Abstract
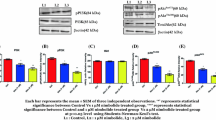
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor super family comprises of members that induce two distinct signaling cascades, leading to either cell survival or apoptosis. However, in prostate cancer (PCa), TNF-mediated prosurvival signaling is the predominant pathway that leads to cell survival and resistance to therapy. Although inhibition of TNF signaling by pharmacological agents or monoclonal antibodies has gained importance in the field of cancer therapy, toxicity to normal cells has impaired their extensive use for cancer treatment. We previously identified a natural, nontoxic compound psoralidin that inhibited viability and induced apoptosis in androgen independent prostate cancer (AIPC) cells. Thus, the goal of our study is to investigate whether psoralidin inhibits TNF-mediated prosurvival signaling in AIPC cells. Our results suggest that psoralidin inhibits constitutive and TNF-induced expression of TNF-α and its downstream prosurvival signaling molecules such as NF-κB and Bcl-2 in AIPC cells. On the other hand, psoralidin simultaneously induces the death receptor (DR)-mediated apoptotic signaling eventually causing the activation of caspase cascade and resultant induction of apoptosis. Oral administration of psoralidin inhibits expression of TNF-α and NF-κB/p65 in tumor sections, resulting in tumor regression in PC-3 xenografts. Our results suggest that psoralidin inhibits TNF-mediated survival signaling in AIPC and thus is a potent therapeutic agent for prostate cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld JG, Tak PP (2008) Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 117:244–279
Ferrajoli A, Keating MJ, Manshouri T et al (2002) The clinical significance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha plasma level in patients having chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 100:1215–1219
Szlosarek PW, Grimshaw MJ, Kulbe H et al (2006) Expression and regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha in normal and malignant ovarian epithelium. Mol Cancer Ther 5:382–390
Sethi G, Sung B, Aggarwal BB (2008) TNF: a master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front Biosci 13:5094–5107
Hu J, Nakano H, Sakurai H, Colburn NH (2004) Insufficient p65 phosphorylation at S536 specifically contributes to the lack of NF-kappaB activation and transformation in resistant JB6 cells. Carcinogenesis 25:1991–2003
Arnott CH, Scott KA, Moore RJ et al (2002) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha mediates tumour promotion via a PKC alpha- and AP-1-dependent pathway. Oncogene 21:4728–4738
Yan B, Wang H, Rabbani ZN et al (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha is a potent endogenous mutagen that promotes cellular transformation. Cancer Res 66:11565–11570
Babbar N, Casero RA Jr (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases reactive oxygen species by inducing spermine oxidase in human lung epithelial cells: a potential mechanism for inflammation-induced carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 66:11125–11130
Nagata S, Golstein P (1995) The Fas death factor. Science 267:1449–1456
Devin A, Cook A, Lin Y, Rodriguez Y, Kelliher M, Liu Z (2000) The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity 12:419–429
Liu ZG, Han J (2001) Cellular responses to tumor necrosis factor. Curr Issues Mol Biol 3:79–90
Lin Y, Devin A, Rodriguez Y, Liu ZG (1999) Cleavage of the death domain kinase RIP by caspase-8 prompts TNF-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:2514–2526
Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Baladandayuthapani V, Krishnan S, Shishodia S (2007) Targeting cell signaling pathways for drug discovery: an old lock needs a new key. J Cell Biochem 102:580–592
Larmonier N, Cathelin D, Larmonier C et al (2007) The inhibition of TNF-alpha anti-tumoral properties by blocking antibodies promotes tumor growth in a rat model. Exp Cell Res 313:2345–2355
Senzer N, Mani S, Rosemurgy A et al (2004) TNFerade biologic, an adenovector with a radiation-inducible promoter, carrying the human tumor necrosis factor alpha gene: a phase I study in patients with solid tumors. J Clin Oncol 22:592–601
Krippner-Heidenreich A, Grunwald I, Zimmermann G et al (2008) Single-chain TNF, a TNF derivative with enhanced stability and antitumoral activity. J Immunol 180:8176–8183
Kumar R, Srinivasan S, Koduru S et al (2009) Psoralidin, an herbal molecule, inhibits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated Akt signaling in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Cancer Prev Res (Phila Pa) 2:234–243
Chendil D, Ranga RS, Meigooni D, Sathishkumar S, Ahmed MM (2004) Curcumin confers radiosensitizing effect in prostate cancer cell line PC-3. Oncogene 23:1599–1607
Sowmyalakshmi S, Nur EAM, Akbarsha MA, Thirugnanam S, Rohr J, Chendil D (2005) Investigation on Semecarpus Lehyam–a Siddha medicine for breast cancer. Planta 220:910–918
Liu T, Wu LY, Choi JK, Berkman CE (2009) In vitro targeted photodynamic therapy with a pyropheophorbide–a conjugated inhibitor of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Prostate 69:585–594
Srinivasan S, Ranga RS, Burikhanov R, Han SS, Chendil D (2007) Par-4-dependent apoptosis by the dietary compound withaferin A in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:246–253
Srinivasan S, Koduru S, Kumar R, Venguswamy G, Kyprianou N, Damodaran C (2009) Diosgenin targets Akt-mediated prosurvival signaling in human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 125:961–967
Rabiau N, Dechelotte P, Guy L et al (2009) Immunohistochemical staining of mucin 1 in prostate tissues. In Vivo 23:203–207
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS (2002) IAP proteins: blocking the road to death’s door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:401–410
de Bruin EC, Medema JP (2008) Apoptosis and non-apoptotic deaths in cancer development and treatment response. Cancer Treat Rev 34:737–749
Eckelman BP, Salvesen GS (2006) The human anti-apoptotic proteins cIAP1 and cIAP2 bind but do not inhibit caspases. J Biol Chem 281:3254–3260
Chen Y, Cheung YT, Kong LD et al (2008) Transcriptional regulation of corticotrophin releasing factor gene by furocoumarins isolated from seeds of Psoralea corylifolia. Life Sci 82:1117–1121
Pahari P, Rohr J (2009) Total synthesis of psoralidin, an anticancer natural product. J Org Chem 74:2750–2754
Khatune NA, Islam ME, Haque ME, Khondkar P, Rahman MM (2004) Antibacterial compounds from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia. Fitoterapia 75:228–230
Gravallese EM, Galson DL, Goldring SR, Auron PE (2001) The role of TNF-receptor family members and other TRAF-dependent receptors in bone resorption. Arthritis Res 3:6–12
Gasparian AV, Yao YJ, Kowalczyk D et al (2002) The role of IKK in constitutive activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor in prostate carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci 115:141–151
Saleem M, Kweon MH, Yun JM et al (2005) A novel dietary triterpene Lupeol induces fas-mediated apoptotic death of androgen-sensitive prostate cancer cells and inhibits tumor growth in a xenograft model. Cancer Res 65:11203–11213
Wu XX, Ogawa O, Kakehi Y (2004) TRAIL and chemotherapeutic drugs in cancer therapy. Vitam Horm 67:365–383
Earnshaw WC, Martins LM, Kaufmann SH (1999) Mammalian caspases: structure, activation, substrates, and functions during apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 68:383–424
Jiang C, Wang Z, Ganther H, Lu J (2001) Caspases as key executors of methyl selenium-induced apoptosis (anoikis) of DU-145 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:3062–3070
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM et al (1999) Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade: hierarchical activation of caspases-2, -3, -6, -7, -8, and -10 in a caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol 144:281–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, S., Kumar, R., Koduru, S. et al. Inhibiting TNF-mediated signaling: a novel therapeutic paradigm for androgen independent prostate cancer. Apoptosis 15, 153–161 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0416-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0416-9