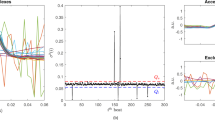
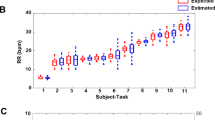
Abstract
A method for estimating respiratory rate from electrocardiogram (ECG) signals is presented. It is based on QRS slopes and R-wave angle, which reflect respiration-induced beat morphology variations. The 12 standard leads, 3 leads from vectorcardiogram (VCG), and 2 additional non-standard leads derived from VCG loops were analyzed. The following series were studied as ECG derived respiration (EDR) signals: slope between the peak of Q and R waves, slope between the peak of R and S waves, and the R-wave angle. Information from several EDR signals was combined in order to increase the robustness of estimation. Evaluation is performed over two databases containing ECG and respiratory signals simultaneously recorded during two clinical tests with different characteristics: tilt test, representing abrupt cardiovascular changes, and stress test representing a highly non-stationary and noisy environment. A combination of QRS slopes and R-wave angle series derived from VCG leads obtained a respiratory rate estimation relative error of 0.50 ± 4.11% (measuring 99.84% of the time) for tilt test and 0.52 ± 8.99% (measuring 96.09% of the time) for stress test. These results outperform those obtained by other reported methods, both in tilt and stress testing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailón, R., L. Mainardi, M. Orini, L. Sörnmo, and P. Laguna. Analysis of heart rate variability during exercise stress testing using respiratory information. Biomed. Signal Process. 5:299–310, 2010.
Bailón, R., L. Sörnmo, and P. Laguna. ECG-derived respiratory frequency estimation. In: Advanced Methods and Tools for ECG Data Analysis, edited by G. Clifford, F. Azuaje, and P. McSharry. Norwood: Artech House Inc., 2006, pp. 215–244.
Bailón, R., L. Sörnmo, P. Laguna. A robust method for ECG-based estimation of the respiratory frequency during stress testing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53(7):1273–1285, 2006.
Blain, G., O. Meste, A. Blain, and S. Bermon. Time-frequency analysis of heart rate variability reveals cardiolocomotor coupling during dynamic cycling exercise in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 296:H1651–H1659, 2009.
Chon, K. H., S. Dash, and K. Ju. Estimation of respiratory rate from photoplethysmogram data using time-frequency spectral estimation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56(8):2054–2063, 2009.
Edenbrandt, L., and O. Pahlm. Vectorcardiogram synthesized from a 12-lead ECG: superiority of the inverse dower matrix. J. Electrocardiol. 21(4):361–367, 2008.
Freeman, R. Assessment of cardiovascular autonomic function. Clin. Neurophysiol. 117(4):716–730, 2006.
Gravelyn, T. R., and J. G. Weg. Respiratory rate as an indicator of acute respiratory dysfunction. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 244(10):1123–1125, 1980.
Grossman P., and K. Wientjes. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia and parasympathetic cardiac control: some basic issues concerning quantification, applications and implications. In: Cardiorespiratory and Cardiosomatic Psycophysiology, edited by P. Grossman, K. Jansenn, and D. Waitl. New York: Plenum Press, 1986, pp. 117–138.
James, N. W., G. M. Adams, and A. F. Wilson. Determination of anaerobic threshold by ventilatory frequency. Int. J. Sports Med. 10(3):192–196, 1989.
Lázaro, J., A. Alcaine, E. Gil, P. Laguna, and R. Bailón. Electrocardiogram derived respiration from QRS slopes. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE, 2013, pp. 3913–3916.
Lázaro J., A. Alcaine, D. Romero, E. Gil, P. Laguna, L. Sörnmo, and R. Bailón. Electrocardiogram derived respiration from QRS slopes: evaluation over stress testing recordings. In: Computing in Cardiology, 2013, pp. 655–658.
Lázaro, J., E. Gil, R. Bailón, A. Mincholé, and P. Laguna. Deriving respiration from photoplethysmographic pulse width. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 51(1–2):233–242, 2013.
Leanderson, S., P. Laguna, and L. Sörnmo. Estimation of the respiratory frequency using spatial information in the VCG. Med. Eng. Phys. 25(6):501–507, 2003.
Martínez, J. P., R. Almeida, S. Olmos, A. P. Rocha, and P. Laguna. A wavelet-based ECG delineator: Evaluation on standard databases. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(4):570–581, 2004.
Mason, C. L., and L. Tarassenko. Quantitative assessment of respiratory derivation algorithms. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2001. Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE, Vol. 2, 2001, pp. 1998–2001.
Mateo, J., and P. Laguna. Analysis of heart rate variability in presence of ectopic beats using the heart timing signal. IEEE. Trans. Biomed. Eng. 50(3):334–343, 2003.
Mazzanti, B., C. Lamberti, and J. de Bie. Validation of an ECG-derived respiration monitoring method. In: Computers in Cardiology, 2003, pp. 613–616 (2003).
Meredith, D. J., D. Clifton, P. Charlton, J. Brooks, C. W. Pugh, and L. Tarassenko. Photoplethysmographic derivation of respiratory rate: a review of relevant physiology. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 36(1):1–7, 2012.
Mincholé, A., E. Pueyo, J. F. Rodríguez, E. Zacur, M. Doblaré, and P. Laguna. Quantification of restitution dispersion from the dynamic changes of the T wave peak to end, measured at the surface ECG. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(5):1172–1182, 2011.
Moody, G. B., R. G. Mark, A. Zoccola, and S. Mantero. Derivation of respiratory signals from multi-lead ECGs. In: Computers in Cardiology, 1985, pp. 383–386.
Pinciroli F., R. Rossi, and L. Vergani. Detection of electrical axis variation for the extraction of respiratory information. In: Computers in Cardiology, 1986, pp. 499–502.
Pueyo, E., L. Sörnmo, and P. Laguna. QRS slopes for detection and characterization of myocardial ischemia. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 55(2):468–477, 2008.
Romero, D., M. Ringborn, P. Laguna, and E. Pueyo. Depolarization changes during acute myocardial ischemia by evaluation of QRS slopes: standard lead and vectorial approach. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(1):110–120, 2011.
Romero, D., M. Ringborn, P. Laguna, and E. Pueyo. Detection and quantification of acute myocardial ischemia by morphologic evaluation of QRS changes by an angle-based method. J. Electrocardiol. 46:204–214, 2013.
Sörnmo, L., and P. Laguna. ECG signal processing. In: Bioelectrical Signal Processing in Cardiac and Neurological Applications, edited by L. Sörnmo and P. Laguna New York: Elsevier, 2005, pp. 453–566.
Varanini, M., M. Emdin, F. Allegri, M. Raciti, F. Conforti, A. Macerata, A. Taddei, R. Francesconi, G. Kraft, A. L. Abbate, and C. Marchesi. Adaptive filtering of ECG signal for deriving respiratory activity. In: Proceedings of the Computers in Cardiology, 1990, pp. 621–624.
Zhang, P. Z., W. N. Tapp, S. S. Reisman, and B. H. Natelson. Respiration response curve analysis of heart rate variability. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 44(4):321–325, 1997.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Dr. A. Mincholé, Dr. L. Sörnmo, Dr. G. Blain and Dr. S. Bermon for providing the authors with datasets. This work is supported by Universidad de Zaragoza under fellowship PIFUZ-2011-TEC-A-003, by Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (MINECO), FEDER; under projects TEC2010-21703-C03-02, TEC2010-19410, TEC2013-42140-R, TIN2013-41998-R and FIS-PI12/00514, by CIBER de Bioingeniería, Biomateriales y Nanomedicina through Instituto de Salud Carlos III, and by Grupo Consolidado BSICoS from DGA (Aragón) and European Social Fund (EU). Esther Pueyo acknowledges the financial support of Ramón y Cajal program from MINECO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Anastasios G. Bezerianos oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lázaro, J., Alcaine, A., Romero, D. et al. Electrocardiogram Derived Respiratory Rate from QRS Slopes and R-Wave Angle. Ann Biomed Eng 42, 2072–2083 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1073-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1073-x