Abstract
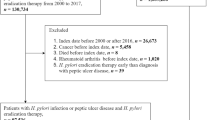
Several previous studies have suggested a relationship between GERD and RA. However, no study has investigated the bidirectional relationship between GERD and RA. This study aimed to evaluate the causal relationships between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Participants aged ≥ 20 years old in the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service-National Sample Cohort from 2002 to 2013 were enrolled. In study I, 132,140 GERD participants were 1:2 matched with 264,280 control I participants. In study II, 6615 RA participants were 1:4 matched with 26,460 control II participants. Both control I and control II groups were matched with their study groups for age, sex, income, and region of residence. The occurrence of RA (study I) and GERD (study II) were followed up in both the study and control groups. The hazard ratios (HRs) of GERD for RA (study I) and of RA for GERD (study II) were analysed using stratified Cox-proportional hazards models. In study I, 0.8% (1,034/132,140) of the GERD group and 0.5% (1,290/264,280) of the control I group had RA (P < 0.001). The GERD group demonstrated a 1.49-fold higher adjusted HR than did the control I group (95% confidence interval (95% CI) = 1.37-1.62, P < 0.001). In study II, 22.5% (1,490/6,615) of the RA group and 15.2% (4,034/26,460) of the control II group had GERD (P < 0.001). The RA group showed a 1.46-fold higher adjusted HR than did the control II group (95% CI = 1.38–1.55, P < 0.001). GERD and RA have bidirectional associations in Korean adult population.
Key Points • Several previous studies have suggested a relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). • However, no study has investigated the bidirectional relationship between GERD and RA. • This is the first study to present a bidirectional relationship between GERD and RA. • GERD and RA have bidirectional relations with each other. |


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB (2016) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 388(10055):2023–2038. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8
Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA (2006) Incidence and prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis, based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36(3):182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.08.006
Won S, Cho SK, Kim D, Han M, Lee J, Jang EJ, Sung YK, Bae SC (2018) Update on the prevalence and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in Korea and an analysis of medical care and drug utilization. Rheumatol Int 38(4):649–656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3925-9
Millar K, Lloyd SM, McLean JS, Batty GD, Burns H, Cavanagh J et al (2013) Personality, socio-economic status and inflammation: cross-sectional, population-based study. PLoS One 8(3):e58256. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058256
Scher JU, Littman DR, Abramson SB (2016) Microbiome in inflammatory arthritis and human rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum 68(1):35–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39259
Li R, Tian C, Postlethwaite A, Jiao Y, Garcia-Godoy F, Pattanaik D, Wei D, Gu W, Li J (2017) Rheumatoid arthritis and periodontal disease: what are the similarities and differences? Int J Rheum Dis 20(12):1887–1901. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13240
Sabharwal UK, Vaughan JH, Fong S, Bennett PH, Carson DA, Curd JG (1982) Activation of the classical pathway of complement by rheumatoid factors. Assessment by radioimmunoassay for C4. Arthritis Rheum 25(2):161–167
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365(23):2205–2219. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1004965
Liao KP (2017) Cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 27(2):136–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcm.2016.07.006
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R, Global Consensus G (2006) The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol 101(8):1900–1920; quiz 43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x
Rubenstein JH, Chen JW (2014) Epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterol Clin N Am 43(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2013.11.006
Mikami DJ, Murayama KM (2015) Physiology and pathogenesis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Clin North Am 95(3):515–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2015.02.006
Souza RF, Bayeh L, Spechler SJ, Tambar UK, Bruick RK (2017) A new paradigm for GERD pathogenesis. Not acid injury, but cytokine-mediated inflammation driven by HIF-2alpha: a potential role for targeting HIF-2alpha to prevent and treat reflux esophagitis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 37:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2017.10.004
Chen Y (2015) Gastroesophageal reflux disease and non-digestive tract diseases. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(5):685–692. https://doi.org/10.1586/17474124.2015.1012495
Linz D, Hohl M, Vollmar J, Ukena C, Mahfoud F, Bohm M (2017) Atrial fibrillation and gastroesophageal reflux disease: the cardiogastric interaction. Europace. 19(1):16–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/euw092
Lin HC, **rasagar S, Lee CZ, Huang CC, Chen CH (2017) The association between gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and subsequent rheumatoid arthritis occurrence: a nested case-control study from Taiwan. BMJ Open 7(11):e016667. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016667
Miura Y, Fukuda K, Maeda T, Kurosaka M (2014) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 24(2):291–295. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2013.843749
Nampei A, Shi K, Ebina K, Tomita T, Sugamoto K, Yoshikawa H et al (2013) Prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms and related factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 52(2):179–184. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.12-83
Kim SY, Kim HJ, Lim H, Kong IG, Kim M, Choi HG (2018) Bidirectional association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and depression: two different nested case-control studies using a national sample cohort. Sci Rep 8(1):11748. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29629-7
Kim SY, Lim JS, Kong IG, Choi HG (2018) Hearing impairment and the risk of neurodegenerative dementia: a longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Sci Rep 8(1):15266. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33325-x
Sung YK, Cho SK, Choi CB, Bae SC (2013) Prevalence and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in South Korea. Rheumatol Int 33(6):1525–1532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2590-2
Cho SK, Sung YK, Choi CB, Kwon JM, Lee EK, Bae SC (2013) Development of an algorithm for identifying rheumatoid arthritis in the Korean National Health Insurance claims database. Rheumatol Int 33(12):2985–2992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-013-2833-x
Quan H, Li B, Couris CM, Fushimi K, Graham P, Hider P, Januel JM, Sundararajan V (2011) Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am J Epidemiol 173(6):676–682. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwq433
Pu D, Luo J, Wang Y, Ju B, Lv X, Fan P, He L (2018) Prevalence of depression and anxiety in rheumatoid arthritis patients and their associations with serum vitamin D level. Clin Rheumatol 37(1):179–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3874-4
Silman AJ, Newman J, MacGregor AJ (1996) Cigarette smoking increases the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Results from a nationwide study of disease-discordant twins. Arthritis Rheum 39(5):732–735. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780390504
Poudel D, George MD, Baker JF (2020) The impact of obesity on disease activity and treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 22(9):56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-020-00933-4
Eslami O, Shahraki M, Bahari A, Shahraki T (2017) Dietary habits and obesity indices in patients with gastro-esophageal reflux disease: a comparative cross-sectional study. BMC Gastroenterol 17(1):132. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-017-0699-1
Eusebi LH, Ratnakumaran R, Yuan Y, Solaymani-Dodaran M, Bazzoli F, Ford AC (2018) Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms: a meta-analysis. Gut. 67(3):430–440. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313589
Schneider A, Merikhi A, Frank BB (2006) Autoimmune disorders: gastrointestinal manifestations and endoscopic findings. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 16(1):133–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giec.2006.01.013
Pagnoux C, Mahr A, Cohen P, Guillevin L (2005) Presentation and outcome of gastrointestinal involvement in systemic necrotizing vasculitides: analysis of 62 patients with polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener granulomatosis, Churg-Strauss syndrome, or rheumatoid arthritis-associated vasculitis. Medicine (Baltimore) 84(2):115–128. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.md.0000158825.87055.0b
Craig E, Cappelli LC (2018) Gastrointestinal and hepatic disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 44(1):89–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2017.09.005
Corning B, Copland AP, Frye JW (2018) The esophageal microbiome in health and disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 20(8):39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-018-0642-9
Vaahtovuo J, Munukka E, Korkeamaki M, Luukkainen R, Toivanen P (2008) Fecal microbiota in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 35(8):1500–1505
Lichtman SN, Wang J, Sartor RB, Zhang C, Bender D, Dalldorf FG et al (1995) Reactivation of arthritis induced by small bowel bacterial overgrowth in rats: role of cytokines, bacteria, and bacterial polymers. Infect Immun 63(6):2295–2301
Ivanov II, Atarashi K, Manel N, Brodie EL, Shima T, Karaoz U et al (2009) Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell 139(3):485–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.09.033
Kuroda T, Tanabe N, Kobayashi D, Sato H, Wada Y, Murakami S, Nakano M, Narita I (2012) Association between clinical parameters and amyloid-positive area in gastroduodenal biopsy in reactive amyloidosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 32(4):933–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1719-4
**e F, Yun H, Bernatsky S, Curtis JR (2016) Brief report: Risk of gastrointestinal perforation among rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving tofacitinib, tocilizumab, or other biologic treatments. Arthritis Rheum 68(11):2612–2617. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39761
Myasoedova E, Talley NJ, Manek NJ, Crowson CS (2011) Prevalence and risk factors of gastrointestinal disorders in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a population-based survey in olmsted county, Minnesota. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2011:745829. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/745829
Ford AC, Forman D, Bailey AG, Axon AT, Moayyedi P (2007) Initial poor quality of life and new onset of dyspepsia: results from a longitudinal 10-year follow-up study. Gut 56(3):321–327. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2006.099846
Miyakoshi N, Kasukawa Y, Sasaki H, Kamo K, Shimada Y (2009) Impact of spinal kyphosis on gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms in patients with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 20(7):1193–1198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-008-0777-x
Imagama S, Hasegawa Y, Wakao N, Hirano K, Hamajima N, Ishiguro N (2012) Influence of lumbar kyphosis and back muscle strength on the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease in middle-aged and elderly people. Eur Spine J 21(11):2149–2157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-012-2207-1
Sugimoto M, Hasegawa T, Nishino M, Sahara S, Uotani T, Ichikawa H, Kagami T, Sugimoto K, Yamato Y, Togawa D, Kobayashi S, Hoshino H, Matsuyama Y, Furuta T (2016) Improvement of gastroesophageal reflux disease in Japanese patients with spinal kyphotic deformity who underwent surgical spinal correction. Dig Endosc 28(1):50–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.12543
Funding
This work was supported in part by a research grant (NRF-2018-R1D1A1A02085328) from the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.Y., Min, C., Park, B. et al. Bidirectional association between GERD and rheumatoid arthritis: two longitudinal follow-up studies using a national sample cohort. Clin Rheumatol 40, 1249–1257 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05400-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05400-0