Abstract
Objectives
To achieve an optimized co-culture ratio of Scheffersomyces stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the production of second generation bioethanol under a cell-recycle batch process.
Results
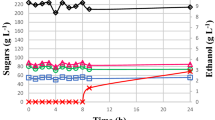
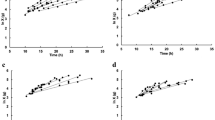
Three Sacc. cerevisiae strains were evaluated in co-culture with Sch. stipitis CBS 5773 at different ratios using synthetic medium containing glucose and xylose. Bioreactor trials indicated that the optimal condition for ethanol production using Sacc. cerevisiae EC1118 and Sch. stipitis co-culture was 1 % of O2 concentration. To increase ethanol production with Sacc. cerevisiae/Sch. stipitis co-culture a cell-recycle batch process was evaluated. Using this process, the maximum ethanol production (9.73 g l−1) and ethanol yield (0.42 g g−1) were achieved exhibiting a tenfold increase in ethanol productivity in comparison with batch process (2.1 g l−1 h−1). In these conditions a stabilization of the cells ratio Sacc. cerevisiae/Sch. stipitis (1:5) at steady state condition was obtained.
Conclusion
Batch cells recycling fermentation is an effective process to use Sch. stipitis/Sacc. cerevisiae co-culture for second generation ethanol production.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbi M, Kuhad RC, Singh A (1996) Bioconversion of pentose sugars to ethanol by free and immobilized cells of Candida shehatae (NCL-3501): fermentation behavior. Process Biochem 31:555–560
Agbogbo FK, Coward-Kelly G (2008) Cellulosic ethanol production using the naturally occurring xylose-fermenting yeast, Pichia stipitis. Biotechnol Lett 30:1515–1524
Bellido C, Bolado S, Coca M, Lucas S, Gonzalez-Benito G, Garcia-Cubero MT (2011) Effect of inhibitors formed during wheat straw pretreatment on ethanol fermentation by Pichia stipitis. Bioresour Technol 102:10868–10874
De Bari I, De Canio P, Cuna D, Liuzzi F, Capece A, Romano P (2013) Bioethanol production from mixed sugars by Scheffersomyces stipitis free and immobilized cells, and co-cultures with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. N Biotechnol 30:591–597
Faraco V, Hadar Y (2011) The potential of lignocellulosic ethanol production in the Mediterranean Basin. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15:252–266
Fu N, Peiris P, Markham J, Bavor J (2009) A novel co-culture process with Zymomonas mobilis and Pichia stipitis for efficient ethanol production on glucose/xylose mixtures. Enzyme Microb Technol 45:210–217
Gírio FM, Fonseca C, Carvalheiro F, Duarte LC, Marques S, Bogel-Lukasik R (2010) Hemicelluloses for fuel ethanol: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4775–4800
Grootjen D, Meijlink L, van der Lans R, Luyben K (1990) Cofermentation of glucose and xylose with immobilized Pichia stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 12:860–864
Gutiérrez-Rivera B, Waliszewski-Kubiak K, Carvajal-Zarrabal O, Aguilar-Uscanga MG (2011) Conversion efficiency of glucose/xylose mixtures for ethanol production using Saccharomyces cerevisiae ITV01 and Pichia stipitis NRRL Y-7124. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 87:263–270
Gutiérrez-Rivera B, Ortiz-Muñiz B, Gómez-Rodríguez J, Cárdenas-Cágal A, Domínguez-González JM, Aguilar-Uscanga MG (2015) Bioethanol production from hydrolyzed sugarcane bagasse supplemented with molasses “B” in a mixed yeast culture. Renew Energy 74:399–405
Hahn-Hagerdal B, Jeppsson H, Skoog K, Prior BA (1994) Biochemistry and physiology of xylose fermentation by yeasts. Enzyme Microb Technol 16:933–943
Ho NWY, Chang SF (1989) Cloning of yeast xylulokinase gene by complementation of E. coli and yeast mutations. Enzyme Microb Technol 11:417–421
Karagöz P, Özkan M (2014) Ethanol production from wheat straw by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Scheffersomyces stipitis co-culture in batch and continuous system. Bioresour Technol 158:286–293
Papini M, Nookaew I, Uhlen M, Nielsen J (2012) Scheffersomyces stipitis: a comparative systems biology study with the Crabtree positive yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Factories 11:1–16
Sarkar N, Ghosh SK, Bannerjee S, Aikat K (2012) Bioethanol production from agricultural wastes: an overview. Renew Energy 37:19–27
Scordia D, Cosentino SL, Lee JW, Jeffries TW (2012) Bioconversion of giant reed (Arundo donax L.) hemicellulose hydrolysate to ethanol by Scheffersomyces stipitis CBS 6054. Biomass Bioenergy 39:296–305
Yadav KS, Naseeruddin S, Prashanthi GS, Sateesh L, Rao LV (2011) Bioethanol fermentation of concentrated rice straw hydrolysate using co-culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis. Bioresour Technol 102:6473–6478
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Egyptian Cultural Affairs and Missions Sector for providing the Grants during the PhD study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashoor, S., Comitini, F. & Ciani, M. Cell-recycle batch process of Scheffersomyces stipitis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-culture for second generation bioethanol production. Biotechnol Lett 37, 2213–2218 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1919-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1919-9