Abstract
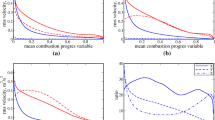
The statistical behaviour of turbulent kinetic energy transport in turbulent premixed flames is analysed using data from three-dimensional Direct Numerical Simulation (DNS) of freely propagating turbulent premixed flames under decaying turbulence. For flames within the corrugated flamelets regime, it is observed that turbulent kinetic energy is generated within the flame brush. By contrast, for flames within the thin reaction zones regime it has been found that the turbulent kinetic energy decays monotonically through the flame brush. Similar trends are observed also for the dissipation rate of turbulent kinetic energy. Within the corrugated flamelets regime, it is demonstrated that the effects of the mean pressure gradient and pressure dilatation within the flame are sufficient to overcome the effects of viscous dissipation and are responsible for the observed augmentation of turbulent kinetic energy in the flame brush. In the thin reaction zones regime, the effects of the mean pressure gradient and pressure dilatation terms are relatively much weaker than those of viscous dissipation, resulting in a monotonic decay of turbulent kinetic energy across the flame brush. The modelling of the various unclosed terms of the turbulent kinetic energy transport equation has been analysed in detail. The predictions of existing models are compared with corresponding quantities extracted from DNS data. Based on this a-priori DNS assessment, either appropriate models are identified or new models are proposed where necessary. It is shown that the turbulent flux of turbulent kinetic energy exhibits counter-gradient (gradient) transport wherever the turbulent scalar flux is counter-gradient (gradient) in nature. A new model has been proposed for the turbulent flux of turbulent kinetic energy, and is found to capture the qualitative and quantitative behaviour obtained from DNS data for both the corrugated flamelets and thin reaction zones regimes without the need to adjust any of the model constants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones, W.P., Launder, B.E.: The calculation of low-Reynolds-number phenomena with a two equation model of turbulence. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 16, 1119–1130 (1973)
Durbin, P.A., Pettersson-Reif, B.A.: Statistical Theory and Modelling of Turbulent Flows, 1st edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2001)
Wilcox, D.C.: Turbulence Modelling for CFD, 2nd edn. D.C.W., La Cañada (2002)
Karlovitz, B., Jr Denniston, D.W., Knapschaefer, D.H., Wells, F.E.: Studies on turbulent flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 4, 613–620 (1953)
Launder, B.E.: Heat and mass transport by turbulence. In: Bradshaw, P. (ed.) Topics in Applied Physics, vol. 12, pp. 231–287, Springer (1976)
Bray, K.N.C.: Studies of the turbulent burning velocity. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 431, 315–355 (1990)
Candel, S., Veynante, D., Lacas, F., Maistret, E., Darabiha, N., Poinsot, T.: Coherent flamelet model: applications and recent extensions. In: Larrouturou, B.E. (ed.) Recent Advances in Combustion Modelling, pp. 19–64. World Scientific, Singapore (1990)
Duclos, J.M., Veynante, D., Poinsot, T.J.: A comparison of flamelet models for premixed turbulent combustion. Combust. Flame. 95, 101–117 (1993)
Mantel, T., Bilger, R.W.: Conditional statistics in a turbulent premixed flame derived from direct numerical simulation. Combust. Sci. Technol. 96(4), 393–417 (1995)
Chakraborty, N., Rogerson, J.W., Swaminathan, N.: A-Priori assessment of closures for scalar dissipation rate transport in turbulent premixed flames using direct numerical simulation. Phys. Fluids. 20, 045106 (2008)
Kolla, H., Rogerson, J.W., Chakraborty, N., Swaminathan, N.: Scalar dissipation rate modelling and its validation. Combust. Sci. Technol. 181, 518–535 (2009)
Bray, K.N.C., Libby, P.A.: Interaction effects in turbulent premixed flames. Phys. Fluids A 19, 1687–1701 (1976)
Moreau, P., Boutier, A.: Laser velocimeter measurements in a turbulent flame. Proc. Combust. Inst. 16, 1747–1756 (1977)
Bray, K.N.C., Libby, P.A., Masuya, G., Moss, J.B.: Turbulence production in premixed turbulent flames. Combust. Sci. Technol. 25, 127–140 (1980)
Borghi, R., Escudie, D.: Assessment of a theoretical model of turbulent combustion by comparison with a simple experiment. Combust. Flame. 56, 149–164 (1984)
Chomiak, J., Nisbet, J.: Modelling variable density effects in turbulent flames. Combust. Flame. 102, 371–386 (1995)
Kuznetsov, V.R.: Estimate of the correlation between pressure pulsations and the divergence of the velocity in subsonic flows of variable density. Fluid Dyn. 14(3), 328–334 (1979)
Strahle, W.C.: Velocity-pressure gradient correlation in turbulent reactive flows. Combust. Sci. Technol. 32, 289–305 (1983)
Rutland, C.J., Cant, R.S.: Turbulent transport in premixed flames, pp.75–94. Proc. of 1994 Summer Program, Centre for Turbulence Research, Stanford University/NASA Ames, Stanford, CA (1994)
Zhang, S., Rutland, C.J.: Premixed flame effects on turbulence and pressure-related terms. Combust. Flame. 102, 447–461 (1995)
Nishiki, S., Hasegawa, T., Borghi, R., Himeno, R.: Modelling of flame generated turbulence based on Direct Numerical Simulation databases. Proc. Combust. Inst. 29, 2017–2022 (2002)
Peters, N.: Turbulent Combustion, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, UK (2000)
Vaishnavi, P., Cant, R.S.: Mechanism of induced turbulence through buoyancy suppression in premixed turbulent combustion. Proc. of 2nd European Combustion Meeting, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium (2005)
Poinsot, T., Echekki, T., Mungal, M.: A study of the laminar flame tip and implications for turbulent premixed combustion. Combust. Sci. Technol. 81(1–3), 45–73 (1992)
Rutland, C., Trouvé, A.: Direct simulations of premixed turbulent flames with nonunity Lewis numbers. Combust. Flame. 94, 41–57 (1993)
Chakraborty, N., Cant, S.: Unsteady effects of strain rate and curvature on turbulent premixed flames in an inflow-outflow configuration. Combust. Flame. 137, 129–147 (2004)
Chakraborty, N., Cant, R.S.: Influence of Lewis number on curvature effects in turbulent premixed flame propagation in the thin reaction zones regime. Phys. Fluids. 17, 105105 (2005)
Treurniet, T.C., Nieuwstadt, F.T.M., Boersma, B.J.: Direct Numerical Simulation of homogeneous turbulence in combination with premixed combustion at low Mach number modeled by the G-equation. J. Fluid Mech. 565, 25–62 (2006)
Chakraborty, N.: Comparison of displacement speed statistics of turbulent premixed flames in the regimes representing combustion in corrugated flamelets and the thin reaction zones. Phys. Fluids 19, 105109 (2007)
Chakraborty, N., Cant, R.S.: Effects of Lewis number on turbulent scalar transport and its modelling in turbulent premixed flames. Combust. Flame. 156, 1427–1444 (2009)
Veynante, D., Trouvé, A., Bray, K.N.C., Mantel, T.: Gradient and counter-gradient scalar transport in turbulent premixed flames. J. Fluid Mech. 332, 263–293 (1997)
Tullis, S., Cant, R.S.: Scalar transport modeling in large eddy simulation of turbulent premixed flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 29, 2097–2104 (2002)
Swaminathan, N., Bray, K.N.C.: Effects of dilatation on scalar dissipation in turbulent premixed flames. Combust. Flame. 143, 549–565 (2005)
Bray, K.N.C., Swaminathan, N.: Scalar dissipation rate and flame surface density in premixed turbulent combustion. Comptes Rendus Mechanique. 334, 466–473 (2006)
Rogerson, J.W., Swaminathan, N.: Correlation between dilatation and scalar dissipation in turbulent premixed flames. Proc. 3rd European Combust. Meeting (2007)
Chakraborty, N., Rogerson, J.W., Swaminathan, N.: A-Priori assessment of closures for scalar dissipation rate transport in turbulent premixed flames using direct numerical simulation. Phys. Fluids 20, 045106 (2008)
Kolla, H., Rogerson, J.W., Chakraborty, N., Swaminathan, N.: Scalar dissipation rate modelling and its validation. Combust. Sci. Technol. 181, 518–535 (2009)
Chakraborty, N., Klein, M.: A Priori direct numerical simulation assessment of algebraic flame surface density models for turbulent premixed flames in the context of large eddy simulation. Phys. Fluids 20, 085108 (2008)
Wray, A.A.: Minimal storage time advancement schemes for spectral methods, Report No. MS 202 A-1, NASA Ames Research Center, California (1990)
Poinsot, T., Lele, S.K.: Boundary conditions for direct simulation of compressible viscous flows. J. Comp. Physiol. 101, 104–129 (1992)
Jenkins, K.W., Cant, R.S.: DNS of turbulent flame kernels. In: Liu, C., Sakell, L., Beautner, T. (eds.) Proc. Second AFOSR Conf. on DNS and LES, pp. 192–202. Kluwer Academic Publishers (1999)
Rogallo, R.S.: Numerical experiments in homogeneous turbulence. NASA TM81315, NASA Ames Research Center, California (1981)
Batchelor, G.K., Townsend, A.A.: Decay of turbulence in final period. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 194, 527–542 (1948)
Poinsot, T., Veynante, D.: Theoretical and Numerical Combustion. R.T. Edwards, Philadelphia, USA (2001)
Haworth, D.C., Poinsot, T.J.: Numerical simulations of Lewis number effects in turbulent premixed flames. J. Fluid Mech. 244, 405–436 (1992)
Peters, N., Terhoeven, P., Chen, J.H., Echekki, T.: Statistics of flame displacement speeds from computations of 2-D unsteady methane-air flames. Proc. Combust. Inst. 27, 833–839 (1998)
Boger, M., Veynante, D., Boughanem, H., Trouvé, A.: Direct numerical simulation analysis of flame surface density concept for Large Eddy Simulation of turbulent premixed combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 27, 917–925 (1998)
Bray, K.N.C., Libby, P.A., Moss, J.B.: Unified modelling approach for premixed turbulent combustion – Part I: general formulation. Combust. Flame. 61, 87–102 (1985)
Veynante, D., Poinsot, T.J.: Effects of pressure gradients on turbulent premixed flames. J. Fluid Mech. 353, 83–114 (1997)
Chakraborty, N., Cant, R.S.: Effects of Lewis number on scalar transport in turbulent premixed flames. Phys. Fluids 21, 035110 (2009)
Chakraborty, N., Cant, R.S.: Physical insight and modelling for Lewis number effects on turbulent heat and mass transport in turbulent premixed flames. Numer. Heat Transf. A 55(8), 762–779 (2009)
Launder, B.L., Reece, G.J., Rodi, W.J.: Progress in the development of a Reynolds stress turbulence closure. J. Fluid Mech. 68, 537–566 (1975)
Bray, K.N.C., Champion, M., Libby, P.A.: Premixed flames in stagnating turbulence part IV: a new theory for the Reynolds stresses and Reynolds fluxes applied to im**ing flows. Combust. Flame 120, 1–18 (2000)
Domingo, P., Bray, K.N.C.: Laminar flamelet expressions for pressure fluctuation terms in second moment models of premixed turbulent combustion. Combust. Flame 121, 555–574 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, N., Katragadda, M. & Cant, R.S. Statistics and Modelling of Turbulent Kinetic Energy Transport in Different Regimes of Premixed Combustion. Flow Turbulence Combust 87, 205–235 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-010-9312-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10494-010-9312-1