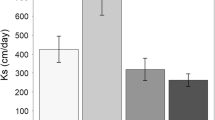
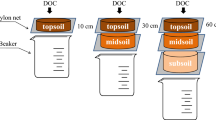
Abstract
Dissolved organic matter (DOM) plays an important role in transporting carbon and nitrogen from forest floor to mineral soils in temperate forest ecosystems. Thus, the retention of DOM via sorption or microbial assimilation is one of the critical steps for soil organic matter formation in mineral soils. The chemical properties of DOM are assumed to control these processes, yet we lack fundamental information that links litter quality, DOM chemistry, and DOM retention. Here, we studied whether differences in litter quality affect solution chemistry and whether changes in litter inputs affect DOM quality and removal in the field. The effects of litter quality on solution chemistry were evaluated using chemical fractionation methods for laboratory extracts and for soil water collected from a temperate coniferous forest where litter inputs had been altered. In a laboratory extraction, litter type (needle, wood, root) and the degree of decomposition strongly influenced solution chemistry. Root litter produced more than 10 times more water-extractable dissolved organic N (DON) than any other litter type, suggesting that root litter may be most responsible for DON production in this forest ecosystem. The chemical composition of the O-horizon leachate was similar under all field treatments (doubled needle, doubled wood, and normal litter inputs). O-horizon leachate most resembled laboratory extracts of well-decomposed litter (that is, a high proportion of hydrophobic acids), in spite of the significant amount of litter C added to the forest floor and a tendency toward higher mean DOM under doubled-Litter treatments. A lag in DOM production from added litter or microbial modification might have obscured chemical differences in DOM under the different treatments. Net DOM removal in this forest soil was strong; DOM concentration in the water deep in the mineral soil was always low regardless of concentrations in water that entered the mineral soil and of litter input manipulation. High net removal of DOM from O-horizon leachate, in spite of extremely low initial hydrophilic neutral content (labile DOM), coupled with the lack of influence by season or soil depth, suggests that DOM retention in the soil was mostly by abiotic sorption.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
JD Aber JM Melillo (1991) Resource Allocation and Net Primary Productivity J Alexander (Eds) Terrestrial Ecosystems Saunders College Publishing Orlando, FL 153–94
JA Aitkenhead–Peterson WH McDowell JC Neff (2003) Sources, production and regulation of allochthonous dissolved organic matter SEG Findlay RL Sinsabaugh (Eds) Aquatic Ecosystems: Interactivity of Dissolved Organic Matter Academic Press San Diego 25–70
RD Boone KJ Nadelhoffer JD Canary JP Kaye (1999) ArticleTitleRoots exert a strong influence on the temperature sensitivity of soil respiration Nature 396 570–2 Occurrence Handle10.1038/25119
ML Cabrera MH Beare (1993) ArticleTitleAlkaline persulfate oxidation for determining total nitrogen in microbial biomass extracts Soil Sci Soc Am J 57 1007–12 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXns1ensQ%3D%3D
MJ Christ MB David (1996) ArticleTitleDynamics of extractable organic carbon in Spodosol forest floors Soil Biol Biochem 28 1171–9 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(96)00128-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XmvFGiurg%3D
WS Currie JD Aber WH McDowell RD Boone AH Magill (1996) ArticleTitleVertical transport of dissolved organic C and N under long-term N amendments in pine and hardwood Biogeochemistry 35 471–505
KH Dai MB David GF Vance (1996) ArticleTitleCharacterization of soil and dissolved carbon in a spruce-fir Spodosol Biogeoehemistry 35 339–65
SJ Grayston D Vaughan D Jones (1996) ArticleTitleRhizosphere carbon flow in trees, in comparison with annual plants: the importance of root exudation and its impact on microbial activity and nutrient availability Appl Soil Ecol 5 29–56 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0929-1393(96)00126-6
M Fröberg D Berggren B Bergkvist C Bryant H Knicker (2003) ArticleTitleContributions of Oi, Oe and Oa horizons to dissolved organic matter in forest floor leachates Geoderma 113 311–22 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00367-1
CC Grier RS Logan (1977) ArticleTitleOld-growth Pseudotsuga menziesii communities of a western Oregon watershed: biomass distribution and production budgets Ecol Monogr 47 373–400
M Gödde MB David MJ Christ M Kaupenjohann GF Vance (1996) ArticleTitleCarbon mobilization from the forest floor under red spruce in the northeastern U.S.A Soil Biol Biochem 28 1181–9 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(96)00130-7
G Guggenberger W Zech H Schulten (1994) ArticleTitleFormation and mobilization pathways of dissolved organic matter: evidence from chemical structural studies of organic matter fractions in acid forest floor solutions Organic Geochem 21 51–66 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0146-6380(94)90087-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2c**tFGqtLw%3D
G Guggenberger K Kaiser (2003) ArticleTitleDissolved organic matter in soil: challenging the paradigm of sorptive preservation Geoderma 113 293–310 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00366-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXhsF2nsLY%3D
Harmon ME. 1992. Long-term experiments on log decomposition at the H. J. Andrews Experimental Forest. USDA Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station. General Technical Report PNW-GTR-280. January
LO Hedin JJ Armesto SH Johonson (1995) ArticleTitlePatterns of nutrient loss from unpolluted, old-growth temperate forests: evaluation of biogeochemical theory Ecology 76 493–509
R Jandl P Sollins (1997) ArticleTitleWater-extractable soil carbon in relation to the belowground carbon cycle Biol Fertil Soil 25 196–201 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003740050303
K Kaiser W Zech (1998) ArticleTitleSoil dissolved organic matter sorption as influenced by organic and sesquioxide coatings and sorbed sulfate Soil Sci Soc Am J 62 129–36 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXhtlarsrc%3D
K Kaiser W Zech (2000) ArticleTitleDissolved organic matter sorption by mineral constituents of subsoil clay fractions J Plant Nutr soil Sci 163 531–5 Occurrence Handle10.1002/1522-2624(200010)163:5<531::AID-JPLN531>3.3.CO;2-E Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnsFOnsb4%3D
K Kaiser G Guggenberger L Haumaier W Zech (1997) ArticleTitleDissolved organic matter sorption on subsoil and minerals studied by 13C-NMR and DRIFT spectroscopy Eur J Soil Sci 48 301–10
K Kaiser G Guggenberger W Zech (2001) ArticleTitleIsotopic fractionation of dissolved organic carbon in shallow forest soils as affected by sorption Eur J Soil Sci 52 585–97 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2389.2001.00407.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XltVKruw%3D%3D
K Kaiser G Guggenberger W Zech (1996) ArticleTitleSorption of DOM and DOM fractions to forest soils Geoderma 74 281–303 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7061(96)00071-7
K Kalbitz S Solinger J-H Park B Michalzik E Matzner (2000) ArticleTitleControls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: a review Soil Sci 165 277–304 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00010694-200004000-00001 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjtVKrsLY%3D
I Kögel–Knabner (1997) ArticleTitle13C and 15N NMR spectroscopy as a tool in soil organic matter studies Geoderma 80 243–70 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7061(97)00055-4
K Lajtha WM Jarrell DW Johnson P Sollins (1999) Collection of Soil Solution GP Robertson BibInstitutionalEditorNameand others (Eds) Standard Soil Methods for Long-Term Ecological Research Oxford University Press New York 166–82
JA Leenheer (1981) ArticleTitleComprehensive approach to preparative isolation and fractionation to dissolved organic carbon from natural waters and wastewaters Environ Sci Technol 15 578–87 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es00087a010 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXlvFaju7Y%3D
H Lünsdorf RW Erb W-R Abraham KN Timmis (2000) ArticleTitle‘Clay hutches’: a novel interaction between bacteria and clay minerals Environ Microbiol 2 161–8 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1462-2920.2000.00086.x Occurrence Handle11220302
WH McDowell GE Likens (1988) ArticleTitleOrigin, composition, and flux of dissolved organic carbon in the Hubbard Brook Valley Ecol Monogr 58 177–95
DD Myrold (1998) Transformations of Nitrogen DM Sylvia BibInstitutionalEditorNameand others (Eds) Principles and Applications of Soil Microbiology Prentice-Hall Upper Saddle River, NJ 259–321
K Nambu K Yonebayashi (2000) ArticleTitleQuantitative relationship between soil properties and adsorption of dissolved organic matter onto volcanic ash and non-volcanic ash soils Soil Sci Plant Nutr 46 559–69
RG Qualls BL Haines (1991) ArticleTitleGeochemistry of dissolved organic nutrients in water percolating through a forest ecosystem Soil Sci Soc Am J 55 1112–23
RG Qualls BL Haines (1992) ArticleTitleBiodegradability of dissolved organic matter in forest throughfall, soil solution, and stream water Soil Sci Soc Am J 56 578–86 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XktFequro%3D
SL Schiff R Aravena SE Trumbore MJ Hinton R Elgood PJ Dillon (1997) ArticleTitleExport of DOC from forested catchments on the Precambrian Shield of central Ontario: clues from 13C and 14C Biogeochemistry 36 43–65 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005744131385 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhvVejur4%3D
Schlesinger WH. 1997. The Biosphere: Biogeochemical Cycling on Land. In: Biogeochemistry — An Analysis of Global Change. San Diego: Academic Press. p 166–223
S Solinger K Kalbitz E Matzner (2001) ArticleTitleControls of the dynamics of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in a central European deciduous forest Biogeochemistry 55 327–49 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1011848326013
P Sollins (1982) ArticleTitleInput and decay of coarse woody debris in coniferous stands in western Oregon and Washington Can J For Res 12 18–28
P Sollins FM McCorison (1981) ArticleTitleNitrogen and carbon solution chemistry of an old growth coniferous forest watershed before and after cutting Water Res Res 17 1409–18 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXmtVals7k%3D
P Sollins CC Grier FM McCorison K Cromack SuffixJr R Fogel RL Fredriksen (1980) ArticleTitleThe internal element cycles of an old-growth Douglas-fir ecosystem in western Oregon Ecol Monogr 50 261–85
Yano Y. 2003. Characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and its stabilization in a forest soil. PhD dissertation, Oregon State University
Y Yano WH McDowell JD Aber (2000) ArticleTitleBiodegradable dissolved organic carbon in forest soil solution and effects of chronic nitrogen deposition Soil Biol Biochem 32 1734–51 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00092-4
W Zech N Senesi G Guggenberger K Kaiser J Lehmann TM Miano A Miltner G Schroth (1997) ArticleTitleFactors controlling humification and mineralization of soil organic matter in the tropics Geoderma 79 117–61 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-7061(97)00040-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXns1Cmu7Y%3D
M Zysset D Berggren (2001) ArticleTitleRetention and release of dissolved organic matter in Podzol B horizons Eur Soil Sci 52 409–21 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2389.2001.00399.x Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXntFKiu7s%3D
Acknowledgments
We thank Kermit Cromack, Mark Harmon, Bob Griffiths, and Jerry Qualls for analytical help and laboratory space; Scott Holub and Julie Spears for assistance with analyses; Shanna Penington and Jay Sexton for help in the field; and Mark Johnson and Dave Myrold for comments and discussion of the manuscript. McKenzie Forest Products and Swanson-Superior Forest Products of Oregon donated the wood material. Funding was provided by NSF DEB-0087081 and by USDA NRICGP 97-35101-4256. Additional support to Y. Yano was provided by the Department of Forest Science and the College of Forestry, Oregon State University. We acknowledge the support provided to the H.J. Andrews Experimental Forest by the Pacific Northwest Station, USDA Forest Service, and the Willamette National Forest. Additional support to the Forest was provided by H.J. Andrews Long Term Ecological Research program, funded by National Science Foundation, Division of Environmental Biology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yano, Y., Lajtha, K., Sollins, P. et al. Chemistry and Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter in a Temperate Coniferous Forest on Andic Soils: Effects of Litter Quality. Ecosystems 8, 286–300 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-005-0022-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-005-0022-9