Abstract
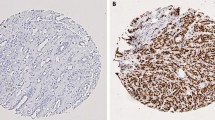
Abl interactor 1 (Abi1) is an adaptor protein involved in cell migration. Previous in vitro work suggested that Abi1 is a regulator of breast cancer proliferation, migration, and invasion. In the present study, we explore the expression of Abi1 and its downstream effector phospho-Akt (p-Akt) in a series of breast cancers and correlate their expression with clinicopathological and survival data. Using tissue microarrays, 988 patients with invasive breast carcinoma were evaluated by immunohistochemistry. Statistical correlation was performed to determine associations between Abi1 and p-Akt expression and standard breast clinicopathological factors. The prognostic value of Abi1 and p-Akt for disease-free (DFS) and overall survival (OS) was also evaluated. Abi1 expression was demonstrated in 33.7% (314/933) of invasive carcinomas, while p-Akt was expressed in 46.7% (441/944). There was a significant association between Abi1 and p-Akt expression (P = 0.001). Abi1 expression showed significant positive correlation with older age at diagnosis and the Ki67 index. Most importantly, it was demonstrated to be an independent predictor of both DFS and OS (HR = 1.6 and 1.5, P < 0.001, respectively). There was no association between p-Akt expression and survival. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study evaluating Abi1 expression in a large group of breast cancers. Our analysis demonstrated that tumors expressing high levels of Abi1 are significantly associated with early recurrence and worse survival on multivariate analysis. This suggests that Abi1 expression has potential as a molecular marker to refine outcome prediction in breast cancer patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Machesky LM (2008) Lamellipodia and filopodia in metastasis and invasion. FEBS Lett 582:2102–2111
Stradal TE, Scita G (2006) Protein complexes regulating Arp2/3-mediated actin assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:4–10
Innocenti M, Zucconi A, Disanza A et al (2004) Abi1 is essential for the formation and activation of a WAVE2 signalling complex. Nat Cell Biol 6:319–327
Stradal TE, Rottner K, Disanza A et al (2004) Regulation of actin dynamics by WASP and WAVE family proteins. Trends Cell Biol 14:303–311
Innocenti M, Frittoli E, Ponzanelli I et al (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase activates Rac by entering in a complex with Eps8, Abi1, and Sos-1. J Cell Biol 160:17–23
Eto K, Nishikii H, Ogaeri T et al (2007) The WAVE2/Abi1 complex differentially regulates megakaryocyte development and spreading: implications for platelet biogenesis and spreading machinery. Blood 110:3637–3647
Kheir WA, Gevrey JC, Yamaguchi H et al (2005) A WAVE2-Abi1 complex mediates CSF-1-induced F-actin-rich membrane protrusions and migration in macrophages. J Cell Sci 118:5369–5379
Leng Y, Zhang J, Badour K et al (2005) Abelson-interactor-1 promotes WAVE2 membrane translocation and Abelson-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation required for WAVE2 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1098–1103
Shi Y, Alin K, Goff SP (1995) Abl-interactor-1, a novel SH3 protein binding to the carboxy-terminal portion of the Abl protein, suppresses v-abl transforming activity. Genes Dev 9:2583–2597
Biesova Z, Piccoli C, Wong WT (1997) Isolation and characterization of e3B1, an eps8 binding protein that regulates cell growth. Oncogene 14:233–241
Kakiuchi S, Daigo Y, Tsunoda T et al (2003) Genome-wide analysis of organ-preferential metastasis of human small cell lung cancer in mice. Mol Cancer Res 1:485–499
Duan Z, Lamendola DE, Duan Y et al (2005) Description of paclitaxel resistance-associated genes in ovarian and breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 55:277–285
Dai Z, Pendergast AM (1995) Abi-2, a novel SH3-containing protein interacts with the c-Abl tyrosine kinase and modulates c-Abl transforming activity. Genes Dev 9:2569–2582
Funato Y, Terabayashi T, Suenaga N et al (2004) IRSp53/Eps8 complex is important for positive regulation of Rac and cancer cell motility/invasiveness. Cancer Res 64:5237–5244
Macoska JA, Xu J, Ziemnicka D et al (2001) Loss of expression of human spectrin src homology domain binding protein 1 is associated with 10p loss in human prostatic adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia 3:99–104
Cui M, Yu W, Dong J et al (2009) Downregulation of ABI1 expression affects the progression and prognosis of human gastric carcinoma. Med Oncol 27:632–639
Xu J, Ziemnicka D, Merz GS et al (2000) Human spectrin Src homology 3 domain binding protein 1 regulates macropinocytosis in NIH 3T3 cells. J Cell Sci 113 Pt 21:3805–3814
Wang C, Navab R, Iakovlev V et al (2007) Abelson interactor protein-1 positively regulates breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Mol Cancer Res 5:1031–1039
Sun X, Li C, Zhuang C et al (2009) Abl interactor 1 regulates Src-Id1-matrix metalloproteinase 9 axis and is required for invadopodia formation, extracellular matrix degradation and tumor growth of human breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 30:2109–2116
Stambolic V, Woodgett JR (2006) Functional distinctions of protein kinase B/Akt isoforms defined by their influence on cell migration. Trends Cell Biol 16:461–466
Katso RM, Pardo OE, Palamidessi A et al (2006) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase C2beta regulates cytoskeletal organization and cell migration via Rac-dependent mechanisms. Mol Biol Cell 17:3729–3744
Nishita M, Wang Y, Tomizawa C et al (2004) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated activation of cofilin phosphatase Slingshot and its role for insulin-induced membrane protrusion. J Biol Chem 279:7193–7198
Stambolic V, Suzuki A, de la Pompa JL et al (1998) Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell 95:29–39
Brader S, Eccles SA (2004) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling pathways in tumor progression, invasion and angiogenesis. Tumori 90:2–8
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D et al (2009) Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 101:736–750
Hugh J, Hanson J, Cheang MC et al (2009) Breast cancer subtypes and response to docetaxel in node-positive breast cancer: use of an immunohistochemical definition in the BCIRG 001 trial. J Clin Oncol 27:1168–1176
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN et al (2007) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:118–145
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M et al (2010) American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:2784–2795
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van’t Veer LJ et al (2002) A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1999–2009
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W et al (2005) Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK). J Natl Cancer Inst 97:1180–1184
Ryu JR, Echarri A, Li R et al (2009) Regulation of cell-cell adhesion by Abi/Diaphanous complexes. Mol Cell Biol 29:1735–1748
Liebau S, Vaida B, Proepper C et al (2007) Formation of cellular projections in neural progenitor cells depends on SK3 channel activity. J Neurochem 101:1338–1350
Yamazaki D, Oikawa T, Takenawa T (2007) Rac-WAVE-mediated actin reorganization is required for organization and maintenance of cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Sci 120:86–100
Proepper C, Johannsen S, Liebau S et al (2007) Abelson interacting protein 1 (Abi-1) is essential for dendrite morphogenesis and synapse formation. EMBO J 26:1397–1409
Wu Y, Mohamed H, Chillar R et al (2008) Clinical significance of Akt and HER2/neu overexpression in African-American and Latina women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 10:R3
Tokunaga E, Kimura Y, Oki E et al (2006) Akt is frequently activated in HER2/neu-positive breast cancers and associated with poor prognosis among hormone-treated patients. Int J Cancer 118:284–289
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10869–10874
van ‘t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ et al (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415:530–536
Chang HY, Sneddon JB, Alizadeh AA et al (2004) Gene expression signature of fibroblast serum response predicts human cancer progression: similarities between tumors and wounds. PLoS Biol 2:E7. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0020007
Kelley LC, Shahab S, Weed SA (2008) Actin cytoskeletal mediators of motility and invasion amplified and overexpressed in head and neck cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 25:289–304
Rothschild BL, Shim AH, Ammer AG et al (2006) Cortactin overexpression regulates actin-related protein 2/3 complex activity, motility, and invasion in carcinomas with chromosome 11q13 amplification. Cancer Res 66:8017–8025
Yu W, Sun X, Clough N et al (2008) Abi1 gene silencing by short hairpin RNA impairs Bcr-Abl-induced cell adhesion and migration in vitro and leukemogenesis in vivo. Carcinogenesis 29:1717–1724
Liu SY, Wu F, Tao YM et al (2009) Increased expression of Abi1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 47:1732–1735
Silva JM, Ezhkova E, Silva J et al (2009) Cyfip1 is a putative invasion suppressor in epithelial cancers. Cell 137:1047–1061
Dai Z, Quackenbush RC, Courtney KD et al (1998) Oncogenic Abl and Src tyrosine kinases elicit the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of target proteins through a Ras-independent pathway. Genes Dev 12:1415–1424
Vestey SB, Sen C, Calder CJ et al (2005) Activated Akt expression in breast cancer: correlation with p53, Hdm2 and patient outcome. Eur J Cancer 41:1017–1025
Bose S, Chandran S, Mirocha JM et al (2006) The Akt pathway in human breast cancer: a tissue-array-based analysis. Mod Pathol 19:238–245
Perez-Tenorio G, Stal O, Southeast Sweden Breast Cancer Group (2002) Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients. Br J Cancer 86:540–545
Galea MH, Blamey RW, Elston CE et al (1992) The Nottingham Prognostic Index in primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 22:207–219
Eifel P, Axelson JA, Costa J et al (2001) National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: adjuvant therapy for breast cancer, November 1–3, 2000. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:979–989
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the Gattuso Chair in Breast Surgical Oncology (DRM). DTT and JCM were supported by the STIHR in Molecular Oncologic Pathology Fellowship at Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CHIR reference number STP-53912) and the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research grant (OICR TSAO-OICR-RF-007). The authors would like to thank the PRP at the University Health Network (Toronto, ON) for technical assistance in performing the immunostaining.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
First two authors contributed equally to this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Tran-Thanh, D., Moreno, J.C. et al. Expression of Abl interactor 1 and its prognostic significance in breast cancer: a tissue-array-based investigation. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129, 373–386 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-1241-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-010-1241-0