Abstract
Background
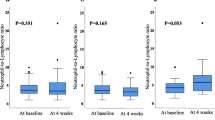
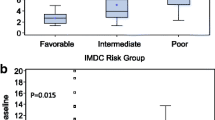
The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with clinical outcomes of various cancers. This study aimed to evaluate whether pretreatment NLR can be used as a prognostic factor in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) receiving targeted therapy.
Methods
In this single-center retrospective study, the Kaplan–Meier method was used to estimate progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of 373 mRCC patients receiving targeted therapy. The survival outcomes of patients with high (≥2.2) and low (<2.2) pretreatment NLRs were compared by log-rank test, and Cox proportional hazard regression model was used to compare OS and PFS between groups.
Results
The overall median PFS and OS times for all 373 patients were 18.4 and 34.3 months, respectively. Patients with high NLRs had significantly shorter median OS (28.8 vs 410 months, P = 0.005) and PFS (15.4 vs 23.9 months, P = 0.001) than those with low NLRs. After adjusting for confounding variables, each unit increase of NLR was associated with a 40 % increase in mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 1.391; 95 % confidence interval [CI] 1.022–1.894; P = 0.036). High NLR was also an independent predictor of poor PFS (HR 1.544; 95 % CI 1.166–2.045; P = 0.002).
Conclusion
Pretreatment NLR may be an independent prognostic factor for mRCC patients who are receiving targeted therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta K, Miller JD, Li JZ et al (2008) Epidemiologic and socioeconomic burden of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): a literature review. Cancer Treat Rev 34:193–205
Athar U, Gentile TC (2008) Treatment options for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a review. Can J Urol 15:3954–3966
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Shin JH, Kim CJ, Jeon EJ et al (2015) Overexpression of C-reactive protein as a poor prognostic marker of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas. J Pathol Transl Med 49:105–111
Beuselinck B, Vano YA, Oudard S et al (2014) Prognostic impact of baseline serum C-reactive protein in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treated with sunitinib. BJU Int 114:81–89
Han S, Huang Y, Li Z et al (2015) The prognostic role of preoperative serum albumin levels in glioblastoma patients. BMC Cancer 15:108
Ito H, Shioi K, Murakami T et al (2012) C-reactive protein in patients with advanced metastatic renal cell carcinoma: usefulness in identifying patients most likely to benefit from initial nephrectomy. BMC Cancer 12:337
Wei X, Huang F, Wei Y et al (2014) Low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio predicts unfavorable prognosis in non-germinal center type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Res 38:694–698
Pichler M, Hutterer GC, Stoeckigt C et al (2013) Validation of the pre-treatment neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in a large European cohort of renal cell carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer 108:901–907
Park YH, Ku JH, Kwak C et al (2014) Post-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting prognosis in patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib as first line therapy. Springerplus 3:243
Gunduz S, Mutlu H, Uysal M et al (2014) Prognostic value of hematologic parameters in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma using tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:3801–3804
Heng DY, **e W, Regan MM et al (2013) External validation and comparison with other models of the international metastatic renal-cell carcinoma database consortium prognostic model: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 14:141–148
Vakkila J, Lotze MT (2004) Inflammation and necrosis promote tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol 4:641–648
Kaynar M, Yildirim ME, Badem H et al (2014) Bladder cancer invasion predictability based on preoperative neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio. Tumour Biol 35:6601–6605
Dalpiaz O, Ehrlich GC, Mannweiler S et al (2014) Validation of pretreatment neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in a European cohort of patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int 114:334–339
Chen J, Hong D, Zhai Y et al (2015) Meta-analysis of associations between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and prognosis of gastric cancer. World J Surg Oncol 13:122
Keizman D, Ish-Shalom M, Huang P et al (2012) The association of pre-treatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with response rate, progression free survival and overall survival of patients treated with sunitinib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 48:202–208
Santoni M, De Giorgi U, Iacovelli R et al (2013) Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio may be associated with the outcome in patients treated with everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 109:1755–1759
Heng DY, **e W, Regan MM et al (2009) Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor–targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol 27:5794–5799
Pensa M, Swede H, Brockmeyer JA et al (2009) Patterns of HER2 testing in the management of primary breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol 33:113–117
Garcia-Donas J, Esteban E, Leandro-Garcia LJ et al (2011) Single nucleotide polymorphism associations with response and toxic effects in patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma treated with first-line sunitinib: a multicentre, observational, prospective study. Lancet Oncol 12:1143–1150
Ye DW, Zhang HL (2014) Critical appraisal of sorafenib in the treatment of Chinese patients with renal cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther 7:925–935
Weitzman SA, Gordon LI (1990) Inflammation and cancer: role of phagocyte-generated oxidants in carcinogenesis. Blood 76:655–663
Kusumanto YH, Dam WA, Hospers GA et al (2003) Platelets and granulocytes, in particular the neutrophils, form important compartments for circulating vascular endothelial growth factor. Angiogenesis 6:283–287
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A et al (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454:436–444
Rosenberg SA (2001) Progress in human tumour immunology and immunotherapy. Nature 411:380–384
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. NSFC 81001131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
G. - M. Zhang and Y. Zhu contribute equally to the work.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, GM., Zhu, Y., Gu, WJ. et al. Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts prognosis in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving targeted therapy. Int J Clin Oncol 21, 373–378 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-015-0894-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-015-0894-4