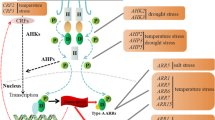
Abstract
Legume plants develop root nodules to recruit nitrogen-fixing bacteria called rhizobia. This symbiotic relationship allows the host plants to grow even under nitrogen limiting environment. Since nodule development is an energetically expensive process, the number of nodules should be tightly controlled by the host plants. For this purpose, legume plants utilize a long-distance signaling known as autoregulation of nodulation (AON). AON signaling in legumes has been extensively studied over decades but the underlying molecular mechanism had been largely unclear until recently. With the advent of the model legumes, L. japonicus and M. truncatula, we have been seeing a great progress including isolation of the AON-associated receptor kinase. Here, we summarize recent studies on AON and discuss an updated view of the long-distance control of nodulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Combier, J.P., Küster, H., Journet, E.P., Hohnjec, N., Gamas, P., and Niebel, A. (2008). Evidence for the involvement in nodulation of the two small putative regulatory peptide-encoding genes MtRALFU and MtDVU. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 21, 1118–1127.
Delves, A.C., Mathews, A., Day, D.A., Carter, A.S., Carroll, B.J., and Gresshoff, P.M. (1986). Regulation of the soybean-Rhizobium nodule symbiosis by shoot and root factors. Plant Physiol. 82, 588–590.
D’Haeze, W., and Holsters, M. (2002). Nod factor structures, responses, and perception during initiation of nodule development. Glycobiology 12, 79–105.
Diévart, A., Dalal, M., Tax, F.E., Lacey, A.D., Huttly, A., Li, J., and Clark, S.E. (2003). CLAVATA1 dominant-negative alleles reveal functional overlap between multiple receptor kinases that regulate meristem and organ development. Plant Cell 15, 1198–1211.
Geurts, R., Fedorova, E., and Bisseling, T. (2005). Nod factor signaling genes and their function in the early stages of Rhizobium infection. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 8, 346–352.
Gleason, C., Chaudhuri, S., Yang, T., Muñoz, A., Poovaiah, B.W., and Oldroyd, G.E. (2006). Nodulation independent of rhizobia induced by a calcium-activated kinase lacking autoinhibition. Nature 441, 1149–1152.
Heckmann, A.B., Lombardo, F., Miwa, H., Perry, J.A., Bunnewell, S., Parniske, M., Wang, T.L., and Downie, J.A. (2006). Lotus japonicus nodulation requires two GRAS domain regulators, one of which is functionally conserved in a non-legume. Plant Physiol. 142, 1739–1750.
Kaló, P., Gleason, C, Edwards, A., Marsh, J., Mitra, R.M., Hirsch, S., Jakab, J., Sims, S., Long, S.R., Rogers, J., et al. (2005). Nodulation signaling in legumes requires NSP2, a member of the GRAS family of transcriptional regulators. Science 308, 1786–1789.
Kawaguchi, M., Imaizumi-Anraku, H., Koiwa, H., Niwa, S., Ikuta, A., Syono, K., and Akao, S. (2002). Root, root hair, and symbiotic mutants of the model legume Lotus japonicus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 15, 17–26.
Kinkema, M., and Gresshoff, P.M. (2008). Investigation of downstream signals of the soybean autoregulation of nodulation receptor kinase GmNARK. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 21, 1337–1348.
Kosslak, R.M., and Bohlool, B.B. (1984). Suppression of nodule development of one side of a split-root system of soybeans caused by prior inoculation of the other side. Plant Physiol. 75, 125–130.
Krusell, L, Madsen, L.H., Sato, S., Aubert, G., Genua, A, Szczy-glowski, K., Due, G., Kaneko, T., Tabata, S., de Bruijn, F., et al. (2002). Shoot control of root development and nodulation is mediated by a receptor-like kinase. Nature 420, 422–426.
Lévy, J., Bres, C, Geurts, R., Chalhoub, B., Kulikova, O., Due, G., Journet, E.P., Ané, J.M., Lauber, E., Bisseling, T., et al. (2004). A putative Ca2+ and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase required for bacterial and fungal symbioses. Science 303, 1361–1364.
Lough, T.J., and Lucas, W.J. (2006). Integrative plant biology: role of phloem long-distance macromolecular trafficking. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57, 203–232.
Madsen, E.B., Madsen, L.H., Radutoiu, S., Olbtyt, M., Rakwalska, M., Szczyglowski, K., Sato, S., Kaneko, T., Tabata, S., Sandal, N., et al. (2003). A receptor kinase gene of the LysM type is involved in legume perception of rhizobial signals. Nature 425, 637–640.
Magori, S., Oka-Kira, E., Shibata, S., Umehara, Y., Kouchi, H., Hase, Y, Tanaka, A., Sato, S., Tabata, S., and Kawaguchi, M. (2009). TOO MUCH LOVE, a root regulator associated with the long-distance control of nodulation in Lotus japonicus. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact, (in press).
Malik, N.S., and Bauer, W.D. (1988). When does the self-regulatory response elicited in soybean root after Inoculation occur? Plant Physiol. 88, 537–539.
Mitra, R.M., Gleason, C.A., Edwards, A., Hadfield, J., Downie, J.A., Oldroyd, G.E., and Long, S.R. (2004). A Ca2/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase required for symbiotic nodule development: Gene identification by transcript-based cloning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 4701–4705.
Miwa, H., Betsuyaku, S., Iwamoto, K, Kinoshita, A, Fukuda, H., and Sawa, S. (2008). The receptor-like kinase SOL2 mediates CLE signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 49, 1752–1757.
Miyahara, A., Hirani, T.A., Oakes, M., Kereszt, A, Kobe, B., Djord-jevic, M.A., and Gresshoff, P.M. (2008). Soybean nodule autoregulation receptor kinase phosphorylates two kinase-associated protein phosphatases in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 25381–25391.
Müller, R., Bleckmann, A, and Simon, R. (2008). The receptor kinase CORYNE of Arabidopsis transmits the stem cell-limiting signal CLAVATA3 independently of CLAVATA1. Plant Cell 20, 934–946.
Murakami, Y., Miwa, H., Imaizumi-Anraku, H., Kouchi, H., Downie, J.A., Kawaguchi, M., and Kawasaki, S. (2006). Positional cloning identifies Lotus japonicus NSP2, a putative transcription factor of the GRAS family, required for NIN and ENOD40 gene expression in nodule initiation. DNA Res. 13, 255–265.
Nakagawa, T, and Kawaguchi, M. (2006). Shoot-applied MeJA suppresses root nodulation in Lotus japonicus. Plant Cell Physiol. 47, 176–180.
Nishimura, R., Hayashi, M., Wu, G.J., Kouchi, H., Imaizumi-Anraku, H., Murakami, Y., Kawasaki, S., Akao, S., Ohmori, M., Nagasawa, M., et al. (2002). HAR1 mediates systemic regulation of symbiotic organ development. Nature 420, 426–429.
Nontachaiyapoom, S., Scott, P.T., Men, A.E., Kinkema, M., Schenk, P.M., and Gresshoff, P.M. (2007). Promoters of orthologous Glycine max and Lotus japonicus nodulation autoregulation genes interchangeably drive phloem-specific expression in transgenic plants. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 20, 769–780.
Nutman, P.S. (1952). Studies on the physiology of nodule formation. III. Experiments on the excision of root-tips and nodules. Ann. Bot. 16, 79–101.
Ogawa, M., Shinohara, H., Sakagami, Y., and Matsubayashi, Y. (2008). Arabidopsis CLV3 peptide directly binds CLV1 ectodo-main. Science 319, 294.
Oka-Kira, E., Tateno, K., Miura, K., Haga, T., Hayashi, M., Harada, K., Sato, S., Tabata, S., Shikazono, N., Tanaka, A., et al. (2005). klavier (klv), a novel hypernodulation mutant of Lotus japonicus affected in vascular tissue organization and floral induction. Plant J. 44, 505–515.
Okamoto, S., Ohnishi, E., Sato, S., Takahashi, H., Nakazono, M., Tabata, S., and Kawaguchi, M. (2009). Nod factor/nitrate-induced CLE genes that drive HAR1-mediated systemic regulation of nodulation. Plant Cell Physiol. 50, 67–77.
Oldroyd, G.E., and Downie, J.A. (2008). Coordinating nodule morphogenesis with rhizobial infection in legumes. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59, 519–546.
Pacios-Bras, C., Schlaman, H.R., Boot, K., Admiraal, P., Langerak, J.M., Stougaard, J., and Spaink, H.P. (2003) Auxin distribution in Lotus japonicus during root nodule development. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 1169–1180.
Penmetsa, R.V., and Cook, D.R. (1997). A legume ethylene-insensitive mutant hyperinfected by its rhizobial symbiont. Science 275, 527–530.
Penmetsa, R.V., Frugoli, J.A., Smith, L.S., Long, S.R., and Cook, D.R. (2003). Dual genetic pathways controlling nodule number in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. 131, 998–1008.
Pierce, M., and Bauer, W.D. (1983). A rapid regulatory response governing nodulation in soybean. Plant Physiol. 73, 286–290.
Postma, J.G., Jacobsen, E., and Feenstra, W. (1988). Three pea mutants with an altered nodulation studied by genetic analysis and grafting. J. Plant Physiol. 132, 424–430.
Prayitno, J., Rolfe, B.G., and Mathesius, U. (2006). The Ethylene-insensitive sickle mutant of Medicago truncatula shows altered auxin transport regulation during nodulation. Plant Physiol. 142, 168–180.
Radutoiu, S., Madsen, L.H., Madsen, E.B., Felle, H.H., Umehara, Y., Granlund, M., Sato, S., Nakamura, Y., Tabata, S., Sandal, N., et al. (2003). Plant recognition of symbiotic bacteria requires two LysM receptor-like kinases. Nature 425, 585–592.
Sagan, M., and Due, G. (1996). Sym28 and Sym29, two new genes involved in regulation of nodulation in pea (Pisum sativum L). Symbiosis 20, 229–245.
Schnabel, E., Journet, E.P., de Carvalho-Niebel, F., Due, G., and Frugoli, J. (2005). The Medicago truncatula SUNN gene encodes a CLV1-like leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase that regulates nodule number and root length. Plant Mol. Biol. 58, 809–822.
Searle, I.R., Men, A.E., Laniya, T.S., Buzas, D.M., Iturbe-Ormaetxe, I., Carroll, B.J., and Gresshoff, P.M. (2003). Long-distance signaling in nodulation directed by a CLAVATA1-like receptor kinase. Science 299, 109–112.
Sheng, C., and Harper, J.E. (1997). Shoot versus root signal involvement in nodulation and vegetative growth in wild-type and hypernodulating soybean genotypes. Plant Physiol. 113, 825–831.
Smit, P., Raedts, J., Portyanko, V., Debellé, F., Gough, C., Bisseling, T., and Geurts, R. (2005). NSP1 of the GRAS protein family is essential for rhizobial Nod factor-induced transcription. Science 308, 1789–1791.
Stacey, G., Libault, M., Brechenmacher, L., Wan, J., and May, G.D. (2006). Genetics and functional genomics of legume nodulation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 9, 110–121.
Sun, J., Cardoza, V., Mitchell, D.M., Bright, L, Oldroyd, G., and Harris, J.M. (2006). Crosstalk between jasmonic acid, ethylene and Nod factor signaling allows integration of diverse inputs for regulation of nodulation. Plant J. 46, 961–970.
Tirichine, L, Imaizumi-Anraku, H., Yoshida, S., Murakami, Y., Madsen, L.H., Miwa, H., Nakagawa, T., Sandal, N., Albrektsen, A.S., Kawaguchi, M., et al. 2006a). Deregulation of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase leads to spontaneous nodule development. Nature 441, 1153–1156.
Tirichine, L, James, EX., Sandal, N., and Stougaard, J. (2006b). Spontaneous root-nodule formation in the model legume Lotus japonicus: a novel class of mutants nodulates in the absence of rhizobia. Mol. Plant-Microbe. 19, 373–382.
van Noorden, G.E., Ross, J.J., Reid, J.B., Rolfe, B.G., and Mathe-sius, U. (2006). Defective long-distance auxin transport regulation in the Medicago truncatula super numeric nodules mutant. Plant Physiol. 140, 1494–1506.
Williams, L, and Fletcher, J.C. (2005). Stem cell regulation in the Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 8, 582–586.
Wopereis, J., Pajuelo, E., Dazzo, F.B., Jiang, Q., Gresshoff, P.M., De Bruijn, F.J., Stougaard, J., and Szczyglowski, K. (2000). Short root mutant of Lotus japonicus with a dramatically altered symbiotic phenotype. Plant J. 23, 97–114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Magori, S., Kawaguchi, M. Long-distance control of nodulation: Molecules and models. Mol Cells 27, 129–134 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0016-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10059-009-0016-0