Abstract
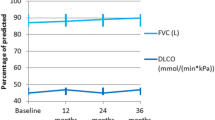
The availability of intravenous cyclophosphamide (CYC) pulse therapy for collagen vascular diseases (CVD)-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD) has been indicated. However, the standard protocol concerning the dosage and the interval of CYC infusion has not yet been established. The aim of this study is to elucidate the efficacy and the safety of our “divided administration” protocol of CYC for the treatment of CVD-ILD. The treatment protocol consists of two steps: step 1, CYC 400–500 mg at 10-day intervals for at least 30 days, and step 2, CYC 500 mg at 14-day intervals for at least 4 weeks. The ILD activities were monitored by respiratory symptoms, serum levels of KL-6 (a serological marker of IP), chest computed tomography (CT), and pulmonary function tests. Seventeen patients [nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), 12 patients; usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP), 4; lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia (LIP), 1] accomplished the study protocol. The sessions of CYC infusion ranged from 5 to 20 (mean, 8.3). In all patients, respiratory symptoms were improved and the serum levels of KL-6 were decreased (from 1572 ± 904 to 978 ± 392 U/ml; P < 0.01). Chest CT findings were improved in 4 patients (23.5%): they were all classified as NSIP; not deteriorated, 13 patients (76.5%). An improvement in the vital capacity percentage (%VC) was recognized in 10 patients (78.6%) and in diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide (%DLco) in 8 patients (61.5%). Nevertheless, mean %VC and mean %DLco did not change significantly. No major adverse event(s) occurred. The efficacy and safety of our “divided administration” protocol of CYC for CVD-ILD was demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Schnabel M Reuter WL Gross (1998) ArticleTitleIntravenous pulse cyclophosphamide in the treatment of interstitial lung disease due to collagen vascular diseases Arthritis Rheum 41 1215–20 Occurrence Handle9663478 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1529-0131(199807)41:7<1215::AID-ART11>3.0.CO;2-Y Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkslWjtLo%3D
SV Kocheril BE Appleton EC Somers EA Kazerooni KR Flaherty FJ Martinez et al. (2005) ArticleTitleComparison of disease progression and mortality of connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease and idiopathic interstitial pneumonia Arthritis Rheum 53 549–57 Occurrence Handle16082627 Occurrence Handle10.1002/art.21322 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2MvisValtg%3D%3D
GW Hunninghake AR Kalica (1995) ArticleTitleApproaches to the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151 915–8 Occurrence Handle7881692 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M7oslCmtA%3D%3D
VD Steen JK Lanz SuffixJr C Conte GR Owens TA Medsger SuffixJr (1994) ArticleTitleTherapy for severe interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. A retrospective study Arthritis Rheum 37 1290–6 Occurrence Handle7945491 Occurrence Handle10.1002/art.1780370904 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2M%2Fjt1ansg%3D%3D
MA Johnson S Kwan NJ Snell AJ Nunn JH Darbyshire M Turner-Warwick (1989) ArticleTitleRandomised controlled trial comparing prednisolone alone with cyclophosphamide and low dose prednisolone in combination in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis Thorax 44 280–8 Occurrence Handle2669218 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1MzkslCgug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1136/thx.44.4.280
AR Eiser HM Shanies (1994) ArticleTitleTreatment of lupus interstitial lung disease with intravenous cyclophosphamide Arthritis Rheum 37 428–31 Occurrence Handle8129799 Occurrence Handle10.1002/art.1780370318 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2c7nsF2qsQ%3D%3D
T Shinohara T Hidaka Y Matsuki T Ishizuka M Takamizawa M Kawakami et al. (1997) ArticleTitleRapidly progressive interstitial lung disease associated with dermatomyositis responding to intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy Intern Med 36 519–23 Occurrence Handle9240505 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2szot1Gjsw%3D%3D
N Kohno S Kyoizumi Y Awaya H Fukuhara M Yamakido M Akiyama (1989) ArticleTitleNew serum indicator of interstitial pneumonitis activity. Sialylated carbohydrate antigen KL-6 Chest 96 68–73 Occurrence Handle2661160 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1M3ovFajtg%3D%3D
N Kohno (1999) ArticleTitleSerum marker KL-6/MUC1 for the diagnosis and management of interstitial pneumonitis J Med Invest 46 151–8 Occurrence Handle10687309 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7ltF2htw%3D%3D
American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277–304
T Fukuda M Setoguchi K Inaba H Shoji T Tahara (1991) ArticleTitleThe antiemetic profile of Y-25130, a new selective 5-HT3 receptor antagonist Eur J Pharmacol 196 299–305 Occurrence Handle1654255 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-2999(91)90443-T Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXkt1Wqu7c%3D
HA Austin Suffix3rd JH Klippel JE Balow NG le Riche AD Steinberg PH Plotz et al. (1986) ArticleTitleTherapy of lupus nephritis. Controlled trial of prednisone and cytotoxic drugs N Engl J Med 314 614–9 Occurrence Handle3511372 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM198603063141004
WJ McCune J Golbus W Zeldes P Bohlke R Dunne DA Fox (1988) ArticleTitleClinical and immunologic effects of monthly administration of intravenous cyclophosphamide in severe systemic lupus erythematosus N Engl J Med 318 1423–31 Occurrence Handle3259286 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c3hs1Ogsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM198806023182203
AD Steinberg SC Steinberg (1991) ArticleTitleLong-term preservation of renal function in patients with lupus nephritis receiving treatment that includes cyclophosphamide versus those treated with prednisone only Arthritis Rheum 34 945–50 Occurrence Handle1859488 Occurrence Handle10.1002/art.1780340803 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3MzhsFKhug%3D%3D
GS Hoffman RY Leavitt TA Fleisher JR Minor AS Fauci (1990) ArticleTitleTreatment of Wegener's granulomatosis with intermittent high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide Am J Med 89 403–10 Occurrence Handle2220874 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-9343(90)90367-M Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M%2Fit1OqsQ%3D%3D
M Haubitz S Schellong U Gobel HJ Schurek D Schaumann KM Koch R Brunkhorst (1998) ArticleTitleIntravenous pulse administration of cyclophosphamide versus daily oral treatment in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and renal involvement: a prospective, randomized study Arthritis Rheum 41 1835–44 Occurrence Handle9778225 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1529-0131(199810)41:10<1835::AID-ART16>3.0.CO;2-Q Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXmvFWmtro%3D
R Giacomelli G Valentini F Salsano P Cipriani P Sambo ML Conforti et al. (2002) ArticleTitleCyclophosphamide pulse regimen in the treatment of alveolitis in systemic sclerosis J Rheumatol 29 731–6 Occurrence Handle11950014 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjtFGltLw%3D
I Pakas JP Ioannidis K Malagari FN Skopouli HM Moutsopoulos PG Vlachoyiannopoulos (2002) ArticleTitleCyclophosphamide with low or high dose prednisolone for systemic sclerosis lung disease J Rheumatol 29 298–304 Occurrence Handle11842824 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhsF2iu78%3D
DJ Helfrich B Banner VD Steen TA Medsger SuffixJr (1989) ArticleTitleNormotensive renal failure in systemic sclerosis Arthritis Rheum 32 1128–34 Occurrence Handle2775321 Occurrence Handle10.1002/anr.1780320911 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1MznsVeltA%3D%3D
WB Gruhn JA Diaz-Buxo (1987) ArticleTitleCyclosporine treatment of steroid resistant interstitial pneumonitis associated with dermatomyositis/polymyositis J Rheumatol 14 1045–7 Occurrence Handle3323505 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c7hvVKmsw%3D%3D
Y Nawata K Kurasawa K Takabayashi S Miike N Watanabe M Hiraguri et al. (1999) ArticleTitleCorticosteroid resistant interstitial pneumonitis in dermatomyositis/polymyositis: prediction and treatment with cyclosporine J Rheumatol 26 1527–33 Occurrence Handle10405940 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXksFemtLY%3D
M Okada K Suzuki T Nakanishi M Nakashima (2006) ArticleTitleThe serum levels of KL-6 are positively correlated with those of CA15-3 in patients with interstitial pneumonia associated with collagen diseases Respirology 11 509–10 Occurrence Handle16771927 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.00881.x
A Yokoyama N Kohno H Hamada M Sakatani E Ueda K Kondo et al. (1998) ArticleTitleCirculating KL-6 predicts the outcome of rapidly progressive idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158 1680–4 Occurrence Handle9817725 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M%2FjsVOlsg%3D%3D
A Yokoyama K Kondo M Nakajima T Matsushima T Takahashi M Nishimura et al. (2006) ArticleTitlePrognostic value of circulating KL-6 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Respirology 11 217–20 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.00834.x
S Bandoh J Fujita Y Ohtsuki Y Ueda S Hojo M Tokuda et al. (2000) ArticleTitleSequential changes of KL-6 in sera of patients with interstitial pneumonia associated with polymyositis/dermatomyositis Ann Rheum Dis 59 257–62 Occurrence Handle10733471 Occurrence Handle10.1136/ard.59.4.257 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3c**vFajtr8%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, M., Suzuki, K., Matsumoto, M. et al. Intermittent intravenous cyclophosphamide pulse therapy for the treatment of active interstitial lung disease associated with collagen vascular diseases. Mod Rheumatol 17, 131–136 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0554-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-007-0554-2