Abstract
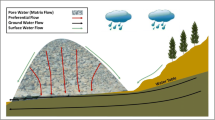
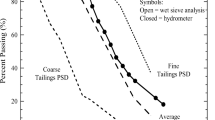
Parent geology, mining operation, construction practice and weathering processes govern the hydrogeological behaviour of waste rock piles. Variable heterogeneity in such earth structures requires site specific correlations. Based on field investigation and laboratory characterization, this paper developed a physical model for the unsaturated East Pile at the Golden Sunlight Mine in Montana, USA. Results indicate that the pile had interfingered dip** beds characterized by a matrix-supported structure in the fine grained layers and a clast-supported structure in the coarse grained layers. Waste rock with at least 45% sand retained water (ψ a = 2–4 kPa, ψ r = 20–40 kPa, k sat = 3.5 × 10−3 cm/s, k unsat = 2–3 orders of magnitude lower at 100 kPa) whereas materials with less than 45% sand drained rapidly (ψ a < 1 kPa, ψ r < 10 kPa, k sat = 1 × 10−1 cm/s, k unsat > 6 orders of magnitude lower at 10 kPa).
Résumé
Le contexte géologique, les opérations minières, le mode de mise en place des stériles et les processus d’altération régissent le comportement hydrogéologique des verses à stériles. La forte hétérogénéité de ce type de structure demande des investigations détaillées. Sur la base de travaux de terrain et de caractérisations au laboratoire, l’article présente un modèle physique pour milieux non saturés, développé pour le stockage Est de la mine de Golden Sunlight au Montana (USA). Les résultats montrent que la verse à stérile est constituée de lits différents interstratifiés suivant un certain pendage, les niveaux à grains fins présentant une structure à matrice portante, les niveaux à grains grossiers présentant une structure à éléments grossiers jointifs. Les stériles avec au moins 45% de sable retiennent l’eau (ψ a = 2–4 kPa, ψ r = 20–40 kPa, k sat = 3.5 × 10−3 cm/s, k unsat = 2–3 ordres de grandeur inférieur au cas saturé, avec une succion de 100 kPa), tandis que les matériaux avec moins de 45% de sable se drainent très rapidement (ψ a < 1 kPa, ψ r < 10 kPa, k sat = 1 × 10−1 cm/s, k unsat > 6 ordres de grandeur inférieur au cas saturé, avec une succion de 10 kPa).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azam S (2000) Collapse and compressibility behavior of arid calcareous soil formations. Bull Eng Geol Environ 59(3):211–217
Diodato DM, Parizek RR (1993) Unsaturated hydrogeologic properties of reclaimed coal strip mines. Groundwater 32:108–118
Fala O, Aubertin M, Molson JW, Bussiere B, Wilson GW, Chapuis R, Martin V (2003) Numerical modeling of unsaturated flow in uniform and heterogeneous waste rock piles. In: Proceedings of the 6th international conference on acid rock drainage, Cairns, Australia 1:895–902
Fredlund DG, Rahardjo H (1993) Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils. Wiley, New York
Fredlund DG, **ng A (1994) Equation for the soil water characteristic curve. Canad Geotech J 31:521–532
Fredlund DG, **ng A, Huang S (1994) Predicting the permeability function for unsaturated soils using the soil water characteristic curve. Canad Geotech J 31:533–546
Herasymuik G, Azam S, Wilson GW, Barbour LS, Nichol C (2006) Hydrological characterization of an unsaturated waste rock dump. In: Proceedings of the 59th Canadian geotechnical conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Indrawan IGB, Rahardjo H, Leong EC (2006) Effects of coarse-grained materials on properties of residual soil. Eng Geol 82(3):154–164
Lefebvre R, Hockley D, Smolensky J, Ge´linas P (2001) Multiphase transfer processes in waste rock piles producing acid mine drainage 1: Conceptual model and system characterization. J Contam Hydrol 52:137–164
Molson JW, Fala O, Aubertin M, Bussière B (2005) Numerical simulations of pyrite oxidation and acid mine drainage in unsaturated waste rock piles. J Contam Hydrol 78:343–371
Morin KA, Jones CE, van Dyk RP (1994) Internal hydrogeologic monitoring of an acidic waste rock dump at Westmin Resources’ Myra Falls operations, BC. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on the abatement of acid drainage, Pittsburgh, USA 1:355–364
Newman LL (1999) Preferential flow in vertically oriented unsaturated soil layers. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Nichol C, Smith L, Beckie R (2000) Hydrogeologic behaviour of unsaturated waste rock: an experimental study. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on acid rock drainage, Denver, Colorado, USA 1:215–224
Swanson DA (1995) Predictive modeling of moisture movement in engineered soil covers for acid generating mine waste. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
Taylor MJ, Greenwood RJ (1985) Classification and surface water control. In: Design on non-impounding mine waste dumps, American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers Inc., New York, USA 1:1–13
Wickland BE, Wilson GW (2005) Self-weight consolidation of mixtures of mine waste rock and tailings. Canad Geotech J 42(2):327–339
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by Placer Dome Inc. and Golden Sunlight Mine. Thanks to Dr. Bruno Bussière of the Université du Québec en Abitibi-Témiscamingue, Canada for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azam, S., Wilson, G.W., Herasymuik, G. et al. Hydrogeological behaviour of an unsaturated waste rock pile: a case study at the Golden Sunlight Mine, Montana, USA. Bull Eng Geol Environ 66, 259–268 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-006-0077-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-006-0077-7