic HuR expression was present in 60 cases (43.2 %). The expression of cytoplasmic HuR was significantly associated with high nuclear grade (P < 0.0001) and ER (P = 0.001) and PR (P = 0.005) status. Multivariate regression analysis further revealed that high nuclear grade (P = 0.023), negative ER status (P = 0.043), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression (P < 0.0001), but not cytoplasmic HuR expression, were significant independent predictors of pCR. Interestingly, multivariate Cox analysis revealed that cytoplasmic HuR expression was a strong independent predictor of reduced LRFS (P = 0.014), DRFS (P = 0.001), RFS (P < 0.0001), and OS (P = 0.019) irrespective of pCR. Furthermore, the patient group with tumors showing both expression of cytoplasmic HuR and non-pCR had a worse prognosis in LRFS (P = 0.048), DRFS (P < 0.0001), RFS (P < 0.0001), and OS (P = 0.001) than did other patient groups; patients with tumors showing negative cytoplasmic expression of HuR and pCR had the best prognosis in all RFS and OS. Cytoplasmic expression of HuR is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Combination analyses of HuR expression and pCR, compared with pCR alone, can better predict clinical outcome in patients with primary breast cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, McGuire SE, Buchholz TA, Tucker SL, Kuerer HM, Rouzier R, Kau SW, Huang EH, Morandi P, Ocana A, Cristofanilli M, Valero V, Buzdar AU, Hortobagyi GN (2005) Factors predictive of distant metastases in patients with breast cancer who have a pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 23:7098–7104
Rastogi P, Anderson SJ, Bear HD, Geyer CE, Kahlenberg MS, Robidoux A, Margolese RG, Hoehn JL, Vogel VG, Dakhil SR, Tamkus D, King KM, Pajon ER, Wright MJ, Robert J, Paik S, Mamounas EP, Wolmark N (2008) Preoperative chemotherapy: updates of national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project protocols B-18 and B-27. J Clin Oncol 26:778–785
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU, Costa SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, Gerber B, Eiermann W, Hilfrich J, Huober J, Jackisch C, Kaufmann M, Konecny GE, Denkert C, Nekljudova V, Mehta K, Loibl S (2012) Definition and impact of pathologic complete response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol 30:1796–1804
Charfare H, Limongelli S, Purushotham AD (2005) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Br J Surg 92:14–23
Weigel MT, Dowsett M (2010) Current and emerging biomarkers in breast cancer: prognosis and prediction. Endocr Relat Cancer 17:R245–R262
Denkert C, Sinn BV, Issa Y, Maria Muller B, Maisch A, Untch M, von Minckwitz G, Loibl S (2011) Prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: new biomarker approaches and concepts. Breast Care (Basel) 6:265–272
Naoi Y, Kishi K, Tanei T, Tsunashima R, Tominaga N, Baba Y, Kim SJ, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Noguchi S (2011) Prediction of pathologic complete response to sequential paclitaxel and 5-fluorouracil/epirubicin/cyclophosphamide therapy using a 70-gene classifier for breast cancers. Cancer 117:3682–3690
Lin Y, Lin S, Watson M, Trinkaus KM, Kuo S, Naughton MJ, Weilbaecher K, Fleming TP, Aft RL (2010) A gene expression signature that predicts the therapeutic response of the basal-like breast cancer to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123:691–699
Hess KR, Anderson K, Symmans WF, Valero V, Ibrahim N, Mejia JA, Booser D, Theriault RL, Buzdar AU, Dempsey PJ, Rouzier R, Sneige N, Ross JS, Vidaurre T, Gomez HL, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2006) Pharmacogenomic predictor of sensitivity to preoperative chemotherapy with paclitaxel and fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:4236–4244
Ignatiadis M, Singhal SK, Desmedt C, Haibe-Kains B, Criscitiello C, Andre F, Loi S, Piccart M, Michiels S, Sotiriou C (2012) Gene modules and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer subtypes: a pooled analysis. J Clin Oncol 30:1996–2004
Gluck S, de Snoo F, Peeters J, Stork-Sloots L, Somlo G (2013) Molecular subty** of early-stage breast cancer identifies a group of patients who do not benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 139:759–767
Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, Ibrahim N, Cristofanilli M, Anderson K, Hess KR, Stec J, Ayers M, Wagner P, Morandi P, Fan C, Rabiul I, Ross JS, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2005) Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 11:5678–5685
Wang J, Guo Y, Chu H, Guan Y, Bi J, Wang B (2013) Multiple functions of the RNA-binding protein HuR in cancer progression, treatment responses and prognosis. Int J Mol Sci 14:10015–10041
Dixon DA, Tolley ND, King PH, Nabors LB, McIntyre TM, Zimmerman GA, Prescott SM (2001) Altered expression of the mRNA stability factor HuR promotes cyclooxygenase-2 expression in colon cancer cells. J Clin Invest 108:1657–1665
Sureban SM, Murmu N, Rodriguez P, May R, Maheshwari R, Dieckgraefe BK, Houchen CW, Anant S (2007) Functional antagonism between RNA binding proteins HuR and CUGBP2 determines the fate of COX-2 mRNA translation. Gastroenterology 132:1055–1065
Young LE, Moore AE, Sokol L, Meisner-Kober N, Dixon DA (2012) The mRNA stability factor HuR inhibits microRNA-16 targeting of COX-2. Mol Cancer Res 10:167–180
Yuan Z, Sanders AJ, Ye L, Wang Y, Jiang WG (2011) Knockdown of human antigen R reduces the growth and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro and affects expression of cyclin D1 and MMP-9. Oncol Rep 26:237–245
Miyata Y, Watanabe S, Sagara Y, Mitsunari K, Matsuo T, Ohba K, Sakai H (2013) High expression of HuR in cytoplasm, but not nuclei, is associated with malignant aggressiveness and prognosis in bladder cancer. PLoS ONE 8:e59095
Wang J, Zhao W, Guo Y, Zhang B, **e Q, **ang D, Gao J, Wang B, Chen Z (2009) The expression of RNA-binding protein HuR in non-small cell lung cancer correlates with vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression and lymph node metastasis. Oncology 76:420–429
Wang J, Wang B, Bi J, Zhang C (2011) Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and poor outcome in lung cancer. Med Oncol 28(Suppl 1):S577–S585
Denkert C, Koch I, von Keyserlingk N, Noske A, Niesporek S, Dietel M, Weichert W (2006) Expression of the ELAV-like protein HuR in human colon cancer: association with tumor stage and cyclooxygenase-2. Mod Pathol 19:1261–1269
Zhang C, Xue G, Bi J, Geng M, Chu H, Guan Y, Wang J, Wang B (2013) Cytoplasmic expression of the ELAV-like protein HuR as a potential prognostic marker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1008-4
Erkinheimo TL, Lassus H, Sivula A, Sengupta S, Furneaux H, Hla T, Haglund C, Butzow R, Ristimaki A (2003) Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with poor outcome and with cyclooxygenase 2 expression in serous ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res 63:7591–7594
Denkert C, Weichert W, Winzer KJ, Muller BM, Noske A, Niesporek S, Kristiansen G, Guski H, Dietel M, Hauptmann S (2004) Expression of the ELAV-like protein HuR is associated with higher tumor grade and increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:5580–5586
Heinonen M, Bono P, Narko K, Chang SH, Lundin J, Joensuu H, Furneaux H, Hla T, Haglund C, Ristimaki A (2005) Cytoplasmic HuR expression is a prognostic factor in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 65:2157–2161
Zhu Z, Wang B, Bi J, Zhang C, Guo Y, Chu H, Liang X, Zhong C, Wang J (2013) Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with P-gp, HER-2 positivity, and poor outcome in breast cancer. Tumour Biol 34:2299–2308
Costantino CL, Witkiewicz AK, Kuwano Y, Cozzitorto JA, Kennedy EP, Dasgupta A, Keen JC, Yeo CJ, Gorospe M, Brody JR (2009) The role of HuR in gemcitabine efficacy in pancreatic cancer: HuR up-regulates the expression of the gemcitabine metabolizing enzyme deoxycytidine kinase. Cancer Res 69:4567–4572
Richards NG, Rittenhouse DW, Freydin B, Cozzitorto JA, Grenda D, Rui H, Gonye G, Kennedy EP, Yeo CJ, Brody JR, Witkiewicz AK (2010) HuR status is a powerful marker for prognosis and response to gemcitabine-based chemotherapy for resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. Ann Surg 252:499–505
Raspaglio G, De Maria I, Filippetti F, Martinelli E, Zannoni GF, Prislei S, Ferrandina G, Shahabi S, Scambia G, Ferlini C (2010) HuR regulates beta-tubulin isotype expression in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 70:5891–5900
Prislei S, Martinelli E, Mariani M, Raspaglio G, Sieber S, Ferrandina G, Shahabi S, Scambia G, Ferlini C (2013) MiR-200c and HuR in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 13:72
Latorre E, Tebaldi T, Viero G, Sparta AM, Quattrone A, Provenzani A (2012) Downregulation of HuR as a new mechanism of doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer 11:13
Hostetter C, Licata LA, Witkiewicz A, Costantino CL, Yeo CJ, Brody JR, Keen JC (2008) Cytoplasmic accumulation of the RNA binding protein HuR is central to tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1496–1506
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, Gion M, Clark GM (2006) Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res Treat 100:229–235
Williams TK, Costantino CL, Bildzukewicz NA, Richards NG, Rittenhouse DW, Einstein L, Cozzitorto JA, Keen JC, Dasgupta A, Gorospe M, Gonye GE, Yeo CJ, Witkiewicz AK, Brody JR (2010) pp32 (ANP32A) expression inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth and induces gemcitabine resistance by disrupting HuR binding to mRNAs. PLoS ONE 5:e15455
Ortega AD, Sala S, Espinosa E, Gonzalez-Baron M, Cuezva JM (2008) HuR and the bioenergetic signature of breast cancer: a low tumor expression of the RNA-binding protein predicts a higher risk of disease recurrence. Carcinogenesis 29:2053–2061
Yuan Z, Sanders AJ, Ye L, Wang Y, Jiang WG (2011) Prognostic value of the human antigen R (HuR) in human breast cancer: high level predicts a favourable prognosis. Anticancer Res 31:303–310
Al-Ahmadi W, Al-Ghamdi M, Al-Souhibani N, Khabar KS (2013) miR-29a inhibition normalizes HuR over-expression and aberrant AU-rich mRNA stability in invasive cancer. J Pathol 230:28–38
Guo X, Wu Y, Hartley RS (2009) MicroRNA-125a represses cell growth by targeting HuR in breast cancer. RNA Biol 6:575–583
Gubin MM, Calaluce R, Davis JW, Magee JD, Strouse CS, Shaw DP, Ma L, Brown A, Hoffman T, Rold TL, Atasoy U (2010) Overexpression of the RNA binding protein HuR impairs tumor growth in triple negative breast cancer associated with deficient angiogenesis. Cell Cycle 9:3337–3346
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Tamara K. Locke from the Department of Scientific Publications, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, for editorial assistance. This study was supported in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30901788 and 81272619) and the Shandong Provincial Nature Science Foundation (Nos. ZR2010HQ038 and ZR2010HM059).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial disclosures or conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, D., Wang, B. et al. Predictive and prognostic significance of cytoplasmic expression of ELAV-like protein HuR in invasive breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 141, 213–224 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2679-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2679-7