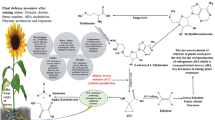
Abstract
Ethylene is an essential plant hormone also known as a stress hormone because its synthesis is accelerated by induction of a variety of biotic and abiotic stress. The plant growth promoting bacteria containing the enzyme 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase enhances plant growth by decreasing plant ethylene levels under stress conditions. The expression of ACC deaminase (acdS) gene in transgenic plants is an alternative approach to overcome the ethylene-induced stress. Several transgenic plants have been engineered to express both bacterial/plant acdS genes which then lowers the stress-induced ethylene levels, thus efficiently combating the deleterious effects of environmental stresses. This review summarizes the current knowledge of various transgenic plants overexpressing microbial and plant acdS genes and their potential under diverse biotic and abiotic stresses. Transcription regulation mechanism of acdS gene from different bacteria, with special emphasis to nitrogen fixing bacteria is also discussed in this review.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnawal D, Bharti N, Maji D, Chanotiya CS, Kalra A (2012) 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase-containing rhizobacteria protect Ocimum sanctum plants during waterlogging stress via reduced ethylene generation. Plant Physiol Biochem 58:227–235
Belimov A, Safronova VI, Sergeyeva TA et al (2001) Characterization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria isolated from polluted soils and containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Can J Microbiol 47:642–652
Belimov A, Dodd IC, Safronova VI, Davies WJ (2009) ACC deaminase-containing rhizobacteria improve vegetative development and yield of potato plants grown under water-limited conditions. Asp Appl Biol 98:163–169
Burd GI, Dixon DG, Glick BR (2000) Plant growth-promoting bacteria that decrease heavy metal toxicity in plants. Can J Microbiol 46:237–245
Cheng Z, Park E, Glick BR (2007) 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from Pseudomonas putida UW4 facilitates the growth of canola in the presence of salt. Can J Microbiol 53:912–918
Cheng Z, Duncker BP, McConkey BJ, Glick BR (2008) Transcriptional regulation of ACC deaminase gene expression in Pseudomonas putida UW4. Can J Microbiol 54:128–136
Dastager SG, Deepa CK, Pandey A (2010) Isolation and characterization of novel plant growth promoting Micrococcus sp NII-0909 and its interaction with cowpea. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:987–992
Farwell AJ, Vesely S, Nero V, Rodriguez H, McCormack K, Shah S, Dixon DG, Glick BR (2007) Tolerance of transgenic canola plants (Brassica napus) amended with plant growth-promoting bacteria to flooding stress at a metal-contaminated field site. Environ Pollut 147:540–545
Fraire-Velázquez S, Rodríguez-Guerra R, Sánchez-Calderón L (2011) Abiotic and biotic stress response crosstalk in plants. In: Shanker AK, Venkateswarlu B (eds) Abiotic stress response in plants -physiological, biochemical and genetic perspectives. InTech, Rijeka, pp 3–26
Fu**o A, Ose T, Yao M, Tokiwano T, Honma M et al (2004) Structural and enzymatic properties of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. J Mol Biol 341:999–1013
Gontia I, Kavita K, Schmid M, Hartmann A, Jha B (2011) Brachybacterium saurashtrense sp. nov., a halotolerant root associated bacterium with plant growth-promoting potential. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2799–2804
Grichko VP, Glick BR (2001) Flooding tolerance of transgenic tomato plants expressing the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase controlled by the 35S, rolD or PRB-1b promoter. Plant Physiol Biochem 39:19–25
Grichko VP, Filby B, Glick BR (2000) Increased ability of transgenic plants expressing the bacterial enzyme ACC deaminase to accumulate Cd Co, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn. J Biotechnol 81:45–53
Grichko VP, Glick BR, Grishko VI, Pauls KP (2005) Evaluation of tomato plants with constitutive, root-specific, and stress-induced ACC deaminase gene expression. Russ J Plant Physiol 52:359–364
Holguin G, Glick BR (2001) Expression of the ACC deaminase gene from Enterobacter cloacae UW4 in Azospirillum brasilense. Microb Ecol 41:281–288
Hontzeas N, Zoidakis J, Glick BR, Abu-Omar MM (2004) Expression and characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane- 1-carboxylate deaminase from the rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida UW4: a key enzyme in bacterial plant growth promotion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1703:11–19
Jalili F, Khavazi K, Pazira E, Nejati A, Rahmani HA, Sadaghiani HR, Miransari M (2009) Isolation and characterization of ACC deaminase producing fluorescent pseudomonads, to alleviate salinity stress on canola (Brassica napus L.) growth. J Plant Physiol 166:667–674
Jha B, Gontia I, Hartmann A (2012) The roots of the halophyte Salicornia brachiata are a source of new halotolerant diazotrophic bacteria with plant growth-promoting potential. Plant Soil 356:265–277
Jia YJ, Kakuta Y, Sugawara M et al (1999) Synthesis and degradation of 1-aminocyclopropane- 1-carboxylic acid by Penicillium citrinum. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63:542–549
Kaneko T, Nakamura Y, Sato S et al (2002) Complete genomic sequence of nitrogen-fixing symbiotic bacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110. DNA Res 9:189–197
Klee HJ, Hayford MB, Kretzmer KA, Barry GF, Kishmore GM (1991) Control of ethylene synthesis by expression of a bacterial enzyme in transgenic tomato plants. Plant Cell 3:1187–1193
Li J, Glick BR (2001) Transcriptional regulation of the Enterobacter cloacae UW4 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase gene (acdS). Can J Microbiol 47:359–367
Lund ST, Stall RE, Klee HJ (1998) Ethylene regulates the susceptible response to pathogen infection in tomato. Plant Cell 10:371–382
Ma W, Guinel FC, Glick BR (2003) Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase promotes nodulation of pea plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4396–4402
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Ryu J, Sa T (2006) Regulation of ethylene levels in canola (Brassica campestris) by 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase-containing Methylobacterium fujisawaense. Planta 224:268–278
Mayak S, Tirosh T, Glick BR (2004) Plant growth-promoting bacteria that confer resistance to water stress in tomato and pepper. Plant Sci 166:525–530
McDonnell L, Plett JM, Andersson-Gunnerås S, Kozela C, Dugardeyn J, Van Der Straeten D, Glick BR, Sundberg B, Regan S (2009) Ethylene levels are regulated by a plant encoded 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase. Physiol Plant 136:94–109
Minami R, Uchiyama K, Murakami T et al (1998) Properties, sequence, and synthesis in Escherichia coli of 1- aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from Hansenula saturnus. J Biochem 123:1112–1118
Nie L, Shah S, Rashid A, Burd GI, Dixon DG, Glick BR (2002) Phytoremediation of arsenate contaminated soil by transgenic canola and the plant growth-promoting bacterium Enterobacter cloacae CAL2. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:355–361
Nukui N, Minamisawa K, Ayabe SI, Aoki T (2006) Expression of the 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase gene requires symbiotic nitrogen-fixing regulator gene nifA2 in Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:4964–4969
Palmer C, Golden K, Danniels L, Ahmad H (2007) ACC deaminase from Issatchenkia occidentalis. J Biol Sci 7:188–193
Plett JM, McDonnell L, Regan S (2009) Plant encoded 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase activity implicated in different aspects of plant development. Plant Signal Behav 4:1186–1189
Reed AJ, Magin KM, Anderson JS et al (1995) Delayed ripening tomato plants expressing the enzyme 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase: molecular characterization, enzyme expression, and fruit ripening traits. J Agric Food Chem 43:1954–1962
Robison MM, Shah S, Tamot B, Pauls KP, Moffatt BA, Glick BR (2001) Reduced symptoms of Verticillium wilt in transgenic tomato expressing a bacterial ACC deaminase. Mol Plant Pathol 2:135–145
Saleem M, Arshad M, Hussain S, Bhatti AS (2007) Perspectives of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) containing ACC deaminase in stress agriculture. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 34:635–648
Saravanakumar D, Samiyappan R (2007) ACC deaminase from Pseudomonas fluorescens mediated saline resistance in groundnut (Arachis hypogea) plants. J Appl Microbiol 102:1283–1292
Sergeeva E, Shah S, Glick BR (2006) Growth of transgenic canola (Brassica napus cv. Westar) expressing a bacterial 1-aminocyclopropane- 1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase gene on high concentrations of salt. World J Microbiol Biotech 22:277–282
Sessitsch A, Coenye T, Sturz AV, Vandamme P, Barka E, Wang-Pruski G, Faure D, Reiter B, Glick BR, Nowak J (2005) Burkholderia phytofirmins sp. Nov., a novel plant-associated bacterium with plant beneficial properties. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1187–1192
Shaharoona B, Arshad M, Zahir ZA (2006) Performance of Pseudomonas spp. containing ACC-deaminase for improving growth and yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in the presence of nitrogenous fertilizer. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2971–2975
Siddikee MA, Glick BR, Chauhan PS, Yim WJ, Sa T (2011) Enhancement of growth and salt tolerance of red pepper seedlings (Capsicum annuum L.) by regulating stress ethylene synthesis with halotolerant bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase activity. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:427–434
Singh N, Kashyap S (2012) In silico identification and characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase from Phytophthora sojae. J Mol Model 18:4101–4111
Stearns JC, Shah S, Greenberg BM, Dixon DG, Glick BR (2005) Tolerance of transgenic canola expressing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase to growth inhibition by nickel. Plant Physiol Biochem 43:701–708
Tamot BK, Pauls KP, Glick BR (2003) Regulation of expression of the prb-1b/ACC deaminase gene by UV-B in transgenic tomatoes. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 12:25–29
Toklikishvili N, Dandurishvili N, Vainstein A (2010) Inhibitory effect of ACC deaminase-producing bacteria on crown gall formation in tomato plants infected by Agrobacterium tumefaciens or A. vitis. Plant Pathol 59:1023–1030
Viterbo A, Landau U, Kim S, Chernin L, Chet I (2010) Characterization of ACC deaminase from the biocontrol and plant growth-promoting agent Trichoderma asperellum T203. FEMS Microbiol Lett 305:42–48
Wang C, Knill E, Glick BR, Défago G (2000) Effect of transferring 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase genes into Pseudomonas fluorescens strain CHA0 and its gacA derivative CHA96 on their growth-promoting and disease-suppressive capacities. Can J Microbiol 46:898–907
Zhang Y, Zhao L, Wang Y, Yang B, Chen S (2008) Enhancement of heavy metal accumulation by tissue specific co-expression of iaaM and ACC deaminase genes in plants. Chemosphere 72:564–571
Zhang Y, He LY, Chen ZJ, Wang QY, Qian M, Sheng XF (2011) Characterization of ACC deaminase-producing endophytic bacteria isolated from copper-tolerant plants and their potential in promoting the growth and copper accumulation of Brassica napus. Chemosphere 83:57–62
Acknowledgments
The author I.G.M. thankfully acknowledges financial support received from Science and Engineering Research Board (Grant # SB/FT/LS-374/2012), Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gontia-Mishra, I., Sasidharan, S. & Tiwari, S. Recent developments in use of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase for conferring tolerance to biotic and abiotic stress. Biotechnol Lett 36, 889–898 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1458-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1458-9