Abstract
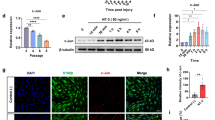
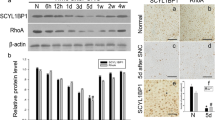
Neuregulin 1 (NRG1) and epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB) signaling pathways control Schwann cells during axonal regeneration in an injured peripheral nervous system. We investigated whether a persistent supply of recombinant NRG1 to the injury site could improve axonal growth and recovery of sensory and motor functions in rats during nerve regeneration. We generated a recombinant adenovirus expressing a secreted form of EGF-like domain from Heregulinβ (sHRGβE-Ad). This virus, sHRGβE-Ad allowed for the secretion of 30-50 ng of small sHRGβE peptides per 107–8 virus particle outside cells and was able to phosphorylate ErbB receptors. Transduction of the concentrated sHRGβE-Ad into an axotomy model of sciatic nerve damage caused an effective promotion of nerve regeneration, as shown by histological features of the axons and Schwann cells, as well as increased expression of neurofilaments, GAP43 and S100 in the distal stump of the injury site. This result is consistent with longer axon lengths and thicker calibers observed in the sHRGβE-Ad treated animals. Furthermore, sensory and motor functions were significantly improved in sHRGβE-Ad treated animals when evaluated by a behavioral test. These results suggest a therapeutic potential for sHRGβE-Ad in treatment of peripheral nerve injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigner, L., Arber, S., Kapfhammer, J.P., Laux, T., Schneider, C., Botteri, F., Brenner, H.-R., and Caroni, P. (1995). Overexpression of the neural growth-associated protein GAP-43 induces nerve sprouting in the adult nervous system of transgenic mice. Cell 83, 269–278.
Avellana-Adalid, V., Bachelin, C., Lachapelle, F., Escriou, C., Ratzkin, E.B., and Baron-Van Evercooren, A. (1998). In vitro and in vivo behaviour of NDF-expanded monkey Schwann cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 291–300.
Baker, A.K., Hoffmann, V.L.H., and Meert, T.F. (2002). Dextromethorphan and ketamine potentiate the antinociceptive effects of [mu]- but not [delta]- or [kappa]-opioid agonists in a mouse model of acute pain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 74, 73–86.
Bederson, J.B., Pitts, L.H., Tsuji, M., Nishimura, M.C., Davis, R.L., and Bartkowski, H. (1986). Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17, 472–476.
Benowitz, L.I., and Routtenberg, A. (1997). GAP-43: an intrinsic determinant of neuronal development and plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 20, 84–91.
Birchmeier, C., and Nave, K.A. (2008). Neuregulin-1, a key axonal signal that drives Schwann cell grwoth and differentiation. Glia 56, 1491–1497.
Bublil, E.M., and Yarden, Y. (2007). The EGF receptor family: spearheading a merger of signaling and therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 19, 124–134.
Buonanno, A., and Fischbach, G.D. (2001). Neuregulin and ErbB receptor signaling pathways in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, 287–296.
Cai, J., Peng, X., Nelson, K.D., Eberhart, R., and Smith, G.M. (2004). Synergistic improvements in cell and axonal migration across sciatic nerve lesion gaps using bioresorbable filaments and heregulin-beta1. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 69, 247–258.
Carroll, S.L., Miller, M.L., Frohnert, P.W., Kim, S.S., and Corbett, J.A. (1997). Expression of neuregulins and their putative receptors, ErbB2 and ErbB3, is induced during Wallerian degeneration. J. Neurosci. 17, 1642–1659.
Chen, L.-E., Liu, K., Seaber, A.V., Katragadda, S., Kirk, C., and Urbaniak, J.R. (1998). Recombinant human glial growth factor 2 (rhGGF 2) improves functional recovery of crushed peripheral nerve (a double-blind study). Neurochem. Int. 33, 341–351.
Chen, S., Velardez, M.O., Warot, X., Yu, Z.X., Miller, S.J., Cros, D., and Corfas, G. (2006). Neuregulin 1-erbB signaling is necessary for normal myelination and sensory function. J. Neurosci. 26, 3079–3086.
Corfas, G., Velardez, M.O., Ko, C.-P., Ratner, N., and Peles, E. (2004). Mechanisms and roles of axon-Schwann cell interactions. J. Neurosci. 24, 9250–9260.
Crovello, C.S., Lai, C., Cantley, L.C., and Carraway, K.L. (1998). Differential signaling by the epidermal growth factor-like growth factors neuregulin-1 and neuregulin-2. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26954–26961.
Delli Bovi, P., Curatola, A.M., Kern, F.G., Greco, A., Ittmann, M., and Basilico, C. (1987). An oncogene isolated by transfection of Kaposi’s sarcoma DNA encodes a growth factor that is a member of the FGF family. Cell 50, 729–737.
Faweett, J.W., and Keynes, R.J. (1990). Peripheral nerve regeneration. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 43–60.
Fazzari, P., Paternain, A.V., Valiente, M., Pla, R., Lujan, R., Lloyd, K., Lerma, J., Marin, O., and Rico, B. (2010). Control of cortical GABA circuitry development by Nrg1 and ErbB4 signalling. Nature 464, 1376–1380.
Flores, A.I., Mallon, B.S., Matsui, T., Ogawa, W., Rosenzweig, A., Okamoto, T., and Macklin, W.B. (2000). Akt-mediated survival of oligodendrocytes induced by neuregulins. J. Neurosci. 20, 7622–7630.
Gerecke, K.M., Wyss, J.M., and Carroll, S.L. (2004). Neuregulin-1b induces neurite extension and arborization in cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 27, 379–393.
Guertin, A.D., Zhang, D.P., Mak, K.S., Alberta, J.A., and Kim, H.A. (2005). Microanatomy of axon/glial signaling during Wallerian degeneration. J. Neurosci. 25, 3478–3487.
Höke, A., and Brushart, T. (2010). Introduction to special issue: Challenges and opportunities for regeneration in the peripheral nervous system. Exp. Neurol. 223, 1–4.
Jaquet, J.B., Luijsterburg, A.J., Kalmijn, S., Kuypers, P.D., Hofman, A., and Hovius, S.E. (2001). Median, ulnar, and combined median-ulnar nerve injuries: functional outcome and return to productivity. J. Trauma 51, 687–692.
Jones, J.T., Akita, R.W., and Sliwkowski, M.X. (1999). Binding specificities and affinities of egf domains for ErbB receptors. FEBS Lett. 447, 227–231.
Joung, I., Kim, H.S., Hong, J.S., Kwon, H., and Kwon, Y.K. (2000). Effective gene transfer into regeneration sciatic nerves by adenoviral vector: potentials for gene therapy of peripheral nerve injury. Mol. Cells 10, 540–545.
Kemp, S.W., Syed, S., Walsh, S., Zochodne, D., and Midha, R. (2009). Collagen nerve conduits promote enhanced axonal regeneration, schwann cell association, and neovascularization compared to silicone conduits. Tissue Eng. Part A 15, 1975–1988.
Kim, D., Chi, S., Lee, K.H., Rhee, S., Kwon, Y.K., Chung, C.H., Kwon, H., and Kang, M.-S. (1999). Neuregulin stimulates myogenic differentiation in an autocrine manner. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 15395–15400.
Kwon, Y.K., Bhattacharyya, A., Alberta, J.A., Giannobile, W.V., Cheon, K., Stiles, C.D., and Pomeroy, S.L. (1997). Activation of ErbB2 during wallerian degeneration of sciatic nerve. J. Neurosci. 17, 8293–8299.
Lai, C. (2005). Peripheral glia: Schwann cells in motion. Curr. Biol. 15, R332–R334.
Lemke, G. (1996). Neuregulins in development. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 7, 247–262.
Marchionni, M.A. (1995). Cell-cell signalling. neu tack on neuregulin. Nature 378, 334–335.
Mei, L., and **ong, W.-C. (2008). Neuregulin 1 in neurla development, synaptic plasticity and schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. 9, 437–452
Meyer, D., and Birchmeier, C. (1994). Distinct isoforms of neuregulin are expressed in mesenchymal and neuronal cells during mouse development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 1064–1068.
Meyer, D., Yamaai, T., Garratt, A.N., Riethmacher-Sonnenberg, E., Kane, D., Theill, L.E., and Birchmeier, C. (1997). Isoform-specific expression and function of neuregulin. Development 124, 3575–3586.
Mittoux, V., Ouary, S., Monville, C., Lisovoski, F., Poyot, T., Conde, F., Escartin, C., Robichon, R., Brouillet, E., Peschanski, M., et al. (2002). Corticostriatopallidal neuroprotection by adenovirus-medoated ciliary neurotrophic factor gene transfer in a rat model of progressive degeneration. J. Neurosci. 22, 4478–4486.
Opalenik, S.R., Shin, J.T., Wehby, J.N., Mahesh, V.K., and Thompson, J.A. (1995). The HIV-1 TAT protein induces the expression and extracellular appearance of acidic fibroblast growth factor. J Biol. Chem. 270, 17457–17467.
Pearson, R.J., Jr., and Carroll, S.L. (2004). ErbB transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptors are expressed by sensory and motor neurons projecting into sciatic nerve. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 52, 1299–1311.
Rieff, H.I., Raetzman, L.T., Sapp, D.W., Yeh, H.H., Siegel, R.E., and Corfas, G. (1999). Neuregulin induces GABA(A) receptor subunit expression and neurite outgrowth in cerebellar granule cells. J. Neurosci. 19, 10757–10766.
Shirakawa, T. (2008). The current status of adenovirus-based cancer gene therapy. Mol. Cells 25, 462–466.
Tannemaat, M.R., Verhaagen, J., and Malessy, M. (2008). The application of viral vectors to enhance regeneration after peripheral nerve repair. Neurol. Res. 30, 1039–1046.
Taveggia, C., Zanazzi, G., Petrylak, A., Yano, H., Rosenbluth, J., Einheber, S., Xu, X., Esper, R.M., Loeb, J.A., Shrager, P., et al. (2005). Neuregulin-1 type III determines the ensheathment fate of axons. Neuron 47, 681–694.
Tollefson, A.E., Hermiston, T.W., and Wold, W.S.M. (1999) Preparation and titration of CsCl-banded adenovirus stock. In Adenovirus Methods and Protocols, W.S.M. Wold, ed. (Totowa, New Jersey, USA: Humana Press), pp. 1–9.
Tria, M.A., Fusco, M., Vantini, G., and Mariot, R. (1994). Phamacokinetics of nerve growth factor (NGF) following different routes of administration to adult rats. Exp. Neurol. 127, 178–183.
Waller, A. (1851). Experiments on the section of the glosso-pharyngeal and hypoglossal nerves of the frog, and observations of the alterations produced thereby in the structure of their primitive fibers. Edinburg. Med. Surg. J. 76, 369–376.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Joung, I., Yoo, M., Woo, J.H. et al. Secretion of EGF-like domain of heregulinβ promotes axonal growth and functional recovery of injured sciatic nerve. Mol Cells 30, 477–484 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0137-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-010-0137-5