Abstract
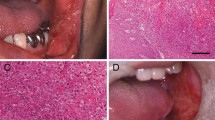
We report an extremely rare case of spindle cell carcinoma of the sinonasal cavity. A 75-year-old man was admitted to our hospital because of right nasal obstruction. Nasal endoscopy showed a polypoid tumor measuring 3 × 3 cm at the nasal septum in the right nasal cavity, and an excisional biopsy was performed. Computed tomography (CT) demonstrated the nasal tumor extended to the maxillary sinus. Histologically, the tumor consisted of malignant spindle cells with hyperchromatic nuclei. Mitotic figures and necrosis were recognized. In some areas, edematous changes were recognized. No apparent differentiation was noted. The tumor cells were free of keratinization and intercellular bridge formations; therefore, there were no squamous cell components. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for pancytokeratin, cytokeratin (CK)5/6, CK18, CK19, high molecular weight CK, p63, and vimentin. The tumor cells were negative for epithelial membrane antigen, CK7, CK14, p53 protein, S100 protein, HMB45, chromogranin, synaptophysin, CD34, CD56, glial fibrillary acidic protein, neuron-specific enolase, neurofilaments, α-smooth muscle actin, neuroblastoma, myoglobin, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), carbohydrate antigen (CA)19-9, CD3, CD20, CD30, CD45RO, and CD45. A pathological diagnosis of spindle cell carcinoma of sinonasal lesion was made. The patient underwent resection of right maxilla followed by chemotherapy and radiation and was alive without metastasis 5 years after initial presentation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terada T, Kawaguchi M, Furukawa K et al (2002) Minute mixed ductal-endocrine carcinoma of the pancreas with predominant intraductal growth. Pathol Int 52:740–746
Terada T (2009) Gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the uterus: a case report with genetic analyses of c-kit and PDGFRA genes. Int J Gynecol Pathol 28:29–34
Terada T (2009) Large endocervical polyp with cartilaginous and osseous metaplasia: a hitherto unreported entity. Int J Gynecol Pathol 28:98–100
Olsen SH, Thomas DG, Lucas DR (2006) Cluster analysis of immunohistochemical profiles in synovial sarcoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, and Ewing sarcoma. Mod Pathol 19:659–668
Folpe AL, Schmidt RA, Chapman D et al (1998) Poorly differentiated synovial sarcoma: immunohistochemical distinction from primitive neuroectodermal tumors and high grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Am J Surg Pathol 22:673–682
Yip YL, Tsao SW (2008) Regulation of p63 expression in primary and immortalized nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Int J Oncol 33:713–724
Nylander K, Vojtesek B, Nenutil R et al (2002) Differential expression of p63 isoforms in normal tissue and neoplastic cells. J Pathol 198:417–427
Minton TJ, Goyal P (2009) Endoscopic treatment of maxillary sinus spindle cell carcinoma. J Otolarungol Head Neck Surg 38:E45–E50
Howard SN, Bond WR, Hong IS et al (2007) Right maxillary sinus sarcomatoid Carcinoma (sarcomatoid/spindle cell carcinoma). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:355–357
Mills SE, Gaffey MJ, Frierson HF Jr (1997) Spindle cell carcinoma. In: Rosai J, Sobin LH (eds) Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Atlas of tumor pathology. Tumors of the upper aerodigestive trac and yeart, 3rd series. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC, pp 76–80
Colby TV, Koss MN, Travis WD (1994) Squamous cell carcinoma and variants. In: Ropsai J, Sobin LH (eds) Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Atlas of tumor pathology. Tumors of the lower respiratory tract, 3rd series. Armed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC, pp 157–178
Lewis JE, Olsen KD, Sebo TJ (1997) Spindle cell carcinoma of the larynx: review of 26 cases including DNA content and immunohistochemistry. Hum Pathol 28:664–673
Rosai J (2004) Respiratory tract. In: Roai J (ed) Rosai and Ackerman’s surgical pathology, 9th edn. St. Louis, Mosby, pp 305–334
Corrin B, Wick MR, Chang YL (2004) Sarcomatoid carcinoma. In: Travis D, Brambillia E, Muller-Hermelink K, Harris CC et al (eds) World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics. Tumor of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. IARC press, Lyon, pp 53–58
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Terada, T., Kawasaki, T. Spindle cell carcinoma of the nasal cavity. Int J Clin Oncol 16, 165–168 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-010-0121-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-010-0121-2