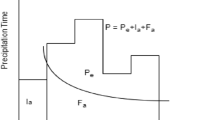
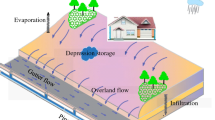
Abstract
There are numerous examples in the literature where numerical modelling has been used as a valuable tool in the study of rainfall-induced landslides. While much attention has been paid to the influence of different rainfall characteristics and patterns, spatial variability or temporal patterns of rainfall intensity, very little attention has been paid to the influence of the temporal resolution of rainfall data used in numerical simulations of rainfall infiltration and slope stability analysis. This is particularly true for deep-seated landslides occurring on slopes composed of soils with relatively low hydraulic conductivity, as in the case of flysch deposits presented in this study. A recently developed 2D numerical model is used to investigate the results of transient infiltration and slope stability analysis for flux boundary conditions derived from three temporal resolutions of realistic rainfall data: (i) 10-min, (ii) hourly and (iii) daily rainfall measurements. The results obtained show that deriving the time-dependent flux boundary conditions using the coarse resolution rainfall data (e.g. daily rainfall measurements) can lead to a calculation of unrealistically high infiltrated volumes, a faster increase in water content and pore water pressure in a slope cross-section, and a reduction in the factor of safety at an unrealistically high rate, resulting in a conservative prediction of the time to slope failure. The results suggest hourly rainfall data as the optimal form of input data for the case study under investigation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbanas Ž, Mihalić Arbanas S, Vivoda M, Peranić J, Dugonjić Jovančević S, Jagodnik V (2014) Identification, monitoring and simulation of landslides in the Rječina River Valley, Croatia. In: Sassa K, Dang Khang Q (eds) Proceedings of the SATREPS workshop on landslide risk assessment technology, 29–30 July 2014. Hanoi, Vietnam, pp 200–213
Arbanas Ž, Mihalić Arbanas S, Vivoda Prodan M et al (2017) Preliminary investigations and numerical simulations of a landslide reactivation. In: Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides. pp 649–657
Benac Č, Arbanas Ž, Jurak V et al (2005) Complex landslide in the Rječina valley (Croatia): Origin and sliding mechanism. Bull Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-005-0002-5
Boger M (1998) Three-dimensional analytical solutions for unsaturated seepage problem. J Hydrol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)1084-0699(1998)3:3(193)
Casagli N, Dapporto S, Ibsen ML et al (2006) Analysis of the landslide triggering mechanism during the storm of 20th-21st November 2000, in Northern Tuscany. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-005-0007-y
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M, Sorbino G (2010) Modeling of rainfall-induced shallow landslides of the flow-type. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000182
Chen P, Lu N, Formetta G et al (2018) Tropical storm-induced landslide potential using combined field monitoring and numerical modeling. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001969
Chen P, Mirus B, Lu N, Godt JW (2017) Effect of hydraulic hysteresis on stability of infinite slopes under steady infiltration. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001724
Cho SE (2016) Stability analysis of unsaturated soil slopes considering water-air flow caused by rainfall infiltration. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.07.008
Collins BD, Znidarcic D (2004) Stability analyses of rainfall induced landslides. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2004)130:4(362)
Comegna L, Damiano E, Greco R et al (2016) Field hydrological monitoring of a slo** shallow pyroclastic deposit. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2015-0344
Comegna L, Picarelli L, Bucchignani E, Mercogliano P (2013) Potential effects of incoming climate changes on the behaviour of slow active landslides in clay. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0339-3
Cotecchia F, Tagarelli V, Pedone G et al (2019) Analysis of climate-driven processes in clayey slopes for early warning system design. Proc Inst Civ Eng Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeen.18.00217
Cotecchia F, Vitone C, Santaloia F et al (2015) Slope instability processes in intensely fissured clays: case histories in the Southern Apennines. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0516-7
Crosta GB, Dal Negro P (2003) Observations and modelling of soil slip-debris flow initiation processes in pyroclastic deposits: the Sarno 1998 event. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-3-53-2003
Ebel BA, Godt JW, Lu N et al (2018) Field and laboratory hydraulic characterization of landslide-prone soils in the oregon coast range and implications for hydrologic simulation. Vadose Zo J. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2018.04.0078
Fan L, Lehmann P, Zheng C, Or D (2020) Rainfall intensity temporal patterns affect shallow landslide triggering and hazard evolution. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL085994
Geoslope (2005) User's guide. GeoStudio 2004, Version 6.13. Geo-Slope Int. Ltd., Calgary, Canada
Godt JW, Baum RL, Lu N (2009) Landsliding in partially saturated materials. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL035996
Godt JW, Şener-Kaya B, Lu N, Baum RL (2012) Stability of infinite slopes under transient partially saturated seepage conditions. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR011408
Gofar N, Lee LM (2008) Extreme rainfall characteristics for surface slope stability in the Malaysian Peninsular. Georisk. https://doi.org/10.1080/17499510802072991
Greco R, Comegna L, Damiano E et al (2013) Hydrological modelling of a slope covered with shallow pyroclastic deposits from field monitoring data. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-17-4001-2013
Green HW, Ampt GA (1911) Studies on soil physics: flow of air and water through soils. J Aric Sci
Kang S, Cho SE, Kim B, Go GH (2020) Effects of two-phase flow ofwater and air on shallow slope failures induced by rainfall: Insights from slope stability assessment at a regional scale. Water (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w12030812
Kim J, Jeong S, Regueiro RA (2012) Instability of partially saturated soil slopes due to alteration of rainfall pattern. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.07.005
Kristo C, Rahardjo H, Satyanaga A (2017) Effect of variations in rainfall intensity on slope stability in Singapore. Int Soil Water Conserv Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2017.07.001
Leach B, Herbert R (1982) The genesis of a numerical model for the study of the hydrogeology of a steep hillside in Hong Kong. Q J Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.qjeg.1982.015.03.09
Leung AK, Ng CWW (2013) Analyses of groundwater flow and plant evapotranspiration in a vegetated soil slope. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2013-0148
Li AG, Yue ZQ, Tham LG et al (2005) Field-monitored variations of soil moisture and matric suction in a saprolite slope. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/t04-069
Liu W, Yang Z, He S (2021) Modeling the landslide-generated debris flow from formation to propagation and run-out by considering the effect of vegetation. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01478-4
Lollino P, Cotecchia F, Elia G et al (2016) Interpretation of landslide mechanisms based on numerical modelling: two case-histories. Eur J Environ Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2014.985851
Lu N, Godt J (2008) Infinite slope stability under steady unsaturated seepage conditions. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR006976
Marino P, Santonastaso GF, Fan X, Greco R (2020) Prediction of shallow landslides in pyroclastic-covered slopes by coupled modeling of unsaturated and saturated groundwater flow. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01484-6
McGuire LA, Rengers FK, Kean JW et al (2016) Elucidating the role of vegetation in the initiation of rainfall-induced shallow landslides: insights from an extreme rainfall event in the Colorado Front Range. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL070741
Mihalić Arbanas S, Sečanj M, Bernat Gazibara S et al. (2015) Identification and Map** of the Valići Lake Landslide (Primorsko-Goranska County, Croatia) In: Procedings of the 2nd Regional Symposium on landslides in the Adriatic-Balkan Region. Belgrade, pp 197–202
Mihalić Arbanas S, Sečanj M, Bernat Gazibara S et al (2017) Landslides in the Dinarides and Pannonian Basin—from the largest historical and recent landslides in Croatia to catastrophic landslides caused by Cyclone Tamara (2014) in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Landslides
Muntohar AS, Ikhsan J, Liao HJ (2013) Influence of rainfall patterns on the instability of slopes. Civ Eng Dimens. https://doi.org/10.9744/ced.15.2.120-128
Nie WB, Li YB, Fei LJ, Ma XY (2017) Approximate explicit solution to the Green-Ampt infiltration model for estimating wetting front depth. Water (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080609
Pagano L, Picarelli L, Rianna G, Urciuoli G (2010) A simple numerical procedure for timely prediction of precipitation-induced landslides in unsaturated pyroclastic soils. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-010-0216-x
Pedone G, Ruggieri G, Trizzino R (2018) Characterisation of climatic variables used to identify instability thresholds in clay slopes. Geotech Lett. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgele.18.00020
Pedone G, Tsiampousi A, Cotecchia F, Zdravkovic L (2016) Effects of soil-vegetation-atmosphere interaction on the stability of a clay slope: a case study. In: E3S Web of Conferences
Pedone G, Tsiampousi A, Cotecchia F, Zdravkovic L (2022) Coupled hydro-mechanical modelling of soil–vegetation– atmosphere interaction in natural clay slopes. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2020-0479
Peranić J, Arbanas Ž (2020) Impact of the wetting process on the hydro-mechanical behavior of unsaturated residual soil from flysch rock mass: preliminary results. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:985–998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01604-0
Peranić J, Arbanas Ž, Cuomo S, Maček M (2018a) Soil-Water characteristic curve of residual soil from a flysch rock mass. Geofluids 2018:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6297819
Peranić J, Arbanas Ž, Foresta V, Cuomo S, Maček M (2018b) Determination of soil water retention curve of residual soil from a flysch rock mass. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Unsaturated Soils (UNSAT2018b). Hong Kong, pp 379–384
Peranić J, Mihalić Arbanas S, Arbanas Ž (2021) Importance of the unsaturated zone in landslide reactivation on flysch slopes: observations from Valići Landslide, Croatia. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01757-8
Peranić J, Moscariello M, Cuomo S, Arbanas Ž (2020a) Hydro-mechanical properties of unsaturated residual soil from a flysch rock mass. Eng Geol 269:105546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105546
Peranić J, Moscariello M, Cuomo S, Arbanas Ž (2020b) Determination of hydraulic conductivity and shear strength properties of unsaturated residual soil from flysch rock mass. E3S Web Conf. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/2020503022
Pirone M, Papa R, Nicotera MV, Urciuoli G (2015) Soil water balance in an unsaturated pyroclastic slope for evaluation of soil hydraulic behaviour and boundary conditions. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.06.005
Rahardjo H, Li XW, Toll DG, Leong EC (2001) The effect of antecedent rainfall on slope stability. Geotech Geol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013129725263
Rahardjo H, Nio AS, Leong EC, Song NY (2010) Effects of groundwater table position and soil properties on stability of slope during rainfall. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000385
Rahardjo H, Ong TH, Rezaur RB, Leong EC (2007) Factors controlling instability of homogeneous soil slopes under rainfall. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2007)133:12(1532)
Rahardjo H, Satyanaga A, Leong EC (2016) Effects of rainfall characteristics on the stability of tropical residual soil slope. In: E3S Web of Conferences
Rahimi A, Rahardjo H, Leong EC (2011) Effect of antecedent rainfall patterns on rainfall-induced slope failure. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000451
Ran H, Yifeng C, Chuangbing Z (2011) Modeling of coupled deformation, water flow and gas transport in soil slopes subjected to rain infiltration. Sci China Technol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-011-4504-z
Srivastava R, Yeh T-CJ (1991) Analytical solutions for one-dimensional, transient infiltration toward the water table in homogeneous and layered soils. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/90WR02772
Sun J, Liu Q, Li J, An Y (2009) Effects of rainfall infiltration on deep slope failure. Sci China, Ser G Physics, Mech Astron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-009-0004-6
Tagarelli V, Cotecchia F (2020a) The effects of slope initialization on the numerical model predictions of the slope-vegetation-atmosphere interaction. Geosci. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences10020085
Tagarelli V, Cotecchia F (2020b) Deep movements in clayey slopes relating to climate: modeling for early warning system design. In: Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering
Tagarelli V, Cotecchia F (2022) Coupled hydro-mechanical analysis of the effects of medium depth drainage trenches mitigating deep landslide activity. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106510
Toll DG, Md Rahim MS, Karthikeyan M, Tsaparas I (2016) Soil-atmosphere interactions for analysing slopes in tropical soils in Singapore. Environ Geotech. https://doi.org/10.1680/jenge.15.00071
Tsiampousi A, Zdravkovic L, Potts DM (2017) Numerical study of the effect of soil–atmosphere interaction on the stability and serviceability of cut slopes in London clay. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2016-0319
Tu G, Huang D, Huang R, Deng H (2019) Effect of locally accumulated crushed stone soil on the infiltration of intense rainfall: a case study on the reactivation of an old deep landslide deposit. Bull Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01460-y
van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x
Vanapalli SK, Fredlund DG, Pufahl DE, Clifton AW (1996) Model for the prediction of shear strength with respect to soil suction. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/t96-060
Vassallo R, Grimaldi GM, Di Maio C (2015) Pore water pressures induced by historical rain series in a clayey landslide: 3D modeling. Landslides. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0508-7
Vivoda M, Benac Č, Žic E et al (2012) Geohazards in the Rječina Valley in the past and present. Hrvat Vode
Vivoda M, Dugonjić Jovančević S, Arbanas Ž (2013) Landslide occurrence prediction in the Rječina River Valley as a base for an early warning system. In: Proceedings of the 1st ReSyLAB. Zagreb, pp 25–26
Vivoda Prodan M, Mileusnić M, Mihalić Arbanas S, Arbanas Ž (2017) Influence of weathering processes on the shear strength of siltstones from a flysch rock mass along the northern Adriatic coast of Croatia. Bull Eng Geol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0881-7
Von Ruette J, Lehmann P, Or D (2014) Effects of rainfall spatial variability and intermittency on shallow landslide triggering patterns at a catchment scale. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR015122
Yeh HF, Tsai YJ (2018) Effect of variations in long-duration rainfall intensity on unsaturated slope stability. Water (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040479
Zaninović K, Gajić-Čapka M, Perčec Tadić M et al (2008) Klimatski Atlas Hrvatske / Climate Atlas of Croatia 1961–1990:1971–2000
Zhang XY, Zhu YM, Fang CH (2009) The role fore air flow in soil slope stability analysis. J Hydrodyn. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(08)60195-X
Zhao N, Hu B, Yi Q et al (2017) The coupling effect of rainfall and reservoir water level decline on the Baijiabao landslide in the three gorges reservoir area, China. Geofluids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3724867
Acknowledgements
The software and research activities were supported by the Croatian Science Foundation under the project IP-2018-01-1503 “Physical modelling of landslide remediation constructions behaviour under static and seismic actions (ModLandRemSS)”. This work has been supported in part by Ministry of Science, Education and Sports of the Republic of Croatia under the project Research Infrastructure for Campus-based Laboratories at the University of Rijeka, number RC.2.2.06-0001. The project has been co-funded from the European Fund for Regional Development (ERDF). Part of the rainfall data used for the statistical analyses was provided by the Meteorological and Hydrological Service of Croatia (MHSC). These supports are gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peranić, J., Arbanas, Ž. The influence of the rainfall data temporal resolution on the results of numerical modelling of landslide reactivation in flysch slope. Landslides 19, 2809–2822 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01937-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01937-0