Abstract
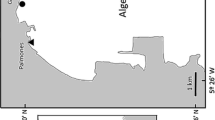
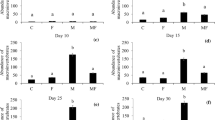
An algal assemblage growing on artificial substrata of fish-farm cages was investigated. Specifically, algal response to the effects of fish-farm facilities was studied, in order to identify a possible future descriptor of biodeposition impact. Some sites were positioned upstream of the farms (at least 750 m; ‘controls’) and other sites were positioned downstream of the farms (‘impacts’). All sites were situated in the Tyrrhenian Sea. Control and impact sites differed significantly with regard to the dissolved nutrient profile. The fouling community (samples were scraped from buoys) displayed a reduction gradient in diversity which increased with the effect of fish farms. A total of 51 taxa were identified (three Cyanophyceae, three Phaeophyceae, five Bacillariophyceae, three Chlorophyceae, six Ulvophyceae and 31 Rhodophyceae), with a dominance of opportunistic species (with r strategy). A general increase in values of the Rhodophyceae by Phaeophyceae ratio (R/P) were recorded, indicating a remarkable impact of nutrient enrichment from fish culture facilities on an algal community structure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MJ, Underwood AJ (1997) Effects of gastropod grazers on recruitment and succession of an estuarine assemblage: a multivariate and univariate approach. Oecologia 109:442–453
Angel DL, Spanier E (2002) An application of artificial reefs to reduce organic enrichment caused by net-cage fish farming: preliminary results. ICES J Mar Sci 59:324–329
Benedetti-Cecchi L, Bulleri F, Acunto S, Cinelli F (2001) Scales of variation in the effects of limpets on rocky shores in the northwest Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 209:131–141
Beveridge MCM (1996) Cage aquaculture, 2nd edn. Blackwell Fishing News books, Oxford
Bray JR, Curtis JT (1957) An ordination of upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol Monogr 27:325–349
Calcagno JA, López Gappa J, Tablado A (1998) Population dynamics of the barnacles Balanus amphitrite in an intertidal area affected by sewage pollution. J Crustac Biol 18:128–137
Clarke K (1993) Nonparametric multivariate analysis of changes in community structure. Austr J Ecol 18:117–143
Clarke KR, Gooley RM (2001) Primer v5: User manual/tutorial. Primer-E Ltd., Plymouth, 91 pp
Diaz P, Gappa JJL, Piriz ML (2002) Symptoms of eutrophication in intertidal macroalgal assemblages of Nuevo Gulf (Patagonia, Argentina). Bot Mar 45:267–273
Díaz Villanueva V, Queimaliños C, Modenutti B, Ayala J (2000) Effects of fish farm effluents on the periphyton of an Andrean stream. Arch Fish Mar Res 48:252–263
Hargrave BT, Phillips GA, Doucette LI, White MJ, Milligan TG, Wildish DJ, Cranston RE (1997) Assessing benthic impacts of organic enrichment from marine aquaculture. Water Air Soil Pollution 99:641–212
Holmer M (1991) Impacts of aquaculture on surrounding sediments: generation of organic-rich sediments. In: Pauw N, Joyce J (eds) Aquaculture and the environment. Aquaculture Society Special Publication, vol 16.155–175
Iwama GK (1991) Interactions between aquaculture and the environment. Crit Rev Environ Cont 21:177–216
Kalaman VV (2001) Fouling Communities of Mussel Aquaculture Installations in the White Sea. Russ J Mar Biol 27:227–237
Kalantzi I, Karakassis I (2006) Benthic impacts of fish farming: Meta-analysis of community and geochemical data. Mar Poll Bull 52:484–493
La Rosa T, Mirto S, Mazzola A, Danovaro R (2001) Differential responses of benthic microbes and meiofauna to fish-farm disturbance in coastal sediments. Environ Poll 112:427–434
Mayer-Pinto M, Junqueira AOR (2003) Effects of organic pollution on the initial development of fouling communities in a tropical bay, Brazil. Mar Pollut Bull 46:1495–1503
Mirto S, La Rosa T, Gambi C, Danovaro R, Mazzola A (2002) Nematode community response to fish-farm impact in the western Mediterranean. Environ Poll 116:203–214
Mook DH (1981) Effects of disturbance and initial settlement on fouling community structure. Ecology 62:522–526
Orfanidis S, Panayotidis P, Stamatis N (2003) An insight to the ecological evaluation index (EEI). Ecol Ind 3:27–33
Pearson TH, Black KD (2000) The environmental impacts of marine fish cage culture. In: Black KD (eds), Environmental Impacts of Aquaculture. Sheffield Academic Press, Sheffield
Rönnberg O, Ådjers K, Ruokolahti C, Bondestam M (1992) Effects of fish farming on growth, epiphytes and nutrient content of Fucus vesiculosus L. in the Åland archipelago, Northern Baltic Sea. Aquat Bot 42:109–120
Ruokolahti C (1988) Effects of fish farming on growth and chlorophyll a content of Cladophora. Mar Poll Bull 19:166–169
Sarà G (2007) A meta-analysis on the ecological effects of aquaculture on the water column: dissolved nutrients. Mar Environ Res 63:390–408
Sarà G, Scilipoti D, Milazzo M, Modica A (2006) Use of stable isotopes to investigate dispersal of waste from fish farms as a function of hydrodynamics. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 313:261–270
Sarà G, Lo Martire M, Buffa G, Mannino AM, Badalamenti F (2007) The fouling community as an indicator of fish farming impact in Mediterranean. Aquacult Res 38:66–75
Strickland JDH and Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of sea-water analysis. J Fish Res Bd Canada, vol 167. 311 pp
Torras X, Pinedo S, Garcia M, Mangialajo L, Ballesteros E (2003) Assessment of coastal environmental qualità based on littoral community cartography: methodological approach. Proceedings of the second mediterranean symposium on marine vegetation. Reports. Athens 12–13 December. UNEP/MAP/RAC/SPA
Underwood AJ (1997) Experiments in ecology. Their logical and interpretation using analysis of variance. Cambridge University Press
Underwood AJ, Anderson MJ (1994) Seasonal and temporal aspects of recruitment and succession in an intertidal estuarine fouling assemblage. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 74:563–584
Wu RSS, Lam KS, Mackay DW, Lau TC, Yam V (1994) Impact of marine fish farming on water quality and bottom sediment: a case study in the sub-tropical environment. Mar Environ Res 38:115–145
Zvyagintsev AY, Korn OM (2003) Life History of the Barnacle Balanus Amphitrite Darwin and its role in fouling communities of Peter the Great Bay, Sea of Japan. Russ J Mar Biol 29:41–48
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Felice Cascio (Ittica Trappeto s.r.l.) for his logistic support and all their students for generous technical support during field sampling and laboratory analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mannino, A.M., Sara, G. Effects of fish-farm biodeposition on periphyton assemblages on artificial substrates in the southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Gulf of Castellammare, Sicily). Aquat Ecol 42, 575–581 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-007-9131-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10452-007-9131-1