Abstract
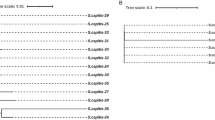
Glycopeptides and linezolid are the most widely used antibiotics to treat infections by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. We report the presence of various isolates of methicillin-resistant S. hominis subsp. hominis with resistance to linezolid and reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides. We studied ten blood culture isolates of S. hominis subsp. hominis from nine patients admitted to our hospital. Etest was used to study susceptibility to antibiotics commonly prescribed against staphylococci. Domain V region of the 23S rRNA gene was amplified and sequenced to detect possible mutations that confer resistance to linezolid. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) was used for the clonality study of isolates. All isolates were resistant to oxacillin, gentamicin, levofloxacin, cotrimoxazole, and linezolid, and susceptible to tigecycline and daptomycin. Nine of the isolates were resistant to erythromycin and clindamycin, and showed heterogeneous resistance to glycopeptides. C2190T, G2603T, and G2474T mutations were detected in domain V of the 23S rRNA gene. PFGE showed the presence of two different clones. This report alerts to the possible appearance of clinical strains of methicillin-resistant staphylococci with intermediate resistance to glycopeptides, resistance to linezolid, and multiple resistance to other second-line antibiotics.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shorr AF, Lipman J (2007) Resistance in the intensive care unit: whose problem is it and how can intensivists help? Crit Care Med 35:299–301
MacKenzie FM, Bruce J, Struelens MJ et al (2007) Antimicrobial drug use and infection control practices associated with the prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in European hospitals. Clin Microbiol Infect 13:269–276
Ruiz de Gopegui E, Oliver A, Galmés MI et al (2005) Consolidation of a Staphylococcus aureus multiresistant clone not related to the Iberian in a hospital from Mallorca. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 23:140–144
Hiramatsu K, Hanaki H, Ino T et al (1997) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clinical strain with reduced vancomycin susceptibility. J Antimicrob Chemother 40:135–136
Chang S, Sievert DM, Hageman JC et al (2003) Infection with vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus containing the vanA resistance gene. N Engl J Med 348:1342–1347
Chiew YF, Charles M, Johnstone MC et al (2007) Detection of vancomycin heteroresistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus and vancomycin intermediate resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis by means of vancomycin screening agar. Pathology 39:375–377
Walsh TR, Bolmström A, Qwärnström A et al (2001) Evaluation of current methods for detection of staphylococci with reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides. J Clin Microbiol 39:2439–2444
Walsh TR, Howe RA (2002) The prevalence and mechanisms of vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:657–675
Ariza J, Pujol M, Cabo J et al (1999) Vancomycin in surgical infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with heterogeneous resistance to vancomycin. Lancet 353:1587–1588
Charles PGB, Ward PB, Johnson PDR et al (2004) Clinical features associated with bacteremia due to heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis 38:448–451
Cha R, Brown WJ, Rybak MJ (2003) Bactericidal activities of daptomycin, quinupristin-dalfopristin, and linezolid against vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3960–3963
Huang YT, Liao CH, Teng LJ et al (2008) Comparative bactericidal activities of daptomycin, glycopeptides, linezolid and tigecycline against blood isolates of gram-positive bacteria in Taiwan. Clin Microbiol Infect 14:124–129
Grau S, Aguado JM, Mateu-de Antonio J et al (2007) Economic evaluation of linezolid versus teicoplanin for the treatment of infections caused by gram-positive microorganisms in Spain. J Chemother 19:398–409
Swaney SM, Aoki H, Ganoza MC et al (1998) The oxazolidinone linezolid inhibits initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42:3251–3255
Tsiodras S, Gold HS, Sakoulas G et al (2001) Linezolid resistance in a clinical isolate of Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 358:207–208
Tarazona RE, Padilla TP, Gómez JC et al (2007) First report in Spain of linezolid non-susceptibility in a clinical isolate of Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Int J Antimicrob Agents 30:277–278
Werner G, Strommenger B, Klare I et al (2004) Molecular detection of linezolid resistance in Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis by use of 5′ nuclease real-time PCR compared to a modified classical approach. J Clin Microbiol 42:5327–5331
Hong T, Li X, Wang J et al (2007) Sequential linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates with G2576T mutation. J Clin Microbiol 45:3277–3280
Kelly S, Collins J, Maguire M et al (2008) An outbreak of colonization with linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis in an intensive therapy unit. J Antimicrob Chemother 61:901–907
Meka VG, Pillai SK, Sakoulas G et al (2004) Linezolid resistance in sequential Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated with a T2500A mutation in the 23S rRNA gene and loss of a single copy of rRNA. J Infect Dis 190:311–317
Mendes RE, Deshpande LM, Castanheira M et al (2008) First report of cfr-mediated resistance to linezolid in human staphylococcal clinical isolates recovered in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:2244–2246
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2007) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; seventeenth informational supplement. CLSI publication M100-S17. CLSI, Wayne, PA, USA
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) Steering Committee (2006) EUCAST technical note on tigecycline. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:1147–1149
Voss A, Mouton JW, van Elzakker EP et al (2007) A multi-center blinded study on the efficiency of phenotypic screening methods to detect glycopeptide intermediately susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (GISA) and heterogeneous GISA (h-GISA). Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 6:9
Murchan S, Kaufmann ME, Deplano A et al (2003) Harmonization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for epidemiological ty** of strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a single approach developed by consensus in 10 European laboratories and its application for tracing the spread of related strains. J Clin Microbiol 41:1574–1585
Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV et al (1995) Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain ty**. J Clin Microbiol 33:2233–2239
Kolar M, Urbanek K, Vagnerova I et al (2006) The influence of antibiotic use on the occurrence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J Clin Pharm Ther 31:67–72
Potoski BA, Adams J, Clarke L et al (2006) Epidemiological profile of linezolid-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin Infect Dis 43:165–171
Perdelli F, Dallera M, Cristina ML et al (2008) A new microbiological problem in intensive care units: environmental contamination by MRSA with reduced susceptibility to glycopeptides. Int J Hyg Environ Health 211:213–218
Simpson RA, Spencer AF, Speller DC et al (1986) Colonization by gentamicin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis in a special care baby unit. J Hosp Infect 7:108–120
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2007) Information about MRSA for Healthcare Personnel [electronic guide]. Available online at: http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dhqp/ar_mrsa_healthcareFS.html [consulted 29 March 2008]
Lincopan N, de Almeida LM, Elmor de Araújo MR et al (2009) Linezolid resistance in Staphylococcus epidermidis associated with a G2603T mutation in the 23S rRNA gene. Int J Antimicrob Agents 34:281–282. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.02.023
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorlozano, A., Gutierrez, J., Martinez, T. et al. Detection of new mutations conferring resistance to linezolid in glycopeptide-intermediate susceptibility Staphylococcus hominis subspecies hominis circulating in an intensive care unit. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 29, 73–80 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-009-0823-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-009-0823-4