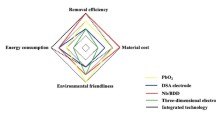
Abstract
Toxic synthetic dyes are polluting industry effluents and waters. Therefore, there is a need for methods to remove organic dyes and clean water. Advanced oxidation processes using Fenton reagent and electrochemical oxidation are efficient methods. It has also been shown that hydrothermally processed nanotubes and nanosheets of semiconductor oxides can decompose organic synthetic dyes. Such a reaction is typically done in the dark with a strong oxidizer such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), without any need for an external radiation or power source. Here, we review current knowledge on such remediation methods.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MN, Ram RN (1992) Removal of basic dye from wastewater using silica as adsorbent. Environ Pollut 77:79–86
Ammar S, Asma M, Oturan N, Abdelhédi R, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical degradation of anthraquinone dye alizarin red: role of the electrode material. Curr Org Chem 16:1978–1985
Auta M, Hameed BH (2012) Modified mesoporous clay adsorbent for adsorption isotherm and kinetics of methylene blue. Chem Eng J 198–199:219–227
Babu BK, Purayil JV, Padinhattayil H, Shukla S, Warrier KGK (2013) Silica-based NTPC-fly ash for dye-removal application and effect of its modification. Int J Appl Ceram Technol 10:186–201
Babu BK, Warrier KGK, Shukla S (2014) Decolorization of aqueous solution containing organic synthetic-dye via dark-catalysis process using hydrothermally synthesized semiconductor-oxides nanotubes. Adv Sci Eng Med 6:173–183
Baiju KV, Shukla S, Biju S, Reddy MLP, Warrier KGK (2009a) Hydrothermal processing of dye-adsorbing one-dimensional hydrogen titanate. Mater Lett 63:923–926
Baiju KV, Shukla S, Biju S, Reddy MLP, Warrier KGK (2009b) Morphology-dependent dye-removal mechanism as observed for anatase-titania photocatalyst. Catal Lett 131:663–671
Boufia-Chergui S, Oturan N, Khalaf H, Oturan MA (2012) Electrochemical and photochemical oxidation of cationic dyes: a comparative study. Curr Org Chem 16:2073–2082
Brillas E, Martinez-Huitle CA (2011) Synthetic diamond films: preparation, electrochemistry, characterization, and applications. Wiley, New Jersey
Brillas E, Sirés I, Oturan MA (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109:6570–6663
Buthelezi SP, Olaniran AO, Pillay B (2012) Textile dye removal from wastewater effluents using bioflocculants produced by indigenous bacterial isolates. Molecules 17:14260–14274
Canizares P, Gadri A, Lobato J, Nasr B, Paz R, Rodrigo MA, Saez C (2009) Electrochemical oxidation of azoic dyes with conductive-diamond anodes. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:3468–3473
Carp O, Huisman CL, Reller A (2004) Photoinduced reactivity of titanium dioxide. Prog Solid State Chem 32:33–177
Chen L, Kueppers S, Wang Z, **ang Cao SW (2014) Online electro-Fenton-mass spectrometry reveals 2,4’,5-trichlorobiphenyl oxidation products and binding to organic matter. Environ Chem Lett 12:329–334
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085
Dhakshinamoorthy A, Navalon S, Alavaro M, Gracia H (2012) Metal nanoparticles as heterogeneous Fenton catalysts. Chem Sus Chem 5:46–64
Diagne M, Sharma VK, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2014) Depollution of indigo dye by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton processes using boron-doped diamond anode. Environ Chem Lett 12:219–224
Fujishima A, Rao TN, Tryk DA (2000) Titanium dioxide photocatalysis. J Photochem Photobiol C 1:1–21
Guivarch E, Oturan MA (2004) The problem of the contamination of waters by synthetic dyes: how to destroy them? Application of the electro-Fenton process? Actual Chimique 277–278:65–69
Guivarch E, Trévin S, Lahitte C, Oturan MA (2003) Degradation of azo dyes in water by electro-Fenton process. Environ Chem Lett 1:39–44
Gupta VK, Suhas (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—a review. J Environ Manag 90:2313–2342
Hammami S, Bellakhal N, Oturan N, Oturan MA, Dachraoui D (2008) Degradation of Acid Orange 7 by electrochemically generated ·OH in acidic aqueous medium using a boron-doped diamond or platinum anode. A mechanistic study. Chemosphere 73:678–684
Hareesh P, Babitha KB, Shukla S (2012) Processing fly ash stabilized hydrogen titanate nano-sheets for industrial dye-removal application. J Hazard Mater 229–230:177–182
Harsha N, Ranya KR, Babitha KB, Shukla S, Biju S, Reddy MLP, Warrier KGK (2011a) Hydrothermal processing of hydrogen titanate/anatase-titania nanotubes and their application as strong dye-adsorbents. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:1175–1187
Harsha N, Ranya R, Shukla S, Biju S, Reddy MLP, Warrier KGK (2011b) Effect of silver and palladium on dye-removal characteristics of anatase-titania nanotubes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11:2440–2449
Harsha N, Priya R, Ranya KR, Shukla S, Biju S, Reddy MLP, Warrier KGK (2011c) Morphology-dependent correlation between photoluminescence and photocatalytic activity of anatase-titania photocatalyst. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 3:503–508
Harsha N, Babitha KB, Shukla S, Warrier KGK (2011d) Comparing effects of silver and iron deposition on dye-adsorption in dark using anatase-titania nanotubes catalyst. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 3:809–814
Houas A, Lachheb H, Ksibi M, Elaloui E, Guillard C, Herrmann JM (2001) Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl Catal B 31:145–157
**g L, Sun X, Shang J, Cai W, Xu Z, Du Y, Fu H (2003) Review of surface photovoltage spectra of nanosized semiconductor and its applications in heterogeneous photocatalysis. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 79:133–151
Jose M, Haridas MP, Shukla S (2014) Predicting dye-adsorption capacity of hydrogen titanate nanotubes via one-step dye-removal method of novel chemically activated catalytic process conducted in dark. J Environ Chem Eng 2:1980–1988
Kumar SG, Gomathi Devi L (2011) Review on modified TiO2 photocatalysis under UV/visible light: selected results and related mechanisms on interfacial charge carrier transfer dynamics. J Phys Chem A 115:13211–13241
Lahkimi A, Chaouch M, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2007) Removal of textile dyes from water by electro-Fenton process. Environ Chem Lett 5:35–39
Liu W, Wang T, Borthwick Wang Y, Yin X, Li X, Ni J (2013) Adsorption of Pb2+, Cd2+, Cu2+ and Cr3+ onto titanate nanotubes: competition and effect of inorganic ions. Sci Total Environ 456–457:171–180
Mahamadi C, Mawere E (2014) High adsorption of dyes by water hyacinth fixed on alginate. Environ Chem Lett 12:313–320
Marselli B, Garcia-Gomez J, Michaud PA, Rodrigo MA, Comninellis C (2003) Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. J Electrochem Soc 150:D79–D83
Martinez-Huitle CA, Brillas E (2009) Decontamination of wastewaters containing synthetic organic dyes by electrochemical methods: a general review. Appl Catal B 87:105–145
Mhemdi A, Oturan MA, Oturan N, Abdelhédi R, Ammar S (2013) Electrochemical advanced oxidation of 2-chlorobenzoic acid using boron doped diamond or Pt anode and carbon felt cathode. J Electroanal Chem 709:111–117
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R (2012) Trends in electro-Fenton process for water and wastewater treatment: an overview. Desalination 299:1–15
Oturan MA (2000) An ecologically effective water treatment technique using electrochemically generated hydroxyl radicals for in situ destruction of organic pollutants. Application to herbicide 2,4-D. J Appl Electrochem 30:477–482
Oturan MA, Aaron JJ (2014) Advanced oxidation processes in water/wastewater treatment: principles and applications. A review. Crtit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44:2577–2641
Oturan MA, Pinson J, Deprez D, Terlain B (1992) Polyhydroxylation of salicylic acid by electrochemically generated ·OH radicals. New J Chem 16:705–710
Oturan MA, Guivarch E, Oturan N, Sirés I (2008) Oxidation pathways of malachite green by Fe3+-catalyzed electro-Fenton process. Appl Catal B 82:244–254
Oturan MA, Edelahi MC, Oturan N, El Kacemi K, Aaron JJ (2010) Kinetics of oxidative degradation/mineralization pathways of the phenylurea herbicides diuron, monuron and fenuron in water during application of the electro-Fenton process. Appl Catal B 97:82–89
Oturan N, Brillas E, Oturan MA (2012) Unprecedented total mineralization of atrazine and cyanuric acid by anodic oxidation and electro-Fenton with a boron-doped diamond anode. Environ Chem Lett 10:165–170
Oturan N, Wu J, Zhang H, Sharma VK, Oturan MA (2013) Electrocatalytic destruction of the antibiotic tetracycline in aqueous medium by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: effect of electrode materials. Appl Catal B 140–141:92–97
Özcan A, Şahin Y, Koparal AS, Oturan MA (2008) Carbon sponge as a new cathode material for the electro-Fenton process. Comparison with carbon felt cathode and application to degradation of synthetic dye Basic Blue 3 in aqueous medium. J Electroanal Chem 616:71–78
Padinhattayil H, Augustine R, Shukla S (2013) Dye-adsorption capacity of high surface-area hydrogen titanate nanosheets processed via modified hydrothermal method. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 13:3035–3045
Panizza M, Cerisola G (2009) Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem Rev 109:6541–6569
Panizza M, Oturan MA (2011) Degradation of alizarin red by electro-Fenton process using a carbon-felt cathode. Electrochim Acta 56:7084–7087
Panizza M, Barbucci A, Ricotti R, Cerisola G (2007) Electrochemical degradation of methylene blue. Sep Purif Technol 54:382–387
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam PT (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol 77:247–255
Rodrigo MA, Oturan N, Oturan MA (2014) Electrochemically assisted remediation of pesticides in soils and water: a review. Chem Rev 114:8720–8745
Sharma P, Kaur R, Bhaskar C, Chung WJ (2010) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous waste using rice husk and rice husk ash. Desalination 259:249–257
Shukla S (2013) Transforming magnetic photocatalyst to magnetic dye-adsorbent catalyst. In: Haghi AK, Zachariah A, Kalariakkal N, Thomas S, Sebastian M, George A, Weimin Y (eds) Nanomaterials: synthesis, characterization and applications, vol vol. 3., of the Advances in nanoscience and nanotechnology book series, Apple Academic Press Inc, Ontario Chapter 9
Shukla S, Padinhattayil H, Narayani H, Jose M, Karunakaran R (Publication Date: 27-November-2014b) Semiconductor-oxides nanotubes-based composite particles useful for dye-removal and processes thereof. WIPO Publication No. WO/2014/188448
Shukla S, Warrier KGK, Babu BK (Publication Date: 20-February-2014a) Methods for decomposition of organic synthetic-dyes using semiconductor-oxides nanotubes via dark-catalysis. WIPO Publication No. WO/2014/027364
Sirés I, Oturan N, Guivarch E, Oturan MA (2008) Efficient removal of triphenylmethane dyes from aqueous medium by in situ electrogenerated Fenton’s reagent at carbon-felt cathode. Chemosphere 72:592–600
Sivaraj R, Namasivayam C, Kadirvelu K (2001) Orange peel as an adsorbent in the removal of acid violet 17 (acid dye) from aqueous solutions. Waste Manag 21:105–110
Sopaj F, Rodrigo MA, Oturan N, Podvorica FI, Pinson J, Oturan MA (2015) Influence of the anode materials on the electrochemical oxidation efficiency. Application to oxidative degradation of the pharmaceutical amoxicillin. Chem Eng J 262:286–294
Sun X, Li Y (2003) Synthesis and characterization of ion-exchangeable titanate nanotubes. Chem Eur J 9:2229–2238
Tachikawa T, Fujitsuka M, Majima T (2007) Mechanistic insight into the TiO2 photocatalytic reactions: design of new photocatalysts. J Phys Chem C 111:5259–5275
Thazhe L, Shereef A, Shukla S, Reshmi CP, Varma MR, Suresh KG, Patil K, Warrier KGK (2010) Magnetic dye-adsorbent catalyst: processing characterization, and application. J Am Ceram Soc 93:3642–3650
Tomat R, Vecchi E (1971) Electrocatalytic production of OH radicals and their oxidative addition to benzene. J Appl Electrochem 1:185–188
Vasudevan S, Oturan MA (2014) Electrochemistry: as cause and cure in water pollution—an overview. Environ Chem Lett 12:97–108
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J 156:11–24
Wang JL, Xu LJ (2012) Advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: formation of hydroxyl radical and application. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:251–325
Wang YQ, Hu GQ, Duan XF, Sun HL, Xue QK (2002) Microstructure and formation mechanism of titanium dioxide nanotubes. Chem Phys Lett 365:427–431
Yates BJ, Darlington R, Zboril R, Sharma VK, Virender K (2014) High-valent iron-based oxidants to treat perfluorooctanesulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid in water. Environ Chem Lett 12:413–417
Zhang G, Qu J, Liu H, Cooper AT, Wu R (2007) CuFe2O4/activated carbon composite: a novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of acid orange II and catalytic regeneration. Chemosphere 68:1058–1066
Acknowledgments
SS thanks CSIR, India, for the financial support (Projects No. NWP0010, OLP216339, and P81113). MAO thanks to the ANR (French National Research Agency) for the financial support (Project No. ANR-13-ECOT-0003-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, S., Oturan, M.A. Dye removal using electrochemistry and semiconductor oxide nanotubes. Environ Chem Lett 13, 157–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0501-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0501-y