Abstract
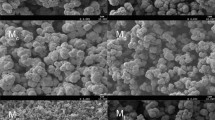
A poly(ionic liquid-glycidylmethacrylate-co-ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate) monolithic column was prepared via in situ free-radical polymerisation and used as an on-line solid-phase extraction column. The obtained monolithic column was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, nitrogen adsorption–desorption measurement, and mercury intrusion porosimetry, which showed a relatively uniform and porous structure. During the on-line solid-phase extraction–high performance liquid chromatography protocol, nifedipine, nitrendipine, and felodipine were separated efficiently from human plasma using a methanol–water linear gradient at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1. The extraction efficiency for the targets was satisfactory with no matrix interference. Under the optimized extraction conditions, the linear regression coefficient was >0.9973; precisions for inter- and intra-day assays presented as relative standard deviations were less than 7.29 %, and the accuracy and recovery was in the range of 96–105 and 90–106 %, respectively. As a result, the polymerization monolithic column exhibited high selectivity and good permeability, and it was feasible to be used as an on-line SPE column. Meanwhile, validation assays also demonstrated acceptable sensitivity and precision for simultaneous quantitative screening of nifedipine, nitrendipine, and felodipine in human plasma.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Magiera S, Hejniak J, Baranowski J (2014) J Chromatogr B 958:22–28
Heidari H, Razmi H, Jouyban A (2014) J Sep Sci 37(12):1467–1474
Handa T, Singh S, Singh IP (2014) J Pharm Biomed Anal 89:6–17
Wang CZ, Li M, Xu HH, Wei YM (2014) J Chromatogr A 1343:195–199
Long CY, Mai ZB, Yang XF, Zhu BH, Xu XM, Huang XD, Zou XY (2011) Food Chem 126:1324–1329
Zeng L, Wu X, Li YX, Lu D, Sun CJ (2015) Anal Methods 7:543–550
Shang DW, Wang XP, Zhao XT, Huang FM, Tian GZ, Lu W, Zhou TY (2011) J Chromatogr B 879:3459–3464
Liu HY, Duan YH, Jia YH, Gu YZ, Li J, Yan CH, Yang GL (2012) J Chromatogr B 889–890:55–60
Wei X, Yin J, Yang G, He C, Chen Y (2007) J Sep Sci 30:2851–2857
Yan H, Sun N, Han Y, Yang C, Wang M, Wu R (2013) J Chromatogr A 1307:21–26
Connolly D, Currivan S, Paull B (2012) Proteomics 12:2904–2917
Arrua RD, Talebi M, Causon TJ, Hilder EF (2012) Anal Chim Acta 738:1–12
Thabano JRE, Breadmore MC, Hutchinson JP, Johns C, Haddad PR (2007) J Chromatogr A 1175:117–126
Vidal L, Parshintsev J, Hartonen K, Canals A, Riekkola M (2012) J Chromatogr A 1226:2–10
Vidal L, Riekkola M, Canals A (2012) Anal Chim Acta 715:19–41
Poole CF, Poole SK (2011) J Sep Sci 34:888–900
González RM, Pinto CG, Pérez JL, Cordero BM (2014) J Sep Sci 37:1448–1455
Yang L, Yu H, Li S, Zhou S (2010) Chromatographia 72:307–311
Guo L, Deng QL, Fang GZ, Gao W, Wang S (2011) J Chromatogr A 1218:6271–6277
Meng Y, Pino V, Anderson JL (2011) Anal Chim Acta 687:141–149
Tang B, Bi W, Tian M, Row KH (2012) J Chromatogr B 904:1–21
Wei X, Yang G, Qi L, Chen Y (2009) Talanta 77:1197–1202
Qin JX, Bai LG, Wang JF, Ma YM, Liu HY, He S, Li TT, An Y (2015) Anal Methods 7:218–222
Acknowledgments
The project was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21505030); the National Science Foundation of Hebei Province (No B2015201024); and the National Science Foundation of Hebei University (Nos. 2013-247, 2014-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the subjects.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Wang, C., He, S. et al. On-line SPE Using Ionic Liquid-Based Monolithic Column for the Determination of Antihypertensives in Human Plasma. Chromatographia 79, 441–449 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3045-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-016-3045-9