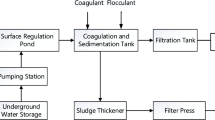
Abstract
The growing demand for water in China’s coal-producing regions requires enhanced coal mine drainage (CMD) utilization. Mine water quality was analyzed for 269 mines distributed in 11 of China’s large coal-producing regions. We found that China’s CMD can be broadly characterized as: slightly contaminated, acidic, high salinity, high sulfate, high fluoride, and containing elevated iron and manganese. When CMD had properties of more than one category, its most distinctive characteristic was used for classification. When this was done, the chemical characteristics tended to correlate with the hydrogeological conditions of the region. Appropriate treatment technologies and pollution prevention measures based on these chemical characteristics could enhance the likelihood of mine water being used to relieve China’s water shortage crisis and promote environmental protection for China’s coal-producing regions.
Zusammenfassung
Der zunehmende Wasserbedarf in Chinas kohleproduzierenden Regionen erfordert eine Ausweitung der Nutzung von Abwässern des Kohlebergbaues. Die chemische Charakteristik des Bergbauwassers wurde für 269 Minen in 11 der größten kohleproduzierenden Regionen Chinas analysiert. Wie stellten fest, daß Chinas Kohlebergbauwässer allgemein folgend qualifiziert werden können: Gering schadstoffhaltig, sauer, hoch salinar, sulfat- und fluorhaltig, und mit erhöhten Gehalten von Eisen und Mangan. Die Klassifikation erfolgte nach dem jeweils ausgeprägtesten Merkmal, auch wenn mehr als eine Kategorie erhöht war; die derart ermittelten Charakteristika zeigten tendenziell eine Korrelation mit der hydrogeologischen Beschaffenheit der Region. Diesen chemischen Charakteristika angepasste Technologien der Wasseraufbereitung und der Vorbeugung von Kontamination könnten die Wahrscheinlichkeit einer Bergbauwassernutzung erhöhen und damit Chinas Wasserversorgungskrise erleichtern; das würde gleichzeitig den Umweltschutz in Chinas kohleproduzierenden Regionen voranbringen.
Resumen
La creciente demanda de agua en las regiones productoras de carbón en China requiere mejorar la utilización del drenaje de mina de carbón (CMD). Se analizó la calidad del agua de mina de 269 minas distribuidas en 11 de las mayores regiones productoras de carbón de China. Se encontró que los CMD en China pueden ser caracterizados como: altamente contaminados, ácidos, alta salinidad, alta concentración de sulfato, alta concentración de fluoruro y altos contenidos en hierro y manganeso. En los casos donde CMD tiene propiedades que se corresponden con más de una categoría, el CMD fue clasificado acorde a su característica más distintiva. Al hacerlo de este modo, las características químicas tendieron a correlacionarse con las condiciones hidrogeológicas de la región. Tecnologías para un tratamiento apropiado y medidas de prevención de la polución basadas en esas características químicas podría aumentar la posibilidad de usar el agua de mina para aliviar la escasez de agua en China y promover la protección ambiental para regiones productoras de carbón en China.
摘要
**煤炭生产地区日益增大的用水需求对提高矿井水(CMD)利用率提出了更高要求。本文分析了**11个产煤区内269个煤矿的矿井水水质资料。**煤矿矿井水大致分为6种类型:轻微污染的、酸性的、高矿化度的、高硫酸盐的、高氟的和高铁-锰的。当矿井水可以被划分为多种类型时,一般以其最显著特征作为划分依据。**矿井水水质类型的差异主要取决于煤矿的水文地质条件。根据水质差异合理选择矿井水处理工艺,可以提高矿井水利用率,缓解煤矿区水资源压力。.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablizi W (2004) Analysis of water treatment measures of Liuhuanggou coal mine. Environ Protect **njiang 2:14–16 (in Chinese)
Banks D, Younger PL, Arnesen R-T, Iversen ER, Banks SB (1997) Mine-water chemistry: the good, the bad and the ugly. Environ Geol 32(3):157–174
Bao D (2001) The character of acid mine water and its cause in Yongding mine area. J Huainan Ind Technol 4:25–27 (in Chinese)
Brady KBC, Hornberger RJ, Fleeger G (1998) Influence of geology on postmining water quality: Northern Appalachian Basin. Coal Mine Drainage Prediction and Pollution Prevention in Pennsylvania. Department of Environmental Protection, Harrisburg, PA, pp 8.1–8.92
Cao J (2007) Brief talk on wastewater treatment of coal mine. Yunnan Environ Sci S1:1–3 (in Chinese)
Chang Y, Wei Z, Zhu X (2001) Comprehensive utilization of draining water resources in Laiwu mining area. China J Geol Haz Contr 1:26–30 (in Chinese)
Chen H, Zhang K (2010) Study of removing iron from mine water in Feicheng Dafeng power plant. Clean Coal Technol 1:120–123 (in Chinese)
Chen N, Fu Y, Cai C (2007) Study on fly ash treatment of acid mine drainage. Energy Environ Protect 4(27–29):32 (in Chinese)
Cravotta CA III (2008a) Dissolved metals and associated constituents in abandoned coal-mine discharges, Pennsylvania, USA. Part 1: constituent quantities and correlations. Appl Geochem 23(2):166–202
Cravotta CA III (2008b) Dissolved metals and associated constituents in abandoned coal-mine discharges, Pennsylvania, USA. Part 2: geochemical controls on constituent concentrations. Appl Geochem 23(2):203–226
Cravotta CA III, Ward SJ (2008) Downflow limestone beds for treatment of net-acidic, oxic, iron-laden drainage from a flooded anthracite mine, Pennsylvania, USA: 1. field evaluation. Mine Water Environ 27:67–85
Cui L, Qiu R, Wu J (2010) Mineralized mine water treatment with combined method of coagulation and electrodialysis. J Shanxi Univ Nat Sci 4:591–595 (in Chinese)
Dai Q (2012) New ideas of the coal mine water treatment and utilization in the Dashucun coal mine. Energy Environ Protect 5:50–52 (in Chinese)
Dong F, Zheng L, Liu Z (2007) Improved gray association analysis of mine water quality in the Fuxin mine region. J Liaoning Tech Univ S2:234–236 (in Chinese)
Dong H, Zhang R, Wu P (2012) Experiment study on treatment of acid mine drainage contaminant by sulfate reducing bacteria. Technol Water Treat 5:31–35 (in Chinese)
Fan H, Han S, Zhou R (2011) Research on the technology and mode for step utilization of water resources in Dongtan coal mine. Energy Environ Protect 4:44–47 (in Chinese)
Feng Q, Wang H, Li X, Hao L (2004) Characteristics and utilization of mine water in east China. J China Univ Min Technol 33(2):193–196
Ge H (2007) Brief talk on treating acid mine water discharged from water inrush accident of coal mine. Yunnan Environ Sci 6:64–65 (in Chinese)
Geidel G, Caruccio FT (2000) Geochemical factors affecting coal mine drainage quality. In: Barnhisel RI, Darmody RG, Daniels L (eds), Reclamation of drastically disturbed lands, 2nd edn, chapter 5. Agronomy Monograph 41, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp 105–129. ISBN:0-89118-146-6
Gu T, Dong H, Li L, Zhang L (2009) Analysis on water quality and drainage of productive waste water in main coal mine of Changji. Arid Environ Monitor 23(1):37–40 (in Chinese)
Guo X (2011) Research on utilization of mine water in Tongchuan mining area. Clean Coal Technol 17(1):80–83 (in Chinese)
Guo Z, Wang S, Zhu L (2008) Applied technology of mine water treatment and utilization. Coal Sci Technol 7:3–5 (in Chinese)
He X, Yang H, He Y (2010) Treatment of mine water high in Fe and Mn by modified manganese sand. Min Sci Technol China 20(4):571–575
Hu W (1998) The technology of treatment and utilization for coal mine water and wastewater. China Coal Industry Press, Bei**g
Huang P, Chen J (2011) The chemical features of ground and FDA model used to distinguish source of water burst in Jiaozuo mine area. Coal Geol Explor 2:42–46 (in Chinese)
Huang Y, Zhang G, Hu J (2010) Application of pellet fluidized bed on coal mine wastewater purification of Nanshan Colliery. Water Wastewater Eng 7:62–66 (in Chinese)
Jiao Z (2012) Treatment and research on containing fluorine mine water. Shanxi Coking Coal Sci Technol 5:30–33 (in Chinese)
Ju J, Dou S, Li X (2009) Basic ideas of circular economy in the mining industry. Conserv Util Miner Resour 5:1–6 (in Chinese)
Kou Y, Zhu Z, **u H (2011) Research on ecological use technology of highly mineralized mine water in Shendong mining area. China Water Wastewater 22:86–89 (in Chinese)
Li A (2008) Research on the exploitation of coal mine drainage and the economy benefit analysis. Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao (in Chinese)
Li L, Jiang Y, Guo Y (1999) The research of a comprehensive industrialization technology on the treatment of mining water containing much more sulphate anion. Coal Geol Explor 6:51–53 (in Chinese)
Li F, Yang J, He X (2006) Characteristics and treatment mechanism of mine water with high concentrations of iron and manganese. J China Coal Soc 6:727–730 (in Chinese)
Li X, Wang L, Liu H (2012) Mine water resource evaluation: with the Fuxin mining area as an example. Coal Geol Explor 2:49–54 (in Chinese)
Liu B, Liao S (2007) The present situation, utilization and protection of water resource. J Southwest Petrol Univ 6:1–11 (in Chinese)
Liu J, Guo J, Ma Z (2005) Preliminary study of comprehensive utilization of mine water in Ningdong mine. NW Coal 1:42–44 (in Chinese)
Liu Y, Wu Q, Zhao X (2013) Mine water quality characteristics and water environment evaluation of inner Mongolia Dongsheng coal field. Clean Coal Technol 1:101–102 (in Chinese)
Lottermoser BG (2010) Mine wastes: characterization, treatment and environmental impacts. Springer, Berlin
NDRC (2012) The mine water utilization development planning of China. National Development and Reform Commission, Bei**g
Plumlee GS, Smith KS, Montour MR, Ficklin WH, Mosier EL (1999) Geologic controls on the composition of natural waters and mine waters draining diverse mineral-deposit types. In: Filipek LH, Plumlee GS (eds) The environmental geochemistry of mineral deposits. Part B: case studies and research topics, vol 6B. Society of Economic Geologists, Littleton, CO, pp 373–432
Qin S, Zhu J, Zhu L (2001) Application of the new technology of iron acid mine drainage treatment. Coal Mine Environ Protect 05:41–43 (in Chinese)
Rose AW, Cravotta CA III (1998) Geochemistry of coal mine drainage. Coal mine drainage prediction and pollution prevention in Pennsylvania. Department of Environmental Protection, Harrisburg, PA, pp 1.1–1.22
Shan Z (1999) Chinese coal industry encyclopedia. China Coal Industry Press, Bei**g
Sun H, Zhao F, Li W (2007) Geochemical characteristics of acid mine drainage and sediments from coal mines. J China Univ Min Technol 02:221–226 (in Chinese)
Sun W, Wu Q, Dong D, Jiao J (2012) Avoiding coal-water conflicts during the development of China’s large coal-producing regions. Mine Water Environ 31:74–78
Wan J, Li Y, Yang R (2004) Mine-environmental-geologic issues and their restoration and treatment in Zaozhuang city. J Geol Haz Environ Preserv 03:26–30 (in Chinese)
Wang J (2000) The environmental influence of coal resource development and its treatment policies—take **azhuang coal mine of Shandong province as an example. J Heibei N Univ 4:544–547 (in Chinese)
Wang J (2009) Study on the purification process optimization for high-iron and manganese mine water. Hebei University of Engineering (in Chinese)
Wang H (2010) Characteristics of acid mine drainage and its pollution control. In: Proceedings of 4th international conference IEEE on Bioinformatics And Biomedical Engineering (ICBBE), pp 1–3
Wang Y, Cheng Q (2007) Experimental study on removing fluoride and sulfate from mine water. Jiangsu Environ Sci Technol 20:18–21 (in Chinese)
Wang H, Tang D, Zhou F (2008) Application of integral water purifier in processing coal mine acidity water with high suspended substances. J Guizhou Univ Technol Nat Sci 5:293–296 (in Chinese)
Wu D (2008) Research on treatment of acid mine water with high salty and high iron. Coal Sci Technol 8:110–112 (in Chinese)
** G (2011) Experimental research on reclamation of coal mine drainage in Bingchang mining area. **’ An University of Science and Technology, **’an (in Chinese)
**ao X, Wei L (2008) The research comprehensive use of the mine drainage of **mei Group. Ind Saf Environ Protect 1:12–13 (in Chinese)
**u H, Zhu Z (2009) Recycle on high-salinity mine water in Shendong mining area. Energy Environ Protect 6:31–33 (in Chinese)
Xu Y (2009) Study on mine water utilization in fourth mine Pindingshan mining area. Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo (in Chinese)
Xu C (2010) A simply analysis of the comprehensive treatment technique of mine water of Lingzhou mine of Shenning industry Group. Shenhua Sci Technol 4:46–48 (in Chinese)
Xu J (2011) Water treatment and utilization of **aotun coal mine. Guizhou Chem Ind 5:42–43 (in Chinese)
Xu G, Yue M, Yan J (2007) Analysis on chemical property of acid mine water and prevention in Sitai coal mine. Coal Sci Technol 9:106–108 (in Chinese)
Yan Y, Huang F, Cai X (2004) Preliminary study on the water chemistry features of the groundwater system in Renlou coal mine. West China Explor Eng 10:89–91 (in Chinese)
Yang H, He X, He Y (2009) Application of reverse osmosis technology in the treatment of highly mineralized mine water. Technol Water Treat 10:82–85 (in Chinese)
Yin G, Deng Y, Zheng J (1997) Source of high content sulphate in underground water of Yuezhuang in Yanzhou mining area. J Jiaozuo Inst Technol 1:18–22 (in Chinese)
Yin G, Fu X, Zhao Q (2002) The source of high fluorine content in groundwater and its geological structure factors in Yongcheng mining area. J Jiaozuo Inst Technol Nat Sci 2:110–113
Yin G, Wang Y, Xu H (2008) The formation mechanism and major treatment technology of acidic mine water. Environ Sci Manage 9:100–102 (in Chinese)
Yuan H, Shi H (2008) Research progress and prospect of coal mine water resource utilization. J Water Resour Water Eng 5:50–56 (in Chinese)
Zhai Y, Li Z, Deng Y, Wang X (2010) Experiment research on modified zeolite applied to adsorb flurine ion from mine water. Coal Sci Technol 9:121–124 (in Chinese)
Zhang X (2004) The research of coal mine drainage resources in Kailuan mine area. Hebei University of Technology, Tangshan (in Chinese)
Zhang X, Yin J (2010) Combination of lime and coagulation removing SO42- and F- from mine water. Energy Environ Protect 5:20–23 (in Chinese)
Zhang J, Shen Z, Li D (2000) Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of drainage water in coal mines of Zibo. Geol Rev 3:263–269 (in Chinese)
Zhao F, Sun H, Li W (2007) Migration of hazardous elements in acid coal mine drainage. J Coal Soc 3:261–266 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from both the Chinese Public Welfare Research Funds for Environmental Protection Industry (201109011) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). We also express our sincere gratitude to Drs. ** Lu, Yan Zhang, Yue Sun, Pei Liu, and **n Wang for their instruction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Q., Li, T., Qian, B. et al. Chemical Characteristics and Utilization of Coal Mine Drainage in China. Mine Water Environ 33, 276–286 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-014-0271-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-014-0271-y