Abstract
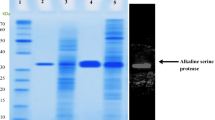
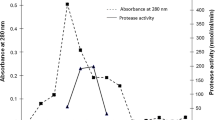
Here we report heterologous expression, enzymatic characterization and structure homology modeling of a subtilisin-like alkaline serine protease (ASP) from Bacillus halodurans C-125. Encoding gene was successfully obtained by PCR and cloned into pMA0911 shuttle vector under the control of strong HpaII promoter and expressed extracellularly. ASP enzyme was successfully expressed in B. subtilis WB800 cell line lacking eight extracellular proteases and produced extracellularly in the culture medium. Km, Vmax and specific activity parameters of the recombinantly produced ASP were identified as 0.2899 mg/ml, 76.12 U/ml and 9500 U/mg, respectively. The purified enzyme revealed remarkable proteolytic activity at highly alkaline conditions with a pH optimum 12.0 and notable thermostability with temperature optimum at 60 °C. Furthermore, substrate-free enzyme revealed remarkable pH stability at pH 12.0 and maintained 93% of its initial activity when incubated at 37 °C for 24 h and 60% of its initial activity upon incubation at 60 °C for 1 h. Theoretically calculated molecular mass of ASP protein was confirmed through SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis (Mw: 28.3 kDa). The secondary and tertiary structures of ASP protein were also identified through homology modeling and further examined in detail. ASP harbors a typical S8/S53 peptidase domain comprising 17 β-sheets and 9 α-helixes within its secondary structure. The structure dynamics analysis of modeled 3D structure further revealed that transient inactivating propeptide chain is the most dynamic region of ASP enzyme with 8.52 Å2 β-Factor value. Additional residue-dependent fluctuation plot analysis also confirmed the elevated structure dynamics patterning of ASP N-terminus which could be the potential prerequisite for the autonomous propeptide removal of alkaline serine peptidases. Yet the functional domain of ASP becomes quite stable after autonomous exclusion of its propeptide. Although the sequence homology between ASP and commercial detergent additive B. lentus protease (PDB ID:1GCI) was moderate (65.4% sequence similarity), their overlaid 3D structures revealed much higher similarity (98.14%) within 0.80 Å RMSD. In conclusions, with remarkable pH stability, notable thermostability and particularly high specific activity at extreme alkaline conditions, the unveiled ASP protein stands out as a novel protease candidate for various industrial sectors such as textile, detergent, leather, feed, waste, pharmaceutical and others.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- dNTP:
-
Deoxynucleoside triphosphate
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- EGTA:
-
Ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid
- Km:
-
Michaelis constant
- Vmax:
-
Maximum velocity
- MCS:
-
Multiple cloning site
- OD:
-
Optical density
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- RMSD:
-
Root-mean-square deviation
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
References
Abbasi Hosseini SM, Eftekhar F, Yakhchali B, Minai D (2011) Cloning and enhanced expression of an extracellular alkaline protease from a soil isolate of Bacillus clausii in Bacillus subtilis. Iran J Biotechnol 9:275–280
Beg QK, Gupta R (2003) Purification and characterization of an oxidation-stable, thiol-dependent serine alkaline protease from Bacillus mojavensis. Enzyme Microb Technol 32(2):294–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(02)00293-4
Belin D, Guzman LM, Bost S, Konakova M, Silva F, Beckwith J (2004) Functional activity of eukaryotic signal sequences in Escherichia coli: the ovalbumin family of serine protease inhibitors. J Mol Biol 335(2):437–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.076
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cheng H, Jiang N (2006) Extremely rapid extraction of DNA from bacteria and yeasts. Biotechnol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-4688-z
Contesini FJ, Melo RRd, Sato HH (2018) An overview of Bacillus proteases: from production to application. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38(3):321–334. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2017.1354354
Cupp-Enyard C (2008) Sigma’s non-specific protease activity assay-casein as a substrate. J Vis Exp. https://doi.org/10.3791/899
Deng AJ, Wu G, Zhang G, Wen T (2011) Molecular and structural characterization of a surfactant-stable high-alkaline protease AprB with a novel structural feature unique to subtilisin family. Biochimie 93(4):783–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2011.01.011
Devi SG, Fathima AA, Sanitha M, Iyappan S, Curtis WR, Ramya M (2016) Expression and characterization of alkaline protease from the metagenomic library of tannery activated sludge. J Biosci Bioeng 122(6):694–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2016.05.012
Dias DR, Vilela DM, Silvestre MPC, Schwan RF (2008) Alkaline protease from Bacillus sp. isolated from coffee bean grown on cheese whey. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(10):2027–2034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9706-6
Doi RH, He XS, McCready P, Bakheit N (1991) Bacillus subtilis: a model system for heterologous gene expression. In: Kelly JW, Baldwin TO (eds) Applications of enzyme biotechnology. Springer, Boston, pp 261–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9235-5_20
Durban M, Silbersack J, Schweder T, Schauer F, Bornscheuer U (2007) High level expression of a recombinant phospholipase C from Bacillus cereus in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Microb Biotechnol 74:634–639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0712-z
Farhadian S, Asoodeh A, Lagzian M (2015) Purification, biochemical characterization and structural modeling of a potential htrA-like serine protease from Bacillus subtilis DR8806. J Mol Catal B Enzym 115:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.02.001
Fu Z, Hamid SB, Razak CN, Basri M, Salleh AB, Rahman RN (2003) Secretory expression in Escherichia coli and single-step purification of a heat-stable alkaline protease. Protein Expr Purif 28(1):63–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1046-5928(02)00637-x
Gomaa EZ (2013) Optimization and characterization of alkaline protease and carboxymethyl-cellulase produced by Bacillus pumillus grown on Ficus nitida wastes. Braz J Microbiol 44:529–537. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822013005000048
Gupta R, Beg Q, Lorenz P (2002) Bacterial alkaline proteases: molecular approaches and industrial applications. Appl Microb Biotechnol 59(1):15–32
Gupta R, Sharma R, Beg QK (2013) Revisiting microbial keratinases: next generation proteases for sustainable biotechnology. Crit Rev Biotechnol 33(2):216–228. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2012.685051
Haddar A, Bougatef A, Agrebi R, Sellami-Kamoun A, Nasri M (2009) A novel surfactant-stable alkaline serine-protease from a newly isolated Bacillus mojavensis A21. Purification and characterization. Process Biochem 44(1):29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.09.003
Jan J, Valle F, Bolivar F, Merino E (2001) Construction of protein overproducer strains in Bacillus subtilis by an integrative approach. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000448
Jaouadi B, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Rhimi, Bejar S (2008) Biochemical and molecular characterization of a detergent-stable serine alkaline protease from Bacillus pumilus CBS with high catalytic efficiency. Biochimie 90(9):1291–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2008.03.004
Johnvesly B, Naik GR (2001) Studies on production of thermostable alkaline protease from thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. JB-99 in a chemically defined medium. Process Biochem 37(2):139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(01)00191-1
Karbalaei-Heidari HR, Ziaee AA, Amoozegar MA, Cheburkin Y, Budisa N (2008) Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a novel zinc-metalloprotease gene from the Salinivibrio sp. strain AF-2004 and its extracellular expression in E. coli. Gene 408(1–2):196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2007.11.002
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Laskowski RA, Macarthur MW, Thornton JM (2012) PROCHECK: validation of protein structure coordinates. Int Tables Crystallogr. https://doi.org/10.1107/97809553602060000882
Li H, Chang Y-Y, Lee JY, Bahar I, Yang L-W (2017) DynOmics: dynamics of structural proteome and beyond. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W374–W380. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx385
Liu B, Zhang J, Li B, Liao X, Du G, Chen J (2013) Expression and characterization of extreme alkaline, oxidation-resistant keratinase from Bacillus licheniformis in recombinant Bacillus subtilis WB600 expression system and its application in wool fiber processing. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(5):825–832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1237-5
Liu Z, Zheng W, Ge C, Cui W, Zhou L, Zhou Z (2019) High-level extracellular production of recombinant nattokinase in Bacillus subtilis WB800 by multiple tandem promoters. BMC Microbiol 19(1):89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-019-1461-3
Nascimento WCAd, Martins MLL (2004) Production and properties of an extracellular protease from thermophilic Bacillus sp. Braz J Microbiol 35:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822004000100015
Nguyen HD, Nguyen QA, Ferreira RC, Ferreira LCS, Tran LT, Schumann W (2005) Construction of plasmid-based expression vectors for Bacillus subtilis exhibiting full structural stability. Plasmid 54(3):241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plasmid.2005.05.001
Nguyen TT, Quyen TD, Le HT (2013) Cloning and enhancing production of a detergent- and organic-solvent-resistant nattokinase from Bacillus subtilis VTCC-DVN-12-01 by using an eight-protease-gene-deficient Bacillus subtilis WB800. Microb Cell Fact 12:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-12-79
Peng Y, Yang X-J, **ao L, Zhang YZ (2004) Cloning and expression of a fibrinolytic enzyme (subtilisin DFE) gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DC-4 in Bacillus subtilis. Res Microbiol 155(3):167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2003.10.004
Phuong ND, Jeong YS, Selvaraj T, Kim SK, Kim YH, Jung KH, Kim J, Yun HD, Wong SL, Lee JK, Kim H (2012) Production of XynX, a large multimodular protein of Thermoanaerobacterium sp., by protease-deficient Bacillus subtilis strains [corrected]. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168(2):375–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9781-x
Ramkumar A, Sivakumar N, Gujarathi AM, Victor R (2018) Production of thermotolerant, detergent stable alkaline protease using the gut waste of Sardinella longiceps as a substrate: optimization and characterization. Sci Rep 8(1):12442. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30155-9
Sadeghi HMM, Rabbani M, Naghitorabi M (2009) Cloning of alkaline protease gene from Bacillus subtilis 168. Res Pharmaceut Sci 4:43–46
Schallmey M, Singh A, Ward OP (2004) Developments in the use of Bacillus species for industrial production. Can J Microbiol 50(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1139/w03-076
Sharma M, Gat Y, Arya S, Kumar V, Panghal A, Kumar A (2019) A review on microbial alkaline protease: an essential tool for various industrial approaches. Ind Biotechnol 15(2):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1089/ind.2018.0032
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J, Thompson JD, Higgins DG (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:539. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.75
Singh J, Batra N, Sobti RC (2001) Serine alkaline protease from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. SSR1. Process Biochem 36(8):781–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(00)00275-2
Tang XM, Shen W, Lakay FM, Shao WL, Wang ZX, Prior BA, Zhuge J (2004) Cloning and over-expression of an alkaline protease from Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol Lett 26(12):975–979. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000030042.91094.38
The UniProt C (2018) UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D506–D515. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1049
Uzuner U, Canakci S, Bektas KI, Sapmaz MT, Belduz AO (2017) Redesigning pH optimum of Geobacillus sp. TF16 endoxylanase through in silico designed DNA swap** strategy. Biochimie 137:174–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2017.03.017
Wu XC, Lee W, Tran L, Wong SL (1991) Engineering a Bacillus subtilis expression-secretion system with a strain deficient in six extracellular proteases. J Bacteriol 173(16):4952–4958. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.16.4952-4958.1991
**ao L, Zhang RH, Peng Y, Zhang YZ (2004) Highly efficient gene expression of a fibrinolytic enzyme (subtilisin DFE) in Bacillus subtilis mediated by the promoter of alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Biotechnol Lett 26(17):1365–1369. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000045634.46909.2b
Yang CH, Wang HY (2007) Cloning, characterization and application of the promoter of alkaline protease gene in Bacillus pumilus. Yi Chuan 29(7):874–880. https://doi.org/10.1360/yc-007-0874
Yang J, Yan R, Roy A, Xu D, Poisson J, Zhang Y (2015) The I-TASSER Suite: protein structure and function prediction. Nat Methods 12(1):7–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3213
Ye R, Kim J-H, Kim B-G, Szarka S, Sihota E, Wong S-L (1999) High-level secretory production of intact, biologically active staphylokinase from Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Bioeng 62(1):87–96
Zhou C, Qin H, Chen X, Zhang Y, Xue Y, Ma Y (2018) A novel alkaline protease from alkaliphilic Idiomarina sp. C9-1 with potential application for eco-friendly enzymatic dehairing in the leather industry. Sci Rep 8:16467. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34416-5
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude and appreciation to Prof. Sabriye Canakci, who provided the related B. subtilis WB800 host strain, B. halodurans C-125 bacterial source and her exceptional guidance throughout this comprehensive study.
Funding
This study was supported by 2214-A Abroad Doctoral Research Fellowship Program of The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (Application Number: 1059B141400371).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tekin, A., Uzuner, U. & Sezen, K. Homology modeling and heterologous expression of highly alkaline subtilisin-like serine protease from Bacillus halodurans C-125. Biotechnol Lett 43, 479–494 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03025-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-020-03025-6