Abstract
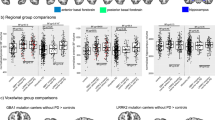
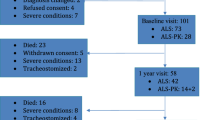
Cerebral atrophy has been detected in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) both with and without dementia, however differentiation based on genetic status has thus far not yielded robust findings. We assessed cortical thickness and subcortical volumes in a cohort of PD patients and healthy controls carriers of the G2019S mutation in the LRRK2 gene and the common GBA mutations, in an attempt to determine whether genetic status influences structural indexes. Cortical thickness and subcortical volumes were computed and compared between six groups of participants; idiopathic PD, GBA-PD, LRRK2-PD, non-manifesting non-carriers (NMNC), GBA-non-manifesting carriers (NMC) and LRRK2-NMC utilizing the FreeSurfer software program. All participants were cognitively intact based on a computerized cognitive assessment battery. Fifty-seven idiopathic PD patients, 9 LRRK2-PD, 12 GBA-PD, 49 NMNC, 41 LRRK2-NMC and 14 GBA-NMC participated in this study. Lower volumes among patients with PD compared to unaffected participants were detected in bilateral hippocampus, nucleus accumbens, caudate, thalamus, putamen and amygdala and the right pallidum (p = 0.016). PD patients demonstrated lower cortical thickness indexes in a majority of regions assessed compared with non-manifesting participants. No differences in cortical thickness and subcortical volumes were detected within each of the groups of participants based on genetic status. Mutations in the GBA and LRRK2 genes are not important determinants of cortical thickness and subcortical volumes in both patients with PD and non-manifesting participants. PD is associated with a general reduction in cortical thickness and sub-cortical atrophy even in cognitively intact patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
As this is an ongoing study with "at risk" population for future development of PD, data will not be accessible to other researchers at this time.
References
Alcalay RN et al (2013) Parkinson disease phenotype in Ashkenazi jews with and without LRRK2 G2019S mutations. Mov Disord 28:1966–1971
Apostolova LG et al (2010) Hippocampal, caudate, and ventricular changes in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. Mov Disord 25:687–695. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22799
Berg D et al (2015) MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 30:1600–1611. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26431
Beutler E, Nguyen NJ, Henneberger MW, Smolec JM, McPherson RA, West C, Gelbart T (1993) Gaucher disease: gene frequencies in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Am J Hum Genet 52:85–88
Brockmann K et al (2011) Clinical and brain imaging characteristics in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2-associated PD and asymptomatic mutation carriers. Mov Disord 26:2335–2342
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis I. Segmentation surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 9:179–194. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.1998.0395
Desikan RS et al (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31:968–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021
Destrieux C, Fischl B, Dale A, Halgren E (2010) Automatic parcellation of human cortical gyri and sulci using standard anatomical nomenclature. Neuroimage 53:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.010
Gan-Or Z et al (2008) Genotype-phenotype correlations between GBA mutations and Parkinson disease risk. and onset. Neurology 70:2277–2283
Gan-Or Z, Bar-Shira A, Mirelman A, Gurevich T, Kedmi M, Giladi N, Orr-Urtreger A (2009) LRRK2 and GBA mutations differentially affect the initial presentation of Parkinson disease. Neurogenetics 11(1):121–125
Goldman JG, Holden S, Ouyang B, Bernard B, Goetz CG, Stebbins GT (2015) Diagnosing PD-MCI by MDS task force criteria: how many and which neuropsychological tests? Mov Disord 30:402–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26084
Helmich RC et al (2015) Reorganization of corticostriatal circuits in healthy G2019S LRRK2 carriers. Neurology 84:399–406
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Ramirez-Ruiz B, Tolosa E, Marti MJ, Valldeoriola F, Bargallo N, Junque C (2008) Hippocampal head atrophy predominance in Parkinson’s disease with hallucinations and with dementia. J Neurol 255:1324–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-0885-8
Koelkebeck K et al (2014) The contribution of cortical thickness and surface area to gray matter asymmetries in the healthy human brain. Hum Brain Mapp 35:6011–6022. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22601
Lee HM, Kwon KY, Kim MJ, Jang JW, Suh SI, Koh SB, Kim JH (2014) Subcortical grey matter changes in untreated, early stage Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20:622–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.03.009
Lyoo CH, Ryu YH, Lee MS (2010) Topographical distribution of cerebral cortical thinning in patients with mild Parkinson’s disease without dementia. Mov Disord 25:496–499. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22975
Mak E, Bergsland N, Dwyer MG, Zivadinov R, Kandiah N (2014) Subcortical atrophy is associated with cognitive impairment in mild Parkinson disease: a combined investigation of volumetric changes, cortical thickness, and vertex-based shape analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:2257–2264. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4055
Menke RA, Szewczyk-Krolikowski K, Jbabdi S, Jenkinson M, Talbot K, Mackay CE, Hu M (2014) Comprehensive morphometry of subcortical grey matter structures in early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp 35:1681–1690. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22282
Mirelman A et al (2013) Fall risk and gait in Parkinson’s disease: the role of the LRRK2 G2019S mutation. Mov Disord 28:1683–1690
Neumann J et al (2009) Glucocerebrosidase mutations in clinical and pathologically proven Parkinson’s disease. Brain 132:1783–1794
Ozelius LJ et al (2006) LRRK2 G2019S as a cause of Parkinson’s disease in Ashkenazi jews. N Engl J Med 354:424–425
Pereira JB, Ibarretxe-Bilbao N, Marti MJ, Compta Y, Junque C, Bargallo N, Tolosa E (2012) Assessment of cortical degeneration in patients with Parkinson’s disease by voxel-based morphometry, cortical folding, and cortical thickness. Hum Brain Mapp 33:2521–2534. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.21378
Thaler A, Ash E, Gan-Or Z, Orr-Urtreger A, Giladi N (2009) The LRRK2 G2019S mutation as the cause of Parkinson’s disease in Ashkenazi jews. J Neural Transm 116:1473–1482
Thaler A et al. (2012) Lower cognitive performance in healthy G2019S LRRK2 mutation carriers. Neurology 79:1027–1032 https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182684646
Thaler A et al (2013) Neural correlates of executive functions in healthy G2019S LRRK2 mutation carriers. Cortex 49:2501–2511
Thaler A et al (2014) A voxel-based morphometry and diffusion tensor imaging analysis of asymptomatic Parkinson’s disease-related G2019S LRRK2 mutation carriers. Mov Disord 29:823–827
Tinaz S, Courtney MG, Stern CE (2011) Focal cortical and subcortical atrophy in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26:436–441. https://doi.org/10.1002/23453
Tomlinson CL, Stowe R, Patel S, Rick C, Gray R, Clarke CE (2010) Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25:2649–2653. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23429
Uribe C et al (2016) Patterns of cortical thinning in nondemented Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov Disord 31:699–708. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26590
Vilas D et al (2016) Nigral and striatal connectivity alterations in asymptomatic LRRK2 mutation carriers: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Mov Disord 31:1820–1828. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.26799
Zarei M et al (2013) Cortical thinning is associated with disease stages and dementia in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84:875–881. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2012-304126
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the MJFF for supporting this work. A special thanks to Dr. Moran Artzi for art assistance with the figure. This work has been made possible by the help of the MJFF.
Funding
Avner Thaler reports receiving funding for consulting from AbbVie pharmaceuticals. Tanya Gurevich reports receiving funding for travel and speaker honoraria from the National Parkinson Foundation, Solvay pharmaceuticals, TEVA, RAFA, Medtronic, Novartis, Medison, Allergan, GlaxoSmithKline, Perrigo and Intecpharma. Avi Orr-Urtreger reports receiving research support from the Israeli Science Foundation Legacy Heritage Fund, the Chief Scientist Department of Health, Israel, the ALS Association USA and the Kahn Foundation Israel. Nir Giladi reports serving on the advisory boards of Teva-Lundbeck, NeuroDerm, Intec Pharma and Chairing the Data monitoring safety committee of Teva LTD. Receiving funding for travel and honoraria from Teva-Lundbeck, UCB and NeuroDerm. Serving on the editorial board of the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease. Being a consultant for LTI, NeuroDerm and Intec Pharma. Receiving grants from the NPF, MJFF, Biogen. Anat Mirelman reports receiving funding from the Israeli Science Foundation, Israeli Ministry of Science and Technology, MJFF. Efrat Kliper, Inbal Maidan, Talia Herman, Keren Rosenberg-Katz, Noa Bregman, Tamara Shiner, and Jeffrey M Hausdorff have no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The paper has not been previously published and is not under review by another journal and no conflict of interest was identified among all authors.
Ethical Approval
The method section contains a statement that the local institute review board has approved this study and that each participant signed an informed consent form.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Irena Rektorova.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thaler, A., Kliper, E., Maidan, I. et al. Cerebral Imaging Markers of GBA and LRRK2 Related Parkinson’s Disease and Their First-Degree Unaffected Relatives. Brain Topogr 31, 1029–1036 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-018-0653-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-018-0653-8