Abstract
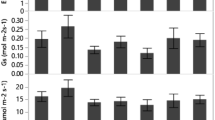
The adaptation responses to different water conditions and the drought tolerance of Sophora davidii seedlings were assessed in a greenhouse experiment. Two-month-old seedlings were subjected to the following water supplies for 95 days: 100, 80, 60, 40 and 20% of field water capacity. The seedlings at 100% FC had the greatest productivity, height, basal diameter, branch number, leaf number and leaf area. Water supply <80% FC was the threshold of drought-initiated negative effects on seedling growth, yield and physiological processes; these parameters were severely reduced at 20% FC, however, there was no plant death during the experiment. Moreover, water stress decreased leaf relative water content, specific leaf area, leaf area ratio, and water-use efficiency (WUE), whereas it increased the biomass allocation to roots, which resulted in a higher root:stem mass ratio under drought. The S. davidii seedlings tolerated drought by maintaining high leaf relative water content and by reducing branching and leaf expansion. However, low productivity and WUE at 20% FC suggested that seedlings did not produce high biomass under severe drought. Therefore, prior to introducing S. davidii in forestation efforts, a water supply >40% FC is recommended for seedlings to maintain growth and productivity. These results provide insights into limitations and opportunities for establishment of S. davidii in arid regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anyia AO, Herzog H (2004) Water-use efficiency, leaf area and leaf gas exchange of cowpeas under mid-season drought. Eur J Agron 20:327–339. doi:10.1016/S1161-0301(03)00038-8
Ares A, Fownes JH (1999) Water supply regulates structure, productivity, and water use efficiency of Acacia koaforest in Hawaii. Oecologia 12:458–466. doi:10.1007/s004420050952
Bacelar EA, Moutinho-Pereira JM, GonÇalves BC et al (2007) Changes in growth, gas exchange, xylem hydraulic properties and water use efficiency of three olive cultivars under contrasting water availability regimes. Environ Exp Bot 60:183–192. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.10.003
Boyer JS (1982) Plant productivity and environment. Science 218:443–448. doi:10.1126/science.218.4571.443
Brouwer R (1963) Some aspects of the equilibrium between overground and underground plant parts. Jaarboek IBS, Wageningen, pp 31–39
Bu CF, Liu GB, Zang WH (2004) Growth of characteristics of Sophora viciifolia population in the hilly and gully region of Loess Plateau. Acta Bot Boreali-Occidentalia Sin 24(10):1792–1797 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Castro-Díez P, Puyravaud JP, Cornelissen JHC (2000) Leaf structure and anatomy as related to leaf mass per area variation in seedlings of a wide range of woody plant species and types. Oecologia 124:476–486. doi:10.1007/PL00008873
Clavel D, Drame NK, Roy-Macauley H et al (2005) Analysis of early responses to drought associated with field drought adaptation in four Sahelian groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars. Environ Exp Bot 54:219–230. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.07.008
Coopman RE, Jara JC, Bravo LA et al (2008) Changes in morpho-physiological attributes of Eucalyptus globulus plants in response to different drought hardening treatments. Electron J Biotechnol 11:1–10. doi:10.2225/vol11-issue2-fulltext-9
Dias PC, Araujo WL, Moraes GABK, Barros RS et al (2007) Morphological and physiological responses of two coffee progenies to soil water availability. J Plant Physiol 164:1639–1647. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2006.12.004
Donovan LA, Ehleringer JR (1994) Water stress and use of summer precipitation in a Great Basin shrub community. Funct Ecol 8:289–297. doi:10.2307/2389821
Engelbrecht BMJ, Kursar TA, Tyree MT (2005) Drought effects on seedling survival in a tropical moist forest. Trees (Berl) 19:312–321. doi:10.1007/s00468-004-0393-0
Feng YL, Li X (2007) The combined effects of soil moisture and irradiance on growth, biomass allocation, morphology and photosynthesis in Amomum villosum. Agrofor Syst 71:89–98. doi:10.1007/s10457-007-9076-3
Gallé A, Haldimann P, Feller U (2007) Photosynthetic performance and water relations in young pubescent oak (Quercus pubescens) trees during drought stress and recovery. New Phytol 174:799–810. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02047.x
Gindaba J, Rozanov A, Negash L (2004) Response of seedlings of two Eucalyptus and three deciduous tree species from Ethiopia to severe water stress. For Ecol Manage 201:119–129
González-Rodríguez AM, Martín-Olivera A, Morales D et al (2005) Physiological responses of tagasaste to a progressive drought in its native environment on the Canary Islands. Environ Exp Bot 53:195–204. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.03.013
Grubb PJ (1977) Control of forest growth and distribution on wet tropical mountains: with special reference to mineral distribution. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 8:83–107. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.08.110177.000503
Guan WB, Ye MS, Ma KM et al (2004) Vegetation classification and the main types of vegetation of the Dry Valley of Minjiang River. J Mt Sci 22(1):679–686
Hubick KT, Farquhar GD, Shorter R (1986) Correlation between water use efficiency and carbon isotope discrimination in diverse peanut (Arachis) germplasm. Aust J Plant Physiol 13:803–816
Kozlowski TT, Pallardy SG (2002) Acclimation and adaptive responses of woody plants to environmental stresses. Bot Rev 68:270–334. doi:10.1663/0006-8101(2002)068[0270:AAAROW]2.0.CO;2
Li C (1999) Carbon isotope composition, water-use efficiency and biomass productivity of Eucalyptus microtheca populations under different water supplies. Plant Soil 214:165–171. doi:10.1023/A:1004708815973
Li FL, Bao WK, Pang XY et al (2008) Seedling emergence, survival and growth of five endemic species in the dry valley of Minjiang River. Acta Ecol Sin (in press) (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Ma KM, Fu BJ, Liu SL et al (2004) Multiple-scale soil moisture distribution and its implications for ecosystem restoration in an arid river valley. Land Degrad Dev 15:75–85. doi:10.1002/ldr.584
Martin PJ, Stephens W (2006) Willow growth in response to nutrients and moisture on a clay landfill cap soil. II: Water use. Bioresour Technol 97:449–458. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.03.004
Monclus R, Dreyer E, Villar M et al (2006) Impact of drought on productivity and water use efficiency in 29 genotypes of Populus deltoids, Populus nigra. New Phytol 69:765–777. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01630.x
Namirembe S, Brook RM, Ong CK (2008) Manipulating phenology and water relations in Senna spectabilis in a water limited environment in Kenya. Agrofor Syst. doi:10.1007/s10457-008-9169-7
Navas ML, Garnier E (2002) Plasticity of whole plant and leaf traits in Rubia peregrina in response to light, nutrient and water availability. Acta Oecol 23:375–383. doi:10.1016/S1146-609X(02)01168-2
Ngugi MR, Doley DH, Mark A et al (2003) Leaf water relations of Eucalyptus cloeziana and Eucalyptus argophloia in response to water deficit. Tree Physiol 23:335–343
Niu SL, Jiang GM, Wan SQ et al (2005) Ecophysiological acclimation to different soil moistures in plants from a semi-arid sandland. J Arid Environ 63:353–365. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2005.03.017
Ogbonnaya CI, Nwalozie MC, Roy-Macauley H et al (1998) Growth and water relations of Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) under water deficit on a sandy soil. Ind Crops Prod 8:65–76. doi:10.1016/S0926-6690(97)10011-5
Puri S, Swamy SL (2001) Growth and biomass production in Azadirachta indica seedling in response to nutrients (N and P) and moisture stress. Agrofor Syst 51:57–68. doi:10.1023/A:1006402212225
Rodiyati A, Arisoesilaningsih E, Isagi Y et al (2005) Responses of Cyperus brevifoliu s (Rottb.) Hassk. and Cyperus kyllingia Endl. to varying soil water availability. Environ Exp Bot 53:259–269. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.03.018
Sánchez-Coronado ME, Coates R, Castro-Colina L et al (2007) Improving seed germination and seedling growth of Omphalea oleifera (Euphorbiaceae) for restoration projects in tropical rain forests. For Ecol Manage 243(1):144–155
Singh B, Singh G (2003) Biomass partitioning and gas exchange in Dalbergia sissoo seedlings under water stress. Photosynthetica 41(3):407–414. doi:10.1023/B:PHOT.0000015465.86985.53
Singh B, Singh G (2006) Effects of controlled irrigation on water potential, nitrogen uptake and biomass production in Dalbergia sissoo seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 55:209–219. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.11.001
Villagra PE, Cavagnaro JB (2006) Water stress effects on the seedling growth of Prosopis argentina and Prosopis alpataco. J Arid Environ 64:390–400. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2005.06.008
Wang C, Bao W, Chen J, Sun H et al (2003) Profile characteristics and nutrients of dry cinnamon soils in dry valley of the upper Minjiang river. Chin J Appl Environ Biol 9(3):230–234 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang HZ, Liang ZS, Han RL et al (2005a) Physiological mechanism of Sophora viciifolia to adapt to soil drought. Agr Res Arid Areas 23(1):106–110 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang HZ, Liang ZS, Han RL, Han L (2005b) Effect of soil drought on seedling growth and dry matter allocation of four native tree species on Loess Plateau. J Plant Res Environ 14(1):10–15 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei Z (1994) Flora of China, vol 40, Leguminosae. Sciences Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Wu N (ed) (2007) Restoration and rehabilitation of degraded mountain ecosystem on the upper Minjiang River. Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, Chendu, pp 181–211 (in Chinese)
Wu FZ, Bao WK, Li FL, Wu N (2008) Effects of drought stress and N supply on the growth, biomass partitioning and water-use efficiency of Sophora davidii seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 63:248–255. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.11.002
Yin CY, Wang X, Duan BL et al (2005) Early growth, dry matter allocation and water use efficiency of two sympatric Populus species as affected by water stress. Environ Exp Bot 53:315–322. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.04.007
Zhao BZ, Kondo M, Maeda M et al (2004) Water-use efficiency and carbon isotope discrimination in two cultivars of upland rice during different developmental stages under three water regimes. Plant Soil 26:61–75. doi:10.1023/B:PLSO.0000035562.79099.55
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Ph.D foundation in Western Light Talent Training Plan of Chinese Academy of Sciences (08C2041100) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30570333). We are grateful to Maoxian Station for Ecosystem Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences for providing facilities and technical assistance, and to Katherine A. Frego and Kenneth A. Albrecht for language improvement and revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10457-009-9252-8
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F.L., Bao, W.K. & Wu, N. Effects of water stress on growth, dry matter allocation and water-use efficiency of a leguminous species, Sophora davidii . Agroforest Syst 77, 193–201 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-008-9199-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10457-008-9199-1