Abstract
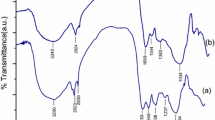
In this study, the marine macroalgae Sargassum cymosum was used for the purification of waters contaminated with trivalent chromium. FTIR analysis revealed a high heterogeneity of the biosorbent surface, as indicated by the different absorption peaks. Biomass titration revealed two main functional groups, carboxylic and hydroxyl. The pK1,H value and the number of carboxylic groups were estimated as 3.05 ± 0.01 and 1.90 ± 0.01 mmol g−1, respectively. An equilibrium model considering the metal speciation in aqueous solution was able to predict the experimental data at different pH values. Adsorption of chromium increases significantly with an increase of the solution pH. Furthermore, the speciation of the binding sites as a function of the solution pH was predicted, showing that Cr(OH)2+ has a higher affinity than Cr3+ to the binding sites. A mass transfer model considering an intraparticle diffusion resistance was able to predict the kinetic data, showing that Cr3+ diffuses faster that CrOH2+.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman VJ, Chapman DJ (1980) Seaweeds and their uses. Chapman and Hall, London
Chapra SC, Canale RP (1998) Numerical methods for engineers, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, Boston
Costa JF, Vilar VJP, Botelho CMS, da Silva EAB, Boaventura RAR (2010) Application of the Nernst–Planck approach to lead ion exchange in Ca-loaded Pelvetia canaliculata. Water Res 44(13):3946–3958. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2010.04.033
Davis TA, Volesky B, Mucci A (2003) A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res 37(18):4311–4330. doi:10.1016/s0043-1354(03)00293-8
Dean JA (ed) (1979) Lange’s handbook of chemistry, 12th edn. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Dittert IM, Vilar VJP, da Silva EAB, de Souza SMAGU, de Souza AAU, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2012) Adding value to marine macro-algae Laminaria digitata through its use in the separation and recovery of trivalent chromium ions from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 193–194:348–357. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.04.048
Espinoza-Quiñones FR, Módenes AN, Câmera AS, Stutz G, Tirao G, Palácio SM, Kroumov AD, Oliveira AP, Alflen VL (2010) Application of high resolution X-ray emission spectroscopy on the study of Cr ion adsorption by activated carbon. Appl Radiat Isot 68(12):2208–2213. doi:10.1016/j.apradiso.2010.06.006
Fahim NF, Barsoum BN, Eid AE, Khalil MS (2006) Removal of chromium(III) from tannery wastewater using activated carbon from sugar industrial waste. J Hazard Mater 136(2):303–309. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.014
Figueira MM, Volesky B, Mathieu HJ (1999) Instrumental analysis study of iron species biosorption by Sargassum biomass. Environ Sci Technol 33(11):1840–1846. doi:10.1021/es981111p
Fourest E, Volesky B (1995) Contribution of sulfonate groups and alginate to heavy metal biosorption by the dry biomass of Sargassum fluitans. Environ Sci Technol 30(1):277–282. doi:10.1021/es950315s
Glueckauf E, Coates JI (1947) Theory of chromatography. Part IV. The influence of incomplete equilibrium on the front boundary of chromatograms and on the effectiveness of separation. J Chem Soc 1315–1321
Gode F, Pehlivan E (2006) Removal of chromium(III) from aqueous solutions using Lewatit S 100: the effect of pH, time, metal concentration and temperature. J Hazard Mater 136(2):330–337. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.021
González Bermúdez Y, Rodríguez Rico IL, Guibal E, Calero de Hoces M, Martín-Lara MÁ (2012) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution by Sargassum muticum brown alga. Application of statistical design for process optimization. Chem Eng J 183:68–76. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.022
Han X, Wong YS, Wong MH, Tam NFY (2007) Biosorption and bioreduction of Cr(VI) by a microalgal isolate, Chlorella miniata. J Hazard Mater 146(1–2):65–72. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.11.053
Marcus Y, Kertes AS (1969) Ion exchange and solvent extraction of metal complexes. Wiley, London
Murphy V, Hughes H, McLoughlin P (2008) Comparative study of chromium biosorption by red, green and brown seaweed biomass. Chemosphere 70(6):1128–1134. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.015
Panda M, Bhowal A, Datta S (2011) Removal of hexavalent chromium by biosorption process in rotating packed bed. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8460–8466. doi:10.1021/es2015346
Park D, Yun Y-S, Park JM (2004) Reduction of hexavalent chromium with the brown seaweed Ecklonia biomass. Environ Sci Technol 38(18):4860–4864. doi:10.1021/es035329+
Park D, Yun Y-S, Jo JH, Park JM (2006) Biosorption process for treatment of electroplating wastewater containing Cr(VI): laboratory-scale feasibility test. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(14):5059–5065. doi:10.1021/ie060002d
Park D, Yun Y-S, Lee DS, Park JM (2011) Optimum condition for the removal of Cr(VI) or total Cr using dried leaves of Pinus densiflora. Desalination 271(1–3):309–314. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.12.053
Percival E, McDowell RH (1967) Chemistry and enzymology of marine algal polysaccharides. Academic Press, London
Pérez Marín AB, Aguilar MI, Meseguer VF, Ortuño JF, Sáez J, Lloréns M (2009) Biosorption of chromium(III) by orange (Citrus cinensis) waste: batch and continuous studies. Chem Eng J 155(1–2):199–206. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2009.07.034
Petzold L (1983) Automatic selection of methods for solving stiff and nonstiff systems of ordinary differential equations. SIAM J Sci Stat Comput 4(1):136–148
Prabhakaran SK, Vijayaraghavan K, Balasubramanian R (2009) Removal of Cr(VI) ions by spent tea and coffee dusts: reduction to Cr(III) and biosorption. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(4):2113–2117. doi:10.1021/ie801380h
Raize O, Argaman Y, Yannai S (2004) Mechanisms of biosorption of different heavy metals by brown marine macroalgae. Biotechnol Bioeng 87(4):451–458. doi:10.1002/bit.20136
Reid RC, Prausnitz JM, Poling BE (eds) (1987) The properties of gases and liquids, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Schiewer S, Volesky B (1995) Modeling of the proton–metal ion exchange in biosorption. Environ Sci Technol 29(12):3049–3058. doi:10.1021/es00012a024
Sheng PX, Ting Y-P, Chen JP, Hong L (2004) Sorption of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel by marine algal biomass: characterization of biosorptive capacity and investigation of mechanisms. J Colloid Interface Sci 275(1):131–141. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.01.036
Silva E, Costa C, Vilar V, Botelho C, Larosi M, Saracho J, Boaventura R (2012) Water remediation using calcium phosphate derived from marine residues. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(3):989–1003. doi:10.1007/s11270-011-0918-2
Sud D, Mahajan G, Kaur MP (2008) Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions—a review. Bioresour Technol 99(14):6017–6027. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.064
Tahir SS, Naseem R (2007) Removal of Cr(III) from tannery wastewater by adsorption onto bentonite clay. Sep Purif Technol 53(3):312–321. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2006.08.008
Uluozlu OD, Sari A, Tuzen M, Soylak M (2008) Biosorption of Pb(II) and Cr(III) from aqueous solution by lichen (Parmelina tiliaceae) biomass. Bioresour Technol 99(8):2972–2980. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.06.052
Vilar VJP, Valle JAB, Bhatnagar A, Santos JC, Guelli U, de Souza SMA, de Souza AAU, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2012) Insights into trivalent chromium biosorption onto protonated brown algae Pelvetia canaliculata: distribution of chromium ionic species on the binding sites. Chem Eng J 200–202:140–148. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.023
Wang J, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27(2):195–226. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.11.002
Yun Y-S, Park D, Park JM, Volesky B (2001) Biosorption of trivalent chromium on the brown seaweed biomass. Environ Sci Technol 35(21):4353–4358. doi:10.1021/es010866k
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support from Projeto MECPETRO—Programa de Formação de Recursos Humanos em Engenharias Mecânica e Química—PRH009/ANP; CAPES, supported by the international cooperation project—Convênio CAPES/FCT n. 279/2010; and the project PEst-C/EQB/LA0020/2011, financed by FEDER through COMPETE—Programa Operacional Factores de Competitividade and FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia. V. J. P. Vilar acknowledges financial support from Programme Ciência 2008 (FCT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Souza, F.B., de Souza, S.M.A.G.U., de Souza, A.A.U. et al. Modeling of trivalent chromium speciation in binding sites of marine macroalgae Sargassum Cymosum . Clean Techn Environ Policy 15, 987–997 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0573-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0573-3